What is biometric authentication exactly? How do these technologies function, and why are industries spanning finance to healthcare swiftly embracing them?
Biometric authentication, at its heart, confirms who you are from your unique biological traits. It includes recognizing fingerprints, faces, or even eye patterns. It’s different from regular security like passwords or PINs, which can be forgotten or stolen.
This blog seeks to shed light on biometric authentication by clarifying its inner workings, advantages, and effective implementation approaches.
What is Biometric Authentication?
Biometric authentication is a security process that relies on the unique biological characteristics of an individual to verify their identity. Unlike traditional authentication methods such as passwords and PINs, which are based on knowledge or things that a person has, biometric authentication is inherently more secure as it is based on who the person is. This method involves recognizing physical or behavioral traits, including fingerprints, facial patterns, voice, or even iris configurations.
Traditional methods like passwords and PINs are susceptible to being forgotten, stolen, or hacked. In contrast, biometric authentication offers a more secure and foolproof method. For instance, a fingerprint scanner provides a more reliable and faster way to access a device than typing a password.
Types of Biometric Data
When exploring security and identity confirmation, biometric information presents itself in various structures, each with particular qualities and uses. Below is an outline of the distinguishing types of biometric authentication and validation techniques:
Physical
This category encompasses biometric data derived from the inherent physical attributes of a person, including fingerprint patterns, facial features, and eye scans, which are used for precise and secure identity verification.
Fingerprints
Fingerprints are well known for their singularity, making them a preferred selection in biometric systems. They can be scanned utilizing diverse techniques, like optical, capacitive, or ultrasonic scanners. Automated Fingerprint Identification System (AFIS) is also in place which is a database used to identify fingerprints.
Fingerprint recognition’s security strength resides in the intricacy of each person’s fingerprint designs. The arrangements of ridges and valleys that constitute fingerprints are profoundly complex, with minuscule inconsistencies from individual to individual. This convoluted nature produces highly distinct examples that are very improbable to be duplicated, even among twins, making fingerprint checks an exceptionally dependable approach to recognize people.
While optical fingerprint scanners catch impressions of fingerprints utilizing light, capacitive fingerprint scanners identify conductance examples in a fingerprint by estimating tiny power levels.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology captures and analyzes numerous facial details, proposing a non-disruptive and easy-to-use verification technique. While this technology is commonly used, it brings significant privacy issues and depends on lighting conditions or facial alterations. It examines various facial features, offering contactless access, but raises questions about how personal biometric data is collected and used.
Further reading: How does facial recognition work?
Additionally, the accuracy of facial recognition technology may differ in various lightings, like direct sunlight, shadows, or artificial light. Even minor changes in facial features over time, such as growing facial hair, can impact performance.
Iris and Retina Scans
While iris and retina scans offer robust identification through the intricate markings in one’s eyes, some find such methods too intrusive or costly. Iris and retina scans capitalize on the intricate patterns etched in each person’s eyes, yielding highly accurate authentication. However, not all welcome the invasion of a biometric reader peering into sensitive ocular anatomy.
In addition, achieving sharp retinal or iris imagery demands sophisticated optical technology beyond the means of some organizations. For those disinclined to undergo a retinal or iris scan, or for entities lacking advanced imaging tools, alternative biometric solutions remain worth considering.
Other Physiological Modalities
While emerging biometric authentication technologies such as hand geometry and vein recognition analyze unique physical attributes similar to fingerprints and facial recognition, examining these characteristics provides additional means of identification.
Hand geometry considers the measurements of an individual’s hand to authenticate their identity, focusing on dimensions such as finger length and width or the shape of the palm.
Behavioral
Behavioral biometrics assess unique individual actions, such as voice patterns, typing rhythms, and signature styles, offering a dynamic approach to identity verification based on habitual behaviors.
Voice Recognition
Voice recognition offers a revolutionary hands-free experience, enabling users to interact with devices through spoken commands alone. This technology leverages individual voice patterns to identify the speaker uniquely.
Environmental factors, such as ambient noise from televisions, music players, or conversations, may interfere with the system’s ability to recognize speech accurately. Background sounds can mask portions of spoken words, making it challenging for the voice recognition system to decipher the intended command.
Additionally, certain health conditions affecting the vocal cords or overall voice quality can impact the system’s accuracy.
Keystroke Dynamics
Keystroke dynamics analyzes the distinctive pattern and cadence of typing motions to recognize particular individuals. It serves as an inconspicuous means of verification that depends on an individual’s unique typing behavior. However, an individual’s typing pattern may fluctuate somewhat depending on their physical or emotional state at the given time as stress, fatigue, or minor injuries could influence the rhythm or force with which they strike the keys.
While offering a less intrusive alternative to passwords or biometrics, keystroke dynamics recognition may produce less reliable results if a user’s health or mental state introduces variations.
