Operating in a complex and ever-evolving landscape, financial institutions face immense pressure to protect their reputation and bottom line. However, it’s challenging to do so without the right measures provided by the sanctions screening process.
Sanctions are penalties governments impose on individuals, entities, or countries involved in illegal activities such as terrorism, money laundering, or nuclear proliferation. These penalties aim to disrupt financial transactions and freeze assets.
In this blog, we’ll explore the vitality of sanctions screening beyond a regulatory requirement – and how you can follow it effectively to shield your institution from penalties and reputational damage.
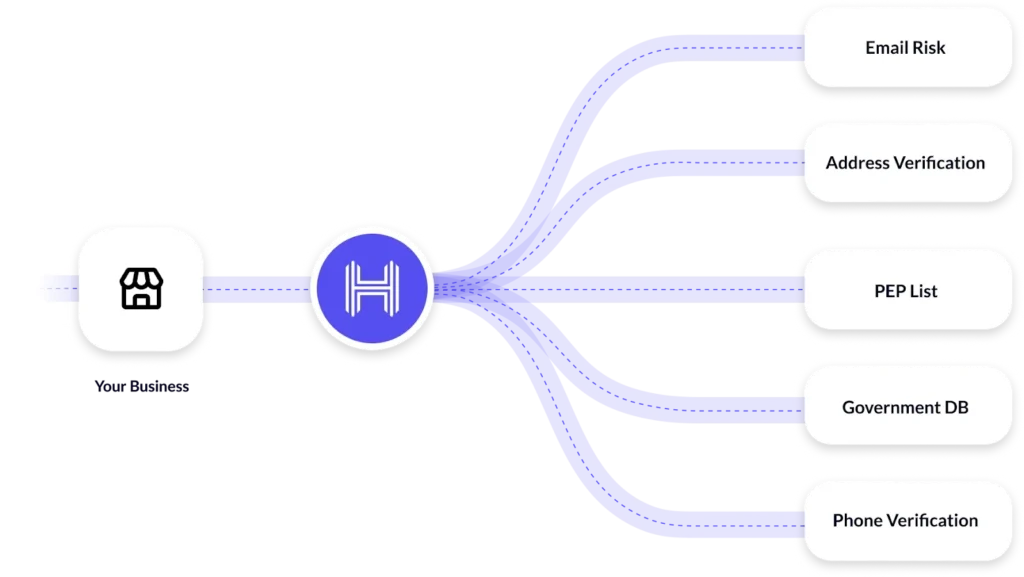
What is sanctions screening
Sanctions screening is the process of cross-referencing individuals, businesses, and transactions against blacklists of sanctioned parties. These lists, maintained by governments and international bodies, include those subject to financial restrictions due to their involvement in illegal activities.
Global watchlists help institutions stay vigilant and avoid risky dealings. By comparing transactions and clients against these watchlists, financial institutions can make sure they don’t engage with those who could jeopardize their operations. This is essential to protect your reputation and avoid hefty penalties.
Sanctions screening is, therefore, a key player in Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorism Financing (CTF) efforts. It stops money from being funneled into illegal activities and helps maintain the integrity of the global financial system.
Why is sanctions screening crucial for financial institutions?
Sanctions screening is a non-negotiable requirement for financial institutions to stay on the right side of the law.
Firstly, there is a strong legal obligation to comply with sanctions regulations. These regulations mandate that institutions thoroughly vet transactions and clients to ensure they do not engage with sanctioned parties. Otherwise, non-compliance can result in expensive fines and legal repercussions.
Beyond compliance, sanctions screening is a powerful risk management tool that helps financial institutions identify and block transactions involving sanctioned entities. This proactive approach also helps avoid potential criminal investigations, maintaining the institution’s integrity and stability.
Sanctions screening has customer protection at its core, safeguarding customers from unknowingly getting tangled in illicit transactions. Financial institutions can help their customers stay compliant and avoid legal troubles, reinforcing trust and reliability in their services.
Types of sanctions
Sanctions come in various forms, each addressing specific types of illegal activities and targeting different aspects of the financial system. Let’s break them down:
Comprehensive sanctions
These are the most far-reaching and stringent form of sanctions, imposing restrictions on a wide range of economic activities—including trade, investment, and financial transactions—within an entire country.
Imposed in response to severe violations of international law or human rights abuses, these sanctions aim to exert maximum pressure on a target nation’s government into changing its behavior.
Related reading: Embargo vs sanctions
Targeted sanctions
Targeted sanctions are a more focused approach that punishes specific individuals, entities, or organizations rather than an entire country.
