From the intricate ridges of our fingerprints to the nuances of our facial patterns and the distinct tones of our voices, we are all unique! Biometric identification revolves around the unique and distinctive biometric features that make each of us one of a kind.
These characteristics are nearly impossible to replicate, making biometrics an important cogwheel in the identity verification engine. This technology plays a critical role in ensuring that the person on the other side is who they claim to be, with a level of certainty that traditional methods can’t match.
This blog will take you through the intricacies of a biometric identity verification system and guide you through specifics of choosing the right biometric identity verification methods.
Table of Contents
- What Is a Biometrics Identity Verification System?
- How Does Biometric Verification Work?
- Common Uses of Biometric Verification Today
- What Are the Different Types of Biometrics?
- How Does Biometric Verification Help Fight Fraud?
- How HyperVerge Can Help
What is a Biometrics Identity Verification System?
Biometrics identity verification systems use biometric data to confirm a person’s identity, such as fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns, voiceprints, or even behavioral biometrics.
Consider fingerprints, a mainstay in all biometric technologies for authentication, which are now vital to facilitating secure transactions and access across sectors. The rise in their use is a direct countermeasure to the daunting $23 billion in losses anticipated from identity fraud over the next decade.
These systems are not confined to personal devices; they are integral to sectors where security is paramount. Airports, for instance, use facial recognition and fingerprint recognition to enhance security and streamline passenger flow. At the same time, financial institutions employ biometric data to safeguard against fraud, a problem that could see potential losses amounting to billions. In healthcare, biometric verification is essential for patient identification, ensuring that medical records are accessed only by authorized individuals.
The scope of biometrics identity verification systems is vast and varied. At its core, the technology offers heightened security and user-centric convenience. As these systems become increasingly sophisticated, they pave the way for a more secure and efficient future, where our unique biological signatures become the keys to our digital lives.
How Does Biometric Verification Work?
Biometric identity verification systems blend unique biological identifiers with cutting-edge technology to create a secure, user-friendly means of identification.
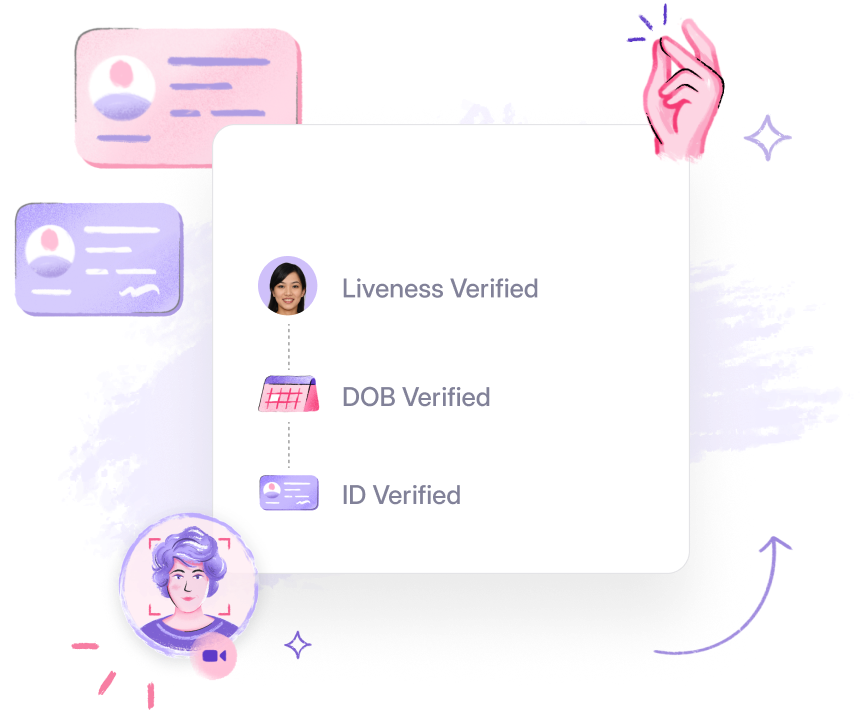
Step-by-Step Biometric Verification Process
- Enrollment: Users start by enrolling their biometric data, such as fingerprints or facial features, into the system.
- Storage: The data is encrypted and can be stored on secure platforms, including blockchain, for enhanced privacy.
- Comparison: Verification is performed by comparing the presented biometrics with stored data to confirm a match.
- Verification: A successful match verifies the user, granting them secure access to the intended service or facility.
Additionally, multimodal biometric systems use at least two or more biometric credentials for verifying an identity.
Industries that Use Biometric Verification
- Banking and Finance: These systems protect online banking and authorize transactions, significantly reducing the risk of fraud.
- Healthcare: Biometrics are crucial in patient privacy and safeguarding access to medical records.
- Travel and Immigration: Biometric systems improve immigration processes and travel document verification.
- Consumer Electronics: Devices now frequently include features like fingerprint scanning and facial recognition for enhanced security.
- Innovations: Multimodal biometrics and continuous authentication are at the forefront of increasing verification accuracy and reliability.
Common Uses of Biometric Authentication Today
The integration of the biometric verification system into our daily lives is a testament to its robustness and versatility. Here’s a deeper look into how it’s being utilized across different spheres:
Online Banking
Financial institutions are championing biometric verification to safeguard their online platforms. By integrating biometrics authentication for access to banking apps and customer onboarding, banks offer a secure and efficient alternative to traditional authentication methods, fortifying against fraud and ensuring KYC compliance.