Signature Recognition
Signature recognition examines the unique characteristics of how an individual signs their name. It has long been used to verify identity, as no two signatures are exactly alike. While signature analysis provides important historical context, it is not as secure or difficult to forge as other biometric authentication methods that use more distinct physical or behavioral traits.
Explore: HyperVerge Signature Verfication API
A signature can be replicated with practice, and external factors like health, age, or environment may cause even a genuine signature to change over time.
These diverse biometric authentication methods offer a range of options for enhanced security and user verification, each with its strengths and limitations.
Benefits of Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication offers a myriad of benefits that significantly outweigh traditional security methods:
Enhanced Security
Biometric authentication utilizes an advanced security mechanism through verification of physical characteristics. Biometric identifiers like fingerprints cannot be easily duplicated or forged, offering stronger protection compared to standard passwords or identification cards. This built-in safety attribute is a primary consideration spurring the implementation of biometric technologies across multiple industries.
Increased Convenience
Biometric authentication methods, like fingerprint scanners or facial recognition systems, provide immense convenience. Users no longer need to remember complex passwords or carry tokens – a simple scan of their biometric data is all it takes for access. This ease of use is user-friendly and speeds up the authentication process.
Improved User Experience
Integrating modern biometric authentication solutions into everyday devices and systems significantly improves user experience. Faster login times and seamless interactions contribute to a more efficient and enjoyable user experience, whether it’s accessing a phone or entering a secure facility.
Reduced Fraud
Utilizing biometric technologies significantly diminishes the chance of stolen credentials or identity theft occurring. Given that biometric information is exclusive to each person, it is exceptionally implausible for deceitful parties to replicate or employ stolen biometric data, rendering systems that leverage biometrics considerably more protected against unauthorized access.
Key Features to Consider in Biometric Authentication Systems
There are a few important things to keep in mind when looking at biometric security systems. Ensuring the system has these qualities will help it work well and be trustworthy. Some key features include:
Accuracy and Liveness Detection
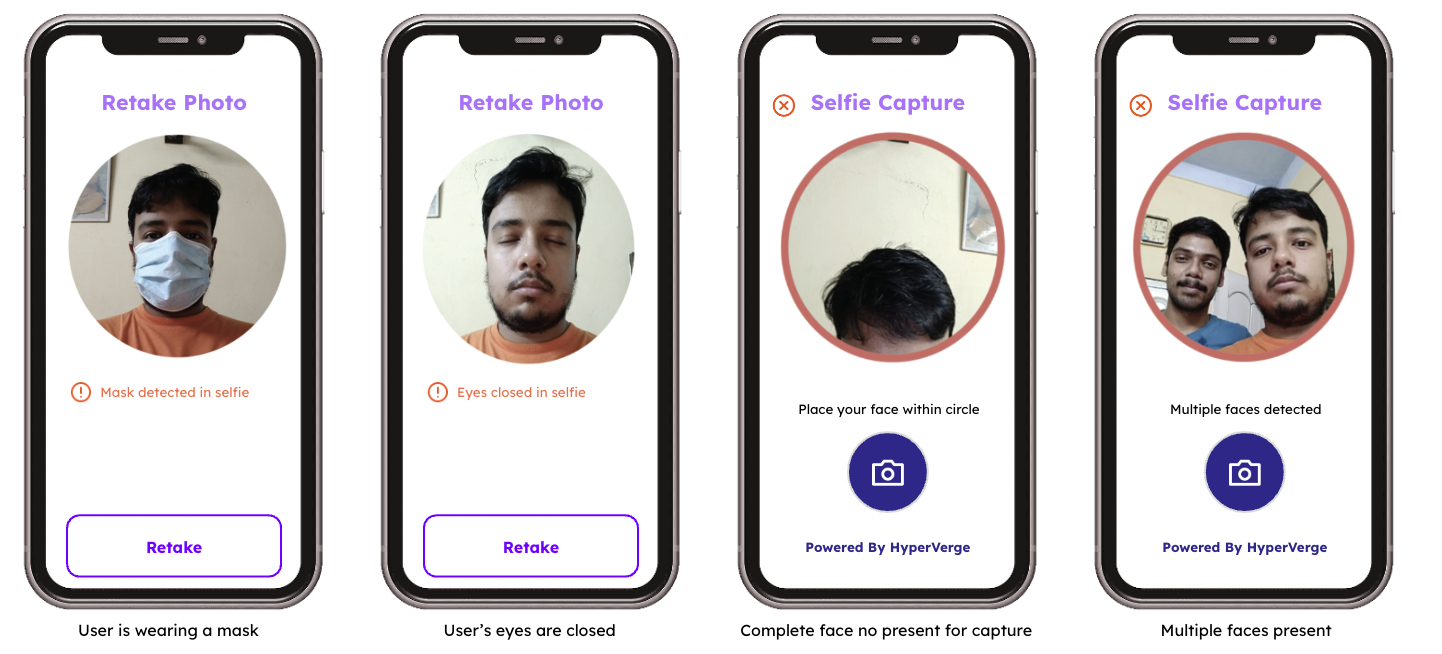
Correct identification in biometric systems is crucial to blocking unauthorized access. Liveness recognition is a technique used to separate real biometric features from artificial ones, for example, masks or photographs. This functionality is essential in stopping spoofing assaults and confirming the individual being authenticated is present.