These measures are designed to directly affect those responsible for illegal activities, such as terrorism, corruption, or human rights violations. They aim to limit collateral damage to the broader population while still exerting pressure on those directly involved in wrongdoing.
Sectoral sanctions
Unlike comprehensive sanctions, which affect the entire target economy, sectoral sanctions restrict economic activity within a particular industry or sector linked to the government’s illegal activities. These sanctions are often used to weaken the economic base of a nation or entity without completely severing all economic ties.
What is a sanctions list?
Sanctions lists are comprehensive databases containing detailed information about individuals, entities, and countries subject to economic sanctions. They are essentially a global blacklist for those involved in illicit activities and are maintained by governments and international organizations.
Some well-known sanction lists include:
- OFAC’s List of Specially Designated Nationals and Blocked Persons (SDN List): Managed by the U.S. Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC), this list includes individuals and entities whose assets are blocked and with whom U.S. persons are prohibited from engaging in transactions.
- EU Consolidated List: This list is maintained by the European Union and provides information on individuals, groups, undertakings, and entities subject to restrictive measures by the EU.
- UN Security Council Sanctions List: Compiled by the United Nations, this list includes names of individuals and entities subject to sanctions imposed by the Security Council.
These lists enforce economic sanctions and ensure compliance with international regulations, so they are constantly updated to reflect the evolving global landscape.
How do sanctions screenings work?

Sanctions screening is a multi-step process that ensures financial institutions and businesses comply with regulations. Here’s a breakdown of the key stages:
Collecting the data
The first step involves gathering comprehensive information about individuals or entities undergoing scrutiny. This includes names, addresses, dates of birth, passport numbers, and other relevant details. Institutions can collect this data from various sources, such as customer onboarding forms, transaction logs, and external databases.
Validating the data
The collected data must be validated for accuracy and completeness. Institutions must cross-reference the information with reliable sources and correct any discrepancies to prevent false positives and ensure accuracy of the data used in the screening process.
Sanction screening
The core of the process, the validated data is compared against current sanction lists. Advanced technology and sophisticated algorithms are used to match names and details with those on the sanction lists to identify potential matches efficiently.
Investigating the results
A match is flagged for further investigation if it is found during the screening. Compliance teams then review the flagged results to determine whether it is a true positive or a false positive. This investigation may involve gathering additional information and conducting due diligence to confirm or rule out the match.
Recordkeeping and reporting
Once the screening and investigation are complete, detailed records are maintained to ensure compliance. This documentation includes screening results, investigative findings, and any remedial actions taken.
Continuous monitoring
Sanctions lists are dynamic and constantly evolving. Hence, sanctions screening is not a one-time process but continuous monitoring. New sanctions or updates to existing lists must be promptly incorporated into the screening systems to ensure ongoing compliance and minimize risks.
When are sanctions screenings performed?
Timing is crucial when it comes to sanctions screening. Here are the main situations when sanctions screening is required:
- Onboarding new customers: Every new customer, whether an individual or a business, must undergo a comprehensive sanctions screening process as part of the customer due diligence (CDD) process, which includes Know Your Customer (KYC) compliance.
This involves verifying a customer’s identity and ownership structure, including identifying Ultimate Beneficial Owners (UBOs). This helps identify who ultimately controls a business and mitigates potential risks – such as money laundering and other financial crimes – associated with the new client.
- Periodically throughout the customer relationship: Existing customers are not exempt from sanctions screening. Regular reviews throughout the customer relationship are necessary to detect any changes in their status or associated risks.
- When processing transactions exceeding certain thresholds: Transactions exceeding specific thresholds often trigger additional scrutiny, including sanctions screening. High-value transactions are scrutinized to prevent large-scale financial crimes and the movement of illicit funds.
Who are the global sanctioning bodies?
Several influential organizations worldwide are responsible for issuing and enforcing sanctions. Here are some of the key players:
- Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) – US: As a part of the U.S. Department of the Treasury, OFAC administers and enforces economic and trade sanctions based on U.S. foreign policy and national security goals.
- Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) – UK: The FCA is the UK’s independent financial conduct regulator, responsible for ensuring that financial markets function well and that financial services are conducted fairly. This includes overseeing sanctions compliance within the UK.
- European Union (EU): The EU implements a standard foreign and security policy, including sanctions. The Council of the European Union is the decision-making body for adopting restrictive measures.
Red flags to watch for
Recognizing potential sanctions violations requires attention to detail. Here are some red flags to watch out for:
- Inconsistencies in customer data: Discrepancies in customer information, such as mismatched addresses, conflicting dates of birth, or unexplained changes in financial status, can be indicators of fraudