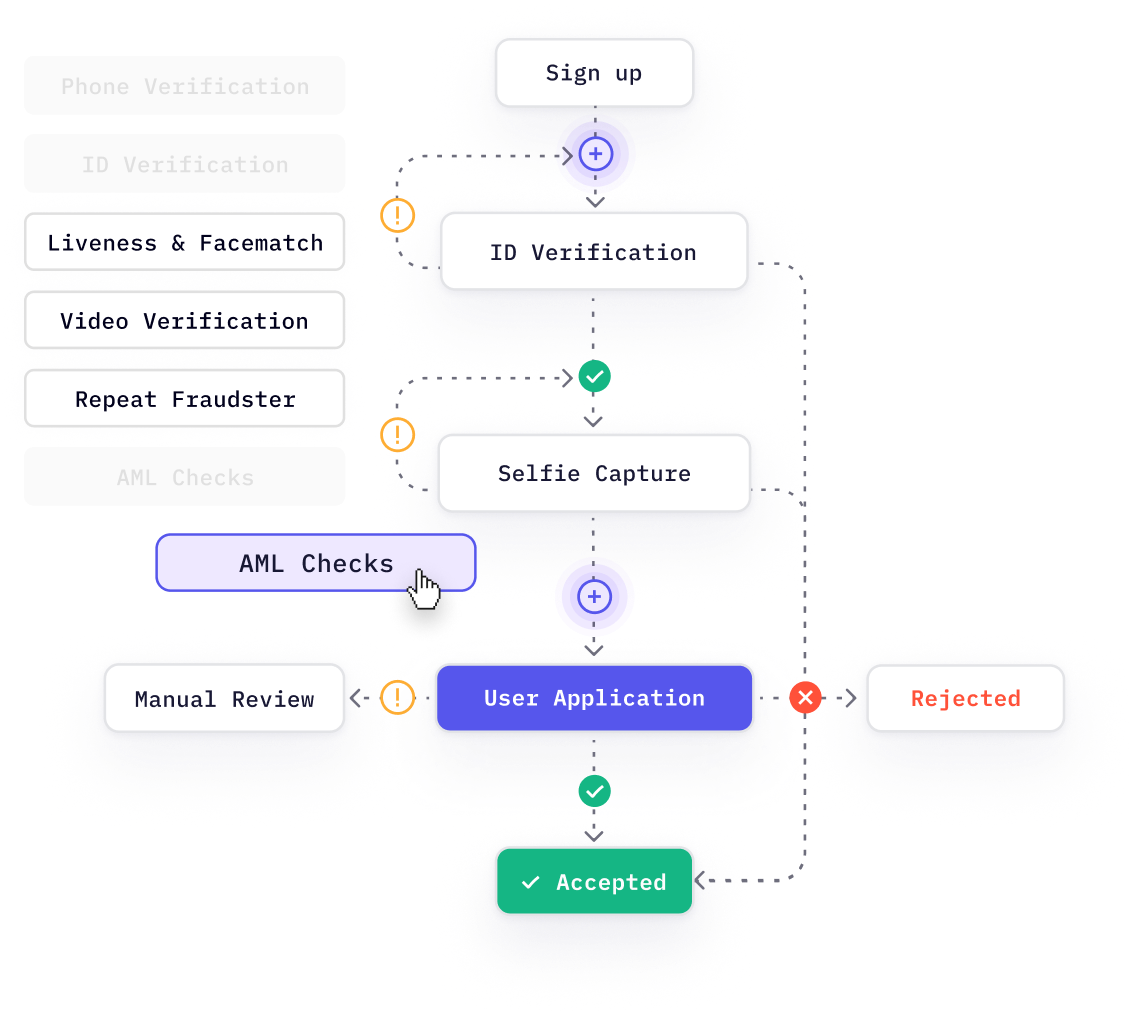
| EDD full form in banking and compliance is Enhanced Due Diligence. It refers to an advanced level of customer verification and risk assessment carried out for high-risk customers under KYC and AML regulations. |
In regulated industries such as banking, NBFCs, fintech, insurance, and crypto, customer onboarding is not only a growth function but also a regulatory obligation. Financial institutions are required to verify customer identities, assess risk exposure, and continuously monitor transactions to comply with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws.
