A person’s face is quite literally their identity. Face recognition technology has come a long way in leveraging facial data to identify people and verify identities.
In our comprehensive guide on ‘How Does Facial Recognition Work?’ we’re unraveling the intricacies of facial recognition technology, providing you with a clear understanding of its mechanics, accuracy benchmarks, and practical examples.
What is Facial Recognition?
Facial recognition, a form of biometric technology, has emerged as a revolutionary method in the realm of identity verification and security. But what exactly is it? At its core, facial recognition is a sophisticated technology designed to identify people or verify a person’s identity using their facial features.
This technology fits snugly within the broader category of biometric identification methods, which also include fingerprint scanning, iris recognition, and voice identification. Each of these methods shares a common goal: to accurately identify individuals based on unique biological characteristics. Facial recognition, in particular, leverages the unique configurations of a person’s facial features, making it a highly efficient and non-intrusive way of verifying an individual’s identity.
Unlike other biometric systems, facial recognition can be performed at a distance, often without the need for physical interaction. This aspect not only enhances user convenience but also broadens its application spectrum, ranging from unlocking smartphones to augmenting security systems at airports.
Facial Recognition Technology Benefits
Facial recognition technology is not just a futuristic concept; it’s a present-day reality with a multitude of benefits. From enhancing security to integrating easily with various systems, this technology is reshaping how we verify identities and secure environments.
Enhance Security
One of the most significant advantages of facial recognition is its ability to improve security. By accurately identifying individuals, it acts as a powerful tool for access control and protection against fraudulent activities and unauthorized access. In high-security areas like airports, banks, and government buildings, facial recognition serves as an added layer of security, ensuring that only authorized personnel gain entry.
Integrate Easily
Another benefit of facial recognition is its ease of integration with existing systems. Whether it’s integrating with document verification systems or syncing with other biometric technologies, facial recognition can be seamlessly incorporated into various platforms. This flexibility allows for widespread adoption across different sectors, from retail to healthcare, enhancing both operational efficiency and user experience.
Improve Accuracy of Identity Verification
Facial recognition technology significantly improves the accuracy of identity verification. By using facial recognition with advanced algorithms and deep learning, it can distinguish between individuals with a high degree of precision. This level of accuracy is crucial in scenarios where mistaken identity can have serious consequences, such as in banking and law enforcement.
Types of Facial Recognition Technology
Facial recognition technology has evolved significantly, incorporating various methods to enhance its accuracy and application. Here’s an overview of the different types of facial recognition technologies:
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): CNNs are a breakthrough in artificial neural networks and AI development. They are popular in deep learning for tasks like image and video classification, using convolutional and pooling layers to detect different imaging features.
Kernel Methods (PCA and SVM): Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is used to reduce data size while preserving relevant information, generating eigenvectors that build up eigenfaces. Support Vector Machine (SVM) is used for distinguishing faces from “not-faces” in a two-group classification approach.
Three-Dimensional Recognition: This technology relies on the unique structure of the human skull and is less affected by factors like makeup or facial hair.
Skin Texture Analysis: This approach uses high-resolution images to analyze unique parameters like moles, skin color, and skin tones. It’s useful in various applications, including face detection and objectionable image filtering.
Thermal Cameras: These use temperature patterns of the human face for recognition, making them effective even with obstructions like makeup or glasses.
FaceNet: Developed by Google, FaceNet uses face recognition benchmark datasets and is known for its high accuracy in extracting face embeddings for training face identification systems.
How Facial Recognition Works
Facial recognition technology works through a series of intricate steps, combining various algorithms and methods. Here’s an overview of the facial recognition process:
Step 1: Face Detection
The initial step involves collecting biometric data and detecting a face. Modern advancements allow for some variations in angle, but the most effective detection occurs when the person is facing the camera directly. This process forms the foundation for further analysis, as seen in real-time face detection.
Step 2: Face Analysis
Once a face is detected, the system captures a photo and begins analyzing it. Key to this step is the identification of various nodal points on the face. Typically, a face is analyzed based on 80 nodal points, which are crucial for the next step in the process.
Step 3: Converting the Image to Data
The facial recognition software then transforms the analysis of the face into a mathematical formula. The data representing the facial features are converted into numerical values, creating a unique code known as a faceprint. This faceprint is akin to a fingerprint in its uniqueness to each individual.
Step 4: Finding a Match
The final step involves comparing the generated faceprint with a database of known faceprints to verify if it is the same person. This comparison can be made against various databases, such as governmental databases. When a match is found, the technology can provide relevant information attached to that faceprint, such as a name or an address.