Remote Identity Verification
With a surge in remote transactions, businesses are adopting biometric-based solutions to meet KYC requirements and combat fraud. By analyzing photo IDs against real-time selfies, AI-powered biometric systems ensure that the person presenting the identity document is its legitimate owner.
Airport Security
Airports have become high-tech fortresses, thanks to biometrics. By using biometric identifiers and employing facial recognition, airports enhance security and improve passenger experience with expedited check-in and boarding processes, using biometrics as both verification and boarding passes.
Mobile Access and Authentication
Our smartphones are hubs of personal information, and biometric verification acts as the gatekeeper. Fingerprint and facial recognition technologies are standard security features for unlocking devices and authenticating transactions. This shift towards biometrically-secured mobile access reflects a significant trend in consumer preference for sophisticated and user-friendly security.
What are the Different Types of Biometrics?
Biometrics encompasses a variety of technologies that use unique physical or behavioral characteristics for identification and verification. Each type has its specific use, accuracy, and level of security.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology maps facial features to create a digital signature. This biometric system is prevalent in smartphones for unlocking and authorizing payments, in surveillance systems for security purposes, and is increasingly being used by marketers to analyze customer responses to ads. Its effectiveness lies in its non-intrusiveness and ease of integration into existing technologies.
Signature
Signature recognition technology captures the distinctive way a person signs their name, including the pressure applied, the speed of the signature, and the stroke order. It is widely used in banking for authorizing transactions and in legal documents as a consent form. Biometric identification tools use Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology to read and recognize characters.
Voice Recognition
Voice or speech recognition identifies and verifies individuals based on their voice patterns. It’s used in customer service for authentication in voice-controlled devices like virtual assistants and is an integral part of many multi-factor authentication systems for its ease of use and improved security.
DNA
DNA biometrics utilize the genetic material unique to each individual for identification. This method is unparalleled in accuracy and is pivotal in applications such as forensic investigations, solving crimes, determining familial relationships in paternity tests, and identifying remains in disaster victim identification. DNA analysis requires a biological sample like saliva or blood, and the detailed genetic profile it provides is nearly impossible to falsify.
Fingerprint
Fingerprint scanners are ubiquitous in law enforcement for identifying individuals, in workplaces for time and attendance systems, and in consumer electronics for device security. They offer a quick, reliable identification method by analyzing the ridges and valleys unique to each finger.
Eye or Retina
Eye-based facial biometrics, such as iris and retina scans, are renowned for their precision. They are utilized when high security is critical, like at border crossings or for accessing secure areas in facilities. They identify the unique patterns found in an individual’s iris or the blood vessels in the retina.
Heartbeat
Heartbeat biometrics detect the unique cardiac rhythm of an individual, which can be used in continuous authentication, a growing trend in wearable health technology. This method is particularly promising because it can provide ongoing verification without interrupting user activity.
How Does a Biometrics Identity Verification System Help Fight Fraud?
The incursion of biometrics into security protocols significantly enhances fraud prevention measures across multiple sectors. Here’s how it makes a difference:
- Eliminating Password Vulnerabilities: Biometrics replace the traditional password, addressing the security gaps posed by easily compromised, forgotten, or reused credentials. Unlike passwords, biometric characteristics are unique to the individual and cannot be easily shared or stolen, providing a more robust defense against credential-based breaches.
- Enhancing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): By incorporating biometrics into MFA, the security of authentication processes is significantly strengthened. Biometrics, as a second factor in MFA, can block a vast majority of automated attacks, offering a user-friendly experience without compromising security.
- Improving Re-verification Processes: Biometrics streamline re-verification processes by reducing reliance on easily exploitable methods like password reset links or knowledge-based authentication. Biometrics remain constant and can’t be forgotten, making them a reliable factor for authentication, even when devices are lost or replaced.
- Securing Digital Onboarding: In digital onboarding, biometrics such as facial recognition can validate that new account holders are who they claim to be, preventing identity theft and fraud. This is particularly crucial in banking and other regulated industries.
- Liveness Detection: To ensure that the person attempting access is actually present and not a fraudulent representation, biometric liveness detection is used. This can differentiate between real users and masks, photos, or other spoofing attempts.

Want to Implement a Biometrics Verification System? HyperVerge Can Help!
If concerns about identity verification are on your radar, you’re not alone. Identity fraud can have far-reaching consequences, not just financially but also for your brand’s reputation.
HyperVerge offers state-of-the-art biometric verification solutions that streamline the authentication process while providing high-quality service and bolstering security. With globally top rated facial recognition and liveness detection, our aim is to make the identity verification process more secure while also ensuring customer satisfaction.
In the face of growing digital fraud, HyperVerge’s identity verification solutions provide a reliable way to protect your business and customers. Utilize our AI-powered technology to ensure you’re always one step ahead of potential threats.
FAQs
Q. Are biometrics safer than passwords?
Yes, biometrics are generally considered safer than passwords. They offer unique identifiers that are difficult to replicate or steal, providing a higher level of security against unauthorized access or breaches.
Q. How to ensure data protection with biometric verification?
Data protection in biometric verification can be ensured by encrypting biometric data, storing it securely, implementing strict access controls, and using advanced technologies like blockchain for data integrity.
Q. Is biometric verification used in Multi-Factor Authentication?
Yes, biometric verification is increasingly used in Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). It adds an extra layer of security by requiring biometric information in addition to passwords or PINs, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.