Under KYC regulations, customer verification is performed using Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and, for higher-risk cases, Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD). While CDD applies to most customers, EDD is mandatory when customers, transactions, or geographies present elevated money-laundering or terrorist-financing risk.
In India, Enhanced Due Diligence is governed by the RBI KYC Master Direction and aligned with FATF risk-based recommendations, making EDD a critical control for regulatory compliance, fraud prevention, and reputational protection.
EDD in Banking
Specifically in banking, EDD represents a deeper, more intensive level of scrutiny applied to customers who are classified as high risk after initial due diligence.
Enhanced Due Diligence goes beyond identity verification and includes deeper analysis of:
- Customer background and reputation
- Source of funds and source of wealth
- Ownership and control structures (UBO)
- Transaction behavior and expected activity patterns
- Adverse media, sanctions, and PEP exposure
Banks and regulated entities are required to apply EDD when standard KYC checks are insufficient to mitigate financial crime risks.
What does EDD (Enhanced Due Diligence) mean?
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is a KYC verification process designed to assess a customer’s risk level and monitor significant financial transactions. It employs a risk-based approach to identify high-risk customers who may not be detected through standard CDD procedures.
Enhanced Due Diligence is usually mandated for customers flagged as high-risk or with high net worth because they can carry out large, risky transactions. Therefore, financial institutions go one step above CDD and perform EDD to properly examine the customer.
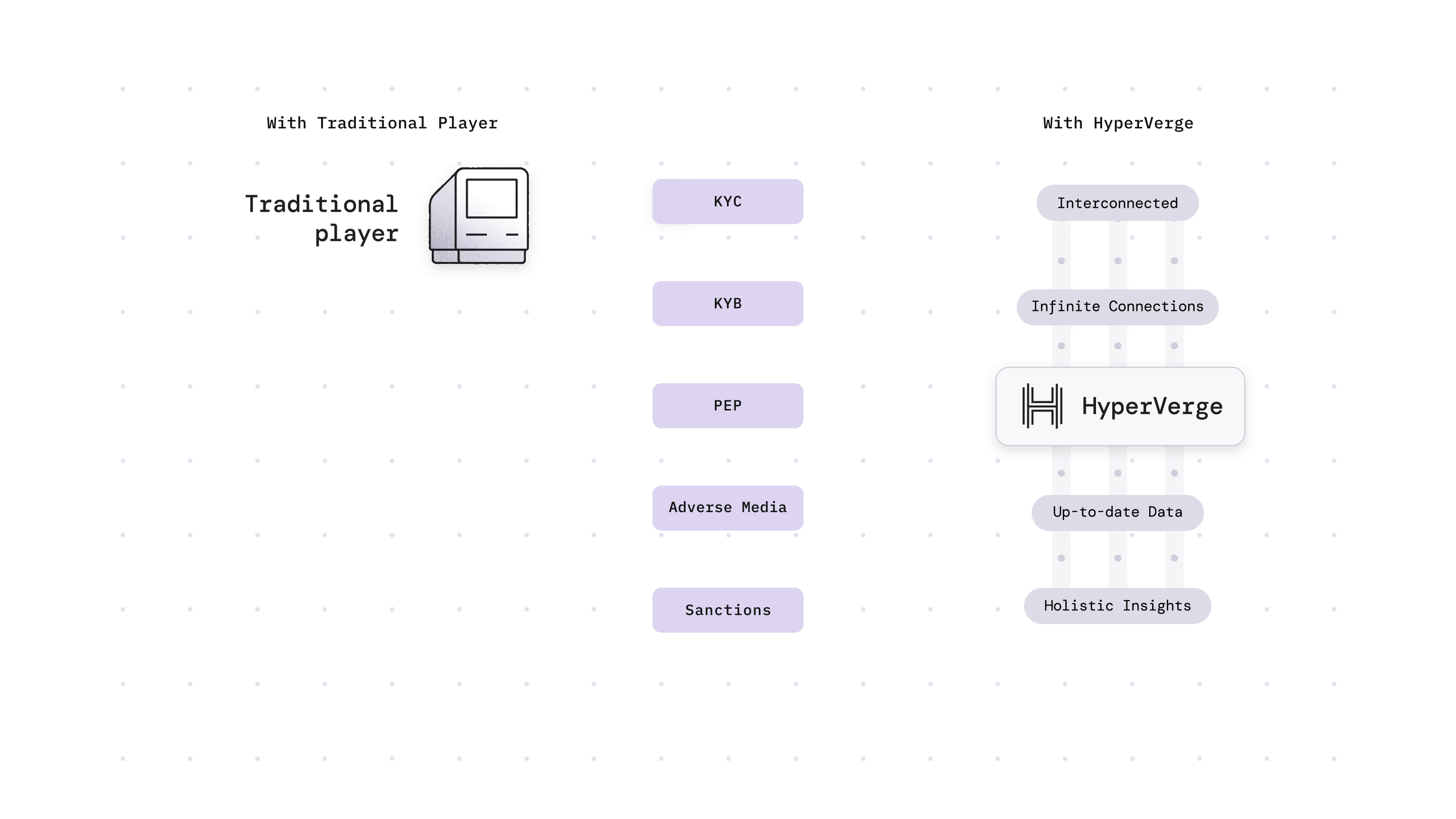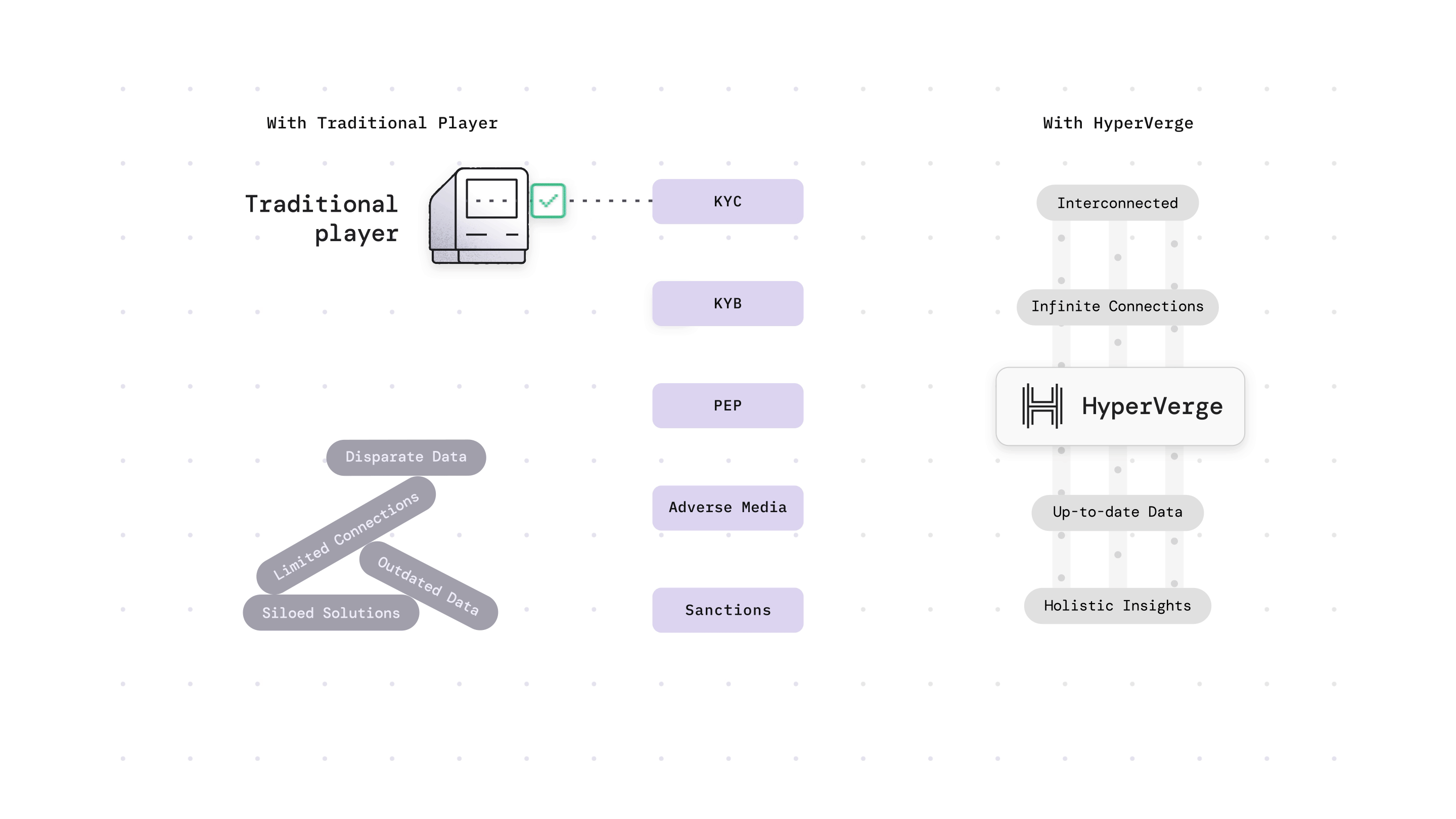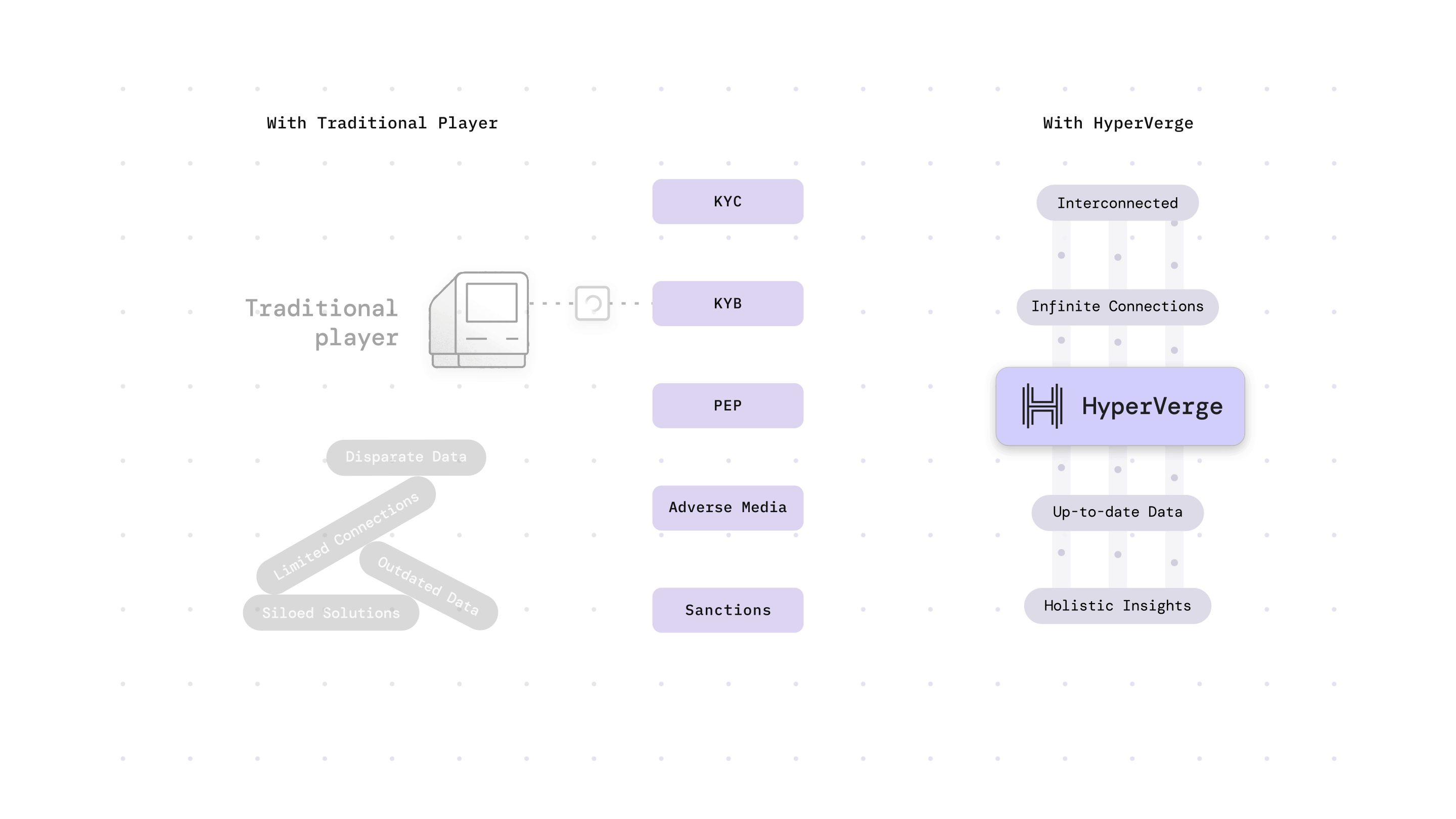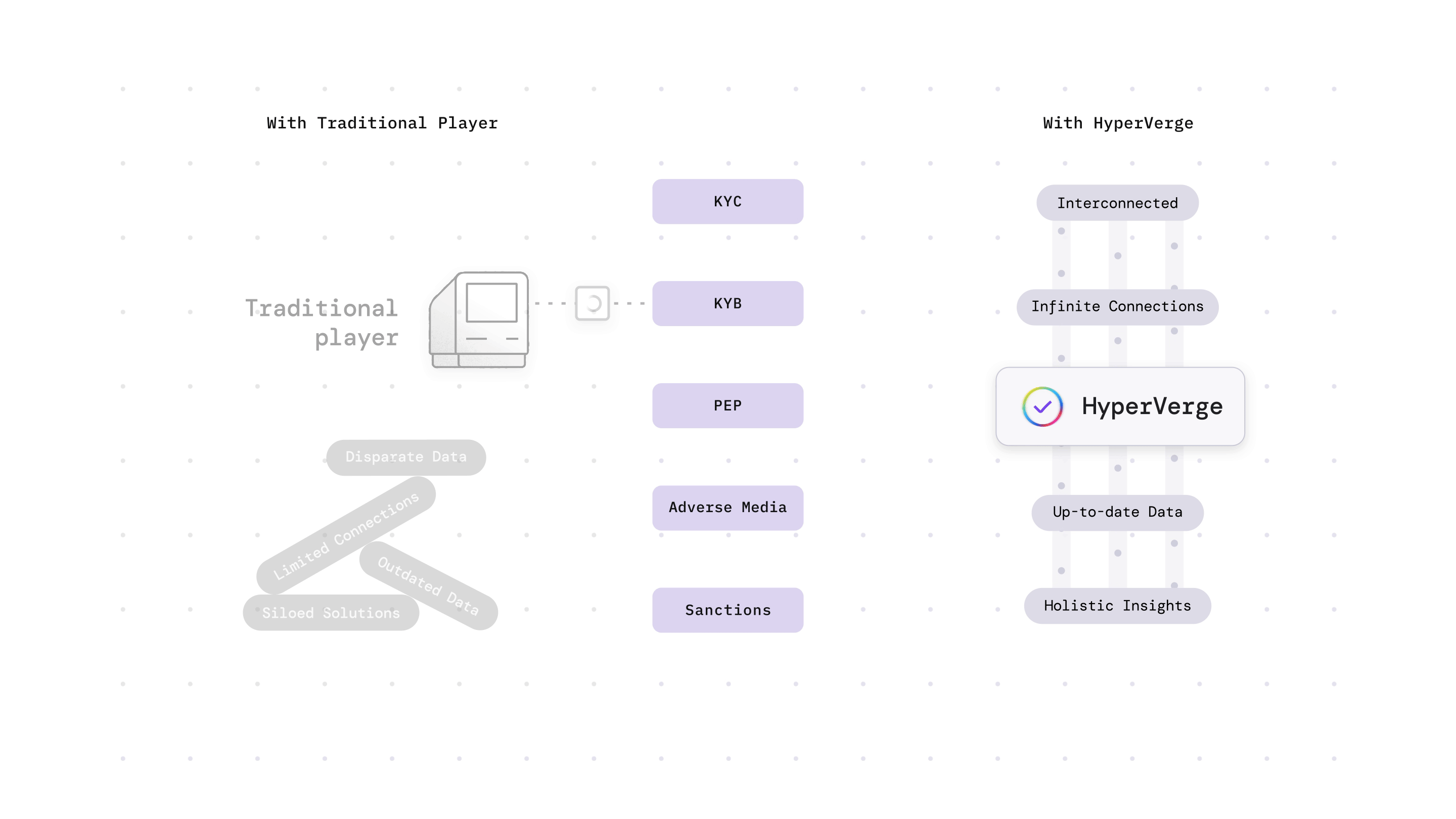
Why is EDD Important?
As technology evolves, fraudsters are discovering new ways of money laundering. As a result, businesses also need to use the latest technologies to combat these cybercrimes. Hence, EDD helps in the fight against money laundering.
In the US, the Patriot Act of 2001 made EDD a compulsory procedure in collaboration with the Bank Secrecy Act. EDD is useful for high-risk cases where large sums of money are at stake, risks that may evade detection through CDD alone. Companies can stay ahead of emerging threats by continuously refining and adapting their EDD practices. This will help them safeguard their reputation and prevent money laundering.
EDD Regulatory Framework in India
In India, Enhanced Due Diligence is mandated under the RBI Master Direction: Know Your Customer (KYC), which requires regulated entities to apply additional checks for high-risk customers and non-face-to-face onboarding scenarios.
According to RBI guidelines, EDD is required when dealing with:
- Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs)
- High-risk countries or jurisdictions
- Complex ownership structures
- Customers with unusually large or suspicious transactions
- Non-face-to-face customer relationships
These requirements are aligned with Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommendations, which promote a risk-based approach to AML compliance globally.
For financial institutions operating in India, failure to implement EDD appropriately can result in supervisory action, penalties, and reputational damage.
CDD vs EDD
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) serves as the basic level of due diligence for all customers irrespective of their risk level. It is used to verify the identity of the customers and their associated risks are measured. This diligence targets the customers who are considered to have a low-risk profile. CDD procedures involve collecting basic information about the customers such as name, address, and identification documents which should be verified against reliable sources.
Enhanced due diligence (EDD) is considered for customers with high-risk factors. The high-risk customer is subjected to a thorough inquiry by employing additional verification steps. This aids in the proper evaluation and monitoring of the business relationship. EDD requires additional verification steps such as background checks, adverse media searches, analysis of funding sources, and, in some cases, on-site visits to verify business operations.
In summary, both CDD and EDD work to meet the regulatory requirements and reduce financial risks. However, EDD is stricter and focuses on high-risk customers and transactions, providing more thorough checks compared to CDD.
When do companies need EDD?
Companies are required to conduct Enhanced Due Diligence when customers or transactions exhibit elevated risk indicators, including but not limited to:
- Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs) and their close associates
- Customers with complex or opaque ownership structures
- High-net-worth individuals with disproportionate source of wealth
- Businesses operating in high-risk or sanctioned jurisdictions
- Shell companies or entities with unclear commercial purpose
- Customers involved in unusually large, complex, or inconsistent transactions
- Negative or adverse media related to financial crime, fraud, or corruption
EDD ensures that such risks are identified, assessed, and mitigated before establishing or continuing a business relationship.
Financial institutions need to be extra careful when doing business with such clients. Hence they should employ edd methods to minimize any risks.
Read more:
- What are the AML red flags?
- What are the three money laundering stages?
- What is layering in money laundering?
- What is a money mule?
- What is Trade Based Money Laundering (TBML)?
- What is Smurfing and How You Can Prevent it Proactively
Enhanced due diligence procedures: Step-by-step approach
To leave nothing to chance, many steps are followed during the EDD verification process. Here’s a list of the major edd measures.
1. Employ a risk-based approach
A risk-based approach will help us identify high-risk clients. It is important to identify the risk factors that are important for the EDD process. These factors include the individual’s country of origin, company’s type, and reputation. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) recommends that companies, especially financial institutions, conduct EDD as part of AML compliance to stay away from businesses/persons engaged in money laundering.
Read more:
- AML risk assessment process: a step-by-step process
- What is a customer identification program (CIP)?
- Anti-Money Laundering Checks Explained: Everything You Need to Know
- KYC and AML: Key Differences and Best Practices
2. Analyzing source of funds and UBO (Ultimate Beneficial Ownership)
To verify the legitimacy of the source of wealth, both the non-financial and financial assets of customers are evaluated. In case of inconsistencies between the actual earnings and overall net worth, the customer may be flagged as unsuitable by the team conducting the EDD process.