Facial Recognition Use Cases
Facial recognition technology has been adopted across various industries, each leveraging how facial recognition offers its unique capabilities to enhance operations, security, and user experience. Here are some notable use cases:
Security and Surveillance: This is one of the most common applications of facial recognition technology. It’s used by law enforcement agencies for identifying suspects and by private companies for securing premises. In public spaces, it helps in crowd monitoring and detecting wanted individuals.
Healthcare: Facial recognition aids in patient management and security in healthcare facilities. It’s also used in innovative applications like identifying genetic disorders and aiding in patient diagnosis through analysis of facial features.
Retail: In the retail sector, facial recognition technology is used for personalized advertising, theft prevention, and enhancing customer service by identifying VIP customers.
Banking and Finance: Banks use facial recognition for secure account access and fraud prevention. It’s also used in ATMs for identity verification, adding an extra layer of security to financial transactions.
Travel and Hospitality: Airlines employ facial recognition for streamlined check-ins and boarding, enhancing passenger experience while maintaining high security. Hotels use it for personalized services and security.
Smartphones and Consumer Electronics: Facial recognition technology is widely used in smartphones for device unlocking and securing mobile payments. It’s also seen in other consumer electronics for personalized user experiences.
Factors to Look For in Facial Recognition Systems
When evaluating face recognition systems, several critical factors must be considered to ensure their effectiveness, accuracy, and ethical use. Here’s a breakdown of these key factors:
Liveness Checks
This feature is crucial to prevent spoofing attacks, where photos, videos, or masks are used to fool the system. Liveness checks ensure that the system is interacting with a live person. It’s an essential security feature, especially in applications like identity verification and secure access.
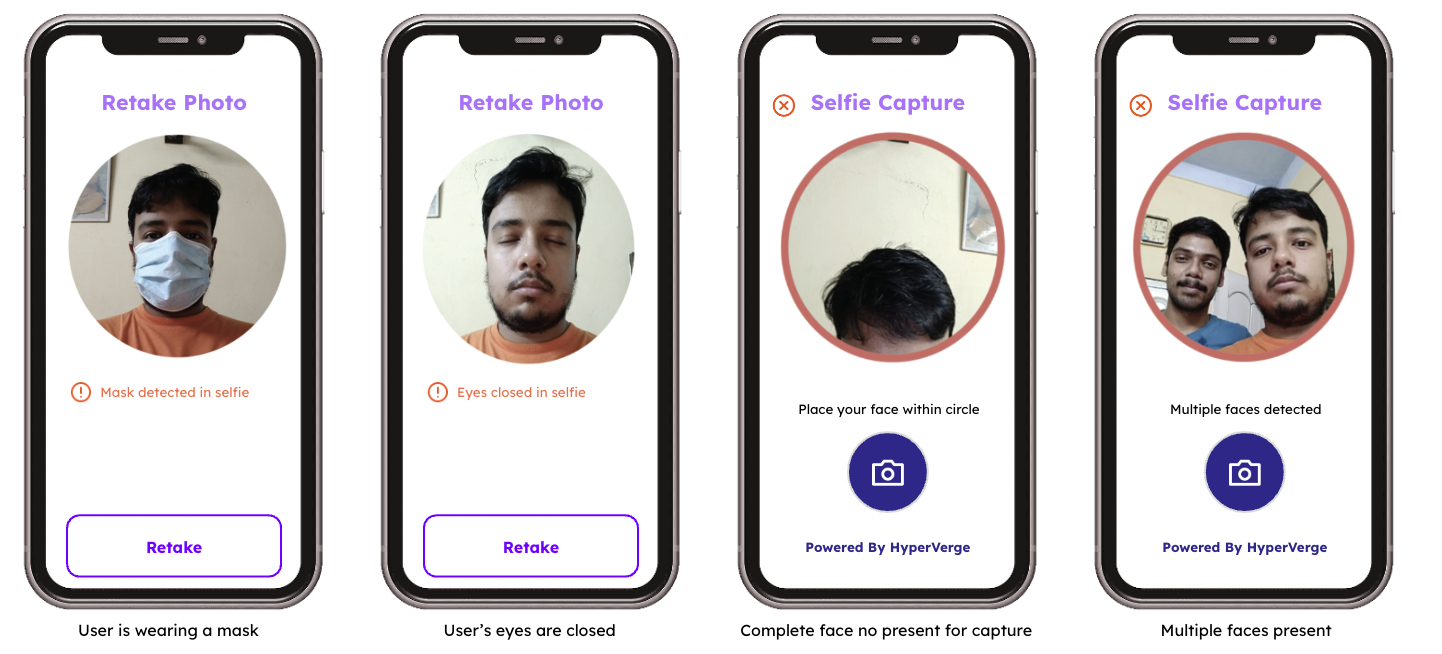
Facial Recognition Algorithms
The choice of algorithms greatly impacts the system’s accuracy and efficiency. Algorithms like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Eigenfaces, and Fisherfaces are popular. AI and machine learning plays a pivotal role in facial recognition systems, enabling them to improve over time as they are exposed to more data. The system’s ability to learn and adapt is key to maintaining high accuracy and efficiency.