Methods for detecting liveness differ in complexity, with some employing sophisticated computer vision technologies certified by independent testing facilities.
Security and Data Privacy
Protecting biometric data from unauthorized access and breaches is a significant concern. Look for systems that employ robust data encryption methods and secure storage practices. Some systems store biometric data in distributed databases, both externally on servers and locally on devices, providing an additional layer of security against cyberattacks.
However, storing biometric data, especially on external cloud-based servers, can be vulnerable during transmission. This emphasizes the importance of robust encryption methods.
Integration and User Experience
For a biometric system to be effective, it should seamlessly integrate with existing systems and applications. A user-friendly interface is crucial for ease of adoption.
Modern biometric systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, with sensors capable of detecting nuances like typing speed, pressure applied to buttons, and how a device is held, enhancing both security and user experience.
Scalability and Flexibility
The chosen biometric system needs to be scalable to accommodate a rising number of end users seamlessly. Moreover, the technology must adapt to changing needs. This might include adding new types of biometric data collection or integrating with emerging technologies in the future.
Choosing a scalable and flexible option allows the system to grow and evolve alongside the organization.
Cost and Maintenance
When contemplating biometric authentication solutions, it is vital to weigh the various expenses that will impact the system long term, like hardware, software licenses, and upkeep costs. These financial aspects incorporate the initial outlay for devices needed to collect biometric data and ongoing subscription fees for the software {to manage the captured information.
Servicing and repairs for any biometric hardware as well as software updates over the lifespan of the installed technology must also figure into cost projections. With maintenance expenses taken into account, a true picture can form of the total cost of ownership beyond just the purchase price.
Latest Trends in Biometric Authentication
The field of biometric authentication is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and a growing need for secure identity verification methods. Two significant trends shaping the future of biometrics are multimodal biometrics and AI-powered systems.
Multimodal Biometrics: This approach combines multiple biometric indicators, such as facial recognition, fingerprints, and voice recognition, to enhance accuracy and security. By using a combination of biometric data, multimodal systems reduce the likelihood of false positives and increase the difficulty for fraudulent activities. According to a Biometric Update article, multimodal biometric authentication is expected to continue growing, with changing privacy regulations influencing its adoption.
AI-Powered Systems: Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing biometric authentication by improving the accuracy and efficiency of biometric systems. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of biometric data more quickly and accurately than traditional methods. As highlighted in a blog post by MobiDev, the integration of AI in biometric technology has been a significant trend, especially with the latest innovations in AI.
The potential future of biometrics lies in these emerging technologies. They promise not only enhanced security but also a more seamless and user-friendly experience. As AI continues to advance and multimodal systems become more sophisticated, we can expect biometric authentication to become an even more integral part of our digital lives, offering unparalleled security and convenience.
Implementing a Biometric Authentication System
Implementing a biometric authentication system requires a thorough and methodical approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Planning and Assessment
During this stage, it’s essential to thoroughly grasp your organization’s requirements and how biometric solutions can fulfill them. This includes evaluating the particular environment where the biometric authentication system will operate and determining the most appropriate data types for your needs.
The biometric system needs to be integrated with existing organizational systems and applications. This requires careful planning to ensure compatibility and minimal disruption to current operations.
Data Security and Privacy
Implementing robust encryption methods for biometric authentication data storage and ensuring compliance with privacy laws and regulations is essential. Establishing clear policies for user consent and data handling is also a part of this process.
User Education
In the final step, users undergo training to familiarize themselves with the new biometric authentication security system. Their concerns about privacy and security are addressed, and the benefits of the biometric system, such as user convenience and enhanced security, are emphasized. This process ensures that users feel comfortable and comprehend the advantages of the new biometric authentication method.
Explore: How to implement biometric identity verification systems
Conclusion
Biometric authentication is at the forefront of security and convenience, providing distinct advantages such as heightened security, user-friendly operation, and an improved overall user experience. From fingerprint recognition to a facial recognition system, biometric technologies are reshaping how we authenticate identities.
As we witness the integration of AI and multimodal systems, the future of biometrics looks promising, poised to offer even more robust and efficient security solutions. Embracing these technologies, while being mindful of challenges like data privacy and accessibility, will be crucial in shaping a secure digital landscape. Biometric authentication, with its continuous advancements, is set to redefine the standards of security and convenience in our increasingly digital world.
Sign up here to dive deeper and discover how HyperVerge can elevate your biometric authentication strategy.