Subsidiaries and shareholders of businesses also get assessed to determine the UBO (Ultimate Beneficial Ownership) of the customer’s organization.
Read more:
- What is sanctions screening?
- What is PEP screening?
Verifiable adverse media searches
Information published by reputed media houses plays a pivotal role in uncovering the secrets of a business or an individual customer. While performing EDD, press articles related to high-risk customers are thoroughly reviewed for red flags. Consequently, this type of research helps to build a detailed customer profile. A negative result indicates that the person or company’s risk level is high. In the event of too many negative reports, financial institutions are alerted about the risk involved in doing business with the evaluated customer.
Read more:
- What is Adverse Media Screening: A Step-by-Step Process
On-site visit
On-site verification is essential for banks and financial institutions. There have been numerous cases where individuals claim a single room in a building as their office to secure loan approvals. Once the amount is credited to their account, these customers avoid the authorities.
Hence, teams conducting EDD cross-reference the physical address provided with the one stated in the submitted documents. In case of discrepancy, the risk-based threshold is deemed as breached.
Read more: what is an address verification service?
Monitoring ongoing transactions
To understand customers properly, it is important to check transaction details closely and understand their purpose and nature. Financial institutions keep this in mind while performing EDD. They also keep an eye on other crucial details like processing time, interested parties, etc. to study customer behavior. Even the purpose of scheduled transactions gets checked to ensure that they are within the expected threshold.
Read more: What is transaction monitoring in AML?
Ongoing Monitoring and Review Frequency
Enhanced Due Diligence does not end at customer onboarding. For high-risk customers, ongoing monitoring and periodic review are mandatory to ensure that the customer’s risk profile remains accurate over time.
Financial institutions are expected to continuously monitor transaction behavior against the expected activity profile established during onboarding. Any deviation—such as sudden spikes in transaction volume, changes in counterparties, or unexpected cross-border flows—must be reviewed and documented.
In addition to real-time monitoring, formal EDD reviews should be conducted periodically, depending on the customer’s risk category:
- High-risk customers: Review at least annually
- Very high-risk or PEP relationships: More frequent reviews (e.g., every 6 months or upon trigger events)
Events that re-trigger EDD
Enhanced Due Diligence must be re-initiated or updated when any of the following occur:
- Change in ownership or control structure (UBO changes)
- Significant change in source of funds or source of wealth
- Entry into new high-risk geographies or jurisdictions
- Adverse media or sanctions exposure
- Material change in transaction behavior or business activity
- Regulatory or policy-driven reclassification of customer risk
Each re-triggered EDD review must be fully documented, approved, and retained for audit purposes.
Preparing reports for further investigation
At the end of the assessment, a comprehensive report is drafted about the customer for future reference. It is worth noting that such reports are developed based on a score-based system, and customers with high scores are approved and considered eligible for business dealings with the organization.
All the reports are stored on a secure server to easily be accessed whenever regulators want. The data is stored by the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) norms, thereby ensuring the security of confidential information.
Read more: What is a Suspicious Activity Report?
Evidence Management and Audit Readiness
A strong Enhanced Due Diligence program is only as effective as its documentation and evidence management. Regulators and auditors assess not just whether EDD was performed, but whether it can be independently verified and reproduced.
Financial institutions must maintain a comprehensive EDD evidence pack for each high-risk customer, typically including:
- Customer and entity identification records
- Beneficial ownership (UBO) documentation and ownership charts
- Source of funds and source of wealth analysis
- Adverse media, sanctions, and PEP screening results
- Risk assessment rationale and approval notes
- Ongoing monitoring alerts and review outcomes
Retention and reproducibility
EDD records should be retained in accordance with regulatory and internal policy requirements, typically for a minimum of 5–10 years after the end of the customer relationship.
Equally important is reproducibility. Institutions must be able to demonstrate:
- When the EDD was conducted
- Who approved it
- What data and sources were used
- Why the customer was approved, rejected, or escalated
Well-maintained evidence ensures faster regulatory responses, smoother audits, and reduced compliance risk.