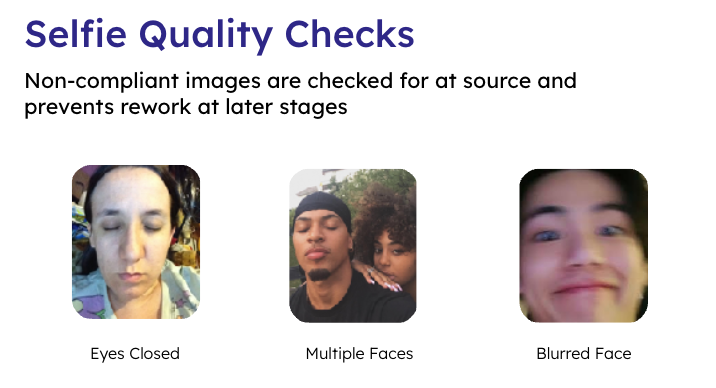
Avoiding AI Bias with a Well-Trained Model
AI bias is a significant concern in facial recognition. A well-trained model, with a diverse dataset, is essential to minimize bias. This includes ensuring the system is equally accurate across different demographics such as age, gender, and ethnicity. Exploring methods to mitigate facial recognition bias is crucial in this regard.

Deepfake Checks
With the rise of synthetic media like deepfakes, facial recognition systems need to distinguish between real and artificially generated faces. This is crucial for maintaining security and trust in digital interactions.
Accuracy
The accuracy of a facial recognition system is paramount. This involves not just the ability to correctly identify faces, but also the system’s precision in challenging conditions like poor lighting, different angles, or partial facial obstructions.
Facial Recognition Accuracy Benchmarks
Regular testing against industry benchmarks is necessary to ensure the system meets the required standards of accuracy. This involves evaluating the system’s performance in various scenarios and comparing it with established metrics and standards.
Get Started with a Powerful Facial Recognition Software
If you’re looking to implement a state-of-the-art facial recognition system, HyperVerge’s technology stands out as a leading choice in the market. We’ve compiled a detailed guide comparing the best face recognition software in the market. Check it out now!
Here are some of the key benefits that make HyperVerge’s face recognition technology powerful:
1. NIST and iBeta Global Certifications: Our facial recognition technology is backed by globally recognized certifications from NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) and iBeta. These certifications are a testament to the reliability, accuracy, and security of the technology.

2. Highest Accuracy in Passive Liveness Checks: We pride ourselves on having the highest accuracy in passive liveness checks. This means our system can effectively distinguish between a live person and a fake or spoof attempt using photos or videos, ensuring a high level of security in identity verification.
Here are some benchmarks:
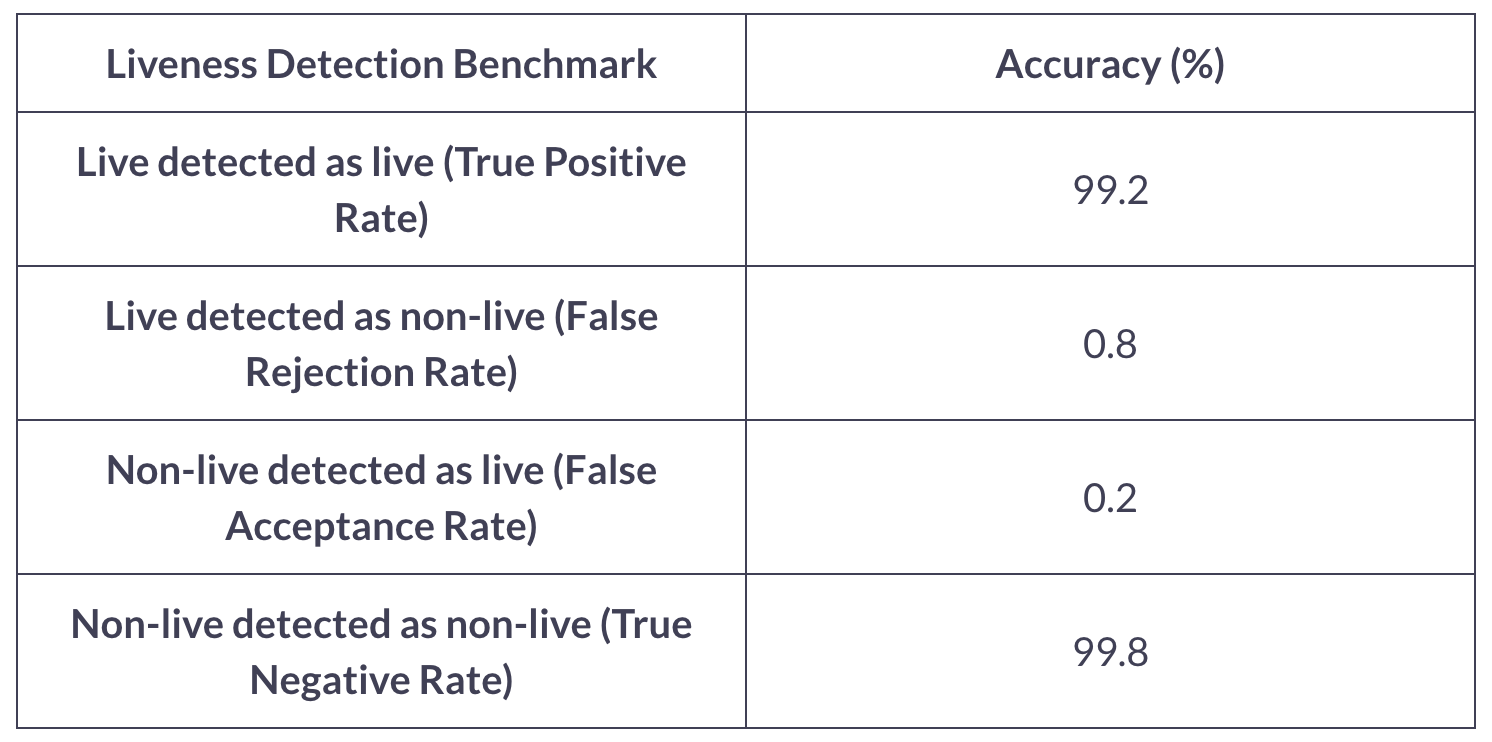
3. AI Algorithms Trained on a Diverse Database: One of the critical strengths of our facial recognition software is the Artificial Intelligence algorithms trained on a diverse database. This training approach significantly reduces racial bias, making the technology more inclusive and fair. By covering a wide range of demographics, we ensure that the face recognition system is equitable and efficient for users from all backgrounds.
Explore more about how HyperVerge’s facial recognition software can benefit your organization.
If you’re ready to take the next step, you can directly sign up to experience the advanced capabilities of HyperVerge’s facial recognition technology and how it can seamlessly integrate into your operations.
FAQs
Q. Is facial recognition technology safe?
Facial recognition technology is generally considered safe when implemented with robust security measures. It includes features like liveness checks to prevent spoofing and is backed by advanced algorithms. However, the safety also depends on how the data is stored and used.
Q. What are other types of biometric identification technology?
Besides facial recognition, there are several other biometric verification methods, including:
- Fingerprint scanning
- Iris recognition
- Voice recognition
- Hand geometry Each of these methods uses unique biological characteristics of an individual for identification and has its specific applications and advantages.
Q. Can face recognition be fooled by photos?
Modern facial recognition systems, especially those equipped with advanced liveness checks, are designed to distinguish between a live person and a photo. While older or less sophisticated fingerprint recognition systems might be susceptible to photo-based spoofing, contemporary technologies have significantly improved in detecting and preventing such attempts.
Q. How does face recognition work in the dark?
Face recognition in the dark is made possible through technologies like infrared imaging or thermal cameras. These systems do not rely on visible light; instead, they detect facial features through infrared or thermal patterns, allowing for recognition in low-light or no-light conditions.
Q. What is face detection?
Face detection is the process of identifying the presence and location of human faces in digital images or video streams. It is the first step in facial recognition systems and is essential for further processes like analysis and identification identify human faces. Face detection algorithms can locate a face or multiple faces within a scene, regardless of orientation, facial expressions, or occlusions.

 US
US
 IN
IN