Common Enhanced Due Diligence Failure Modes
Despite having formal EDD processes, financial institutions often fail audits due to weak execution rather than absence of controls. Some of the most common EDD failure modes include:
Incomplete or unverifiable UBO trail
Institutions approve customers without fully identifying or verifying ultimate beneficial owners, especially in layered or cross-border ownership structures.
Weak source-of-funds or source-of-wealth rationale
EDD files contain documents but lack a clear explanation linking the customer’s financial activity to legitimate income or assets.
No documented monitoring rationale
Transactions are monitored, but there is no documented reasoning explaining why observed behavior is considered acceptable or within expected limits.
“Checkbox EDD” approach
EDD is treated as a compliance formality rather than a risk assessment exercise—resulting in superficial reviews, copied narratives, and poor-quality evidence.
Lack of escalation and accountability
High-risk findings are identified but not escalated to senior compliance or risk teams, leading to regulatory breaches.
Avoiding these failures requires strong governance, trained reviewers, and a risk-based mindset rather than a checklist-driven approach.
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) Checklist
A robust EDD process typically includes the following checks and documentation:
Customer & Entity Verification
- Government-issued identity documents
- Business registration and licensing records
- Ownership and control structure mapping
Risk & Background Assessment
- Politically Exposed Person (PEP) screening
- Sanctions and watchlist screening
- Adverse media and negative news analysis
Financial Analysis
- Source of funds verification
- Source of wealth assessment
- Transaction purpose and expected behavior profiling
Ongoing Controls
- Enhanced transaction monitoring
- Periodic risk reassessment
- Escalation and reporting mechanisms
Maintaining a complete EDD audit trail is essential for regulatory inspections and internal risk reviews.
What Does a Strong EDD Outcome Look Like?
A well-executed Enhanced Due Diligence process results in:
- A clearly documented customer risk profile
- Verified and explainable source of funds and ownership
- Evidence-backed approval or rejection decisions
- Defined monitoring thresholds and review frequency
- Audit-ready documentation aligned with regulatory expectations
Effective EDD is not a one-time activity but an ongoing risk-management control.
Conclusion
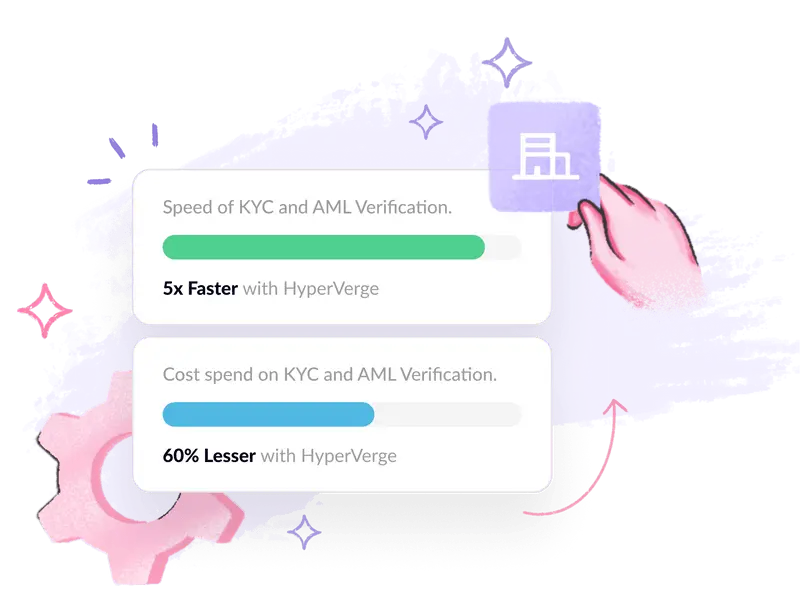
In the recent past, problems related to fraud, cybercrime, money laundering, etc., have been agonizing for financial institutions, and that’s why both eKYC and continuous monitoring procedures are strictly followed before getting a customer on board as part of AML compliance.
HyperVerge can provide AML solutions compliant with regulations. With cutting-edge AI and machine learning technologies, Hyperverge automates the EDD process seamlessly. Sign Up to take the first step towards a safe, compliant future.
Read more: Best AML software and how to choose one.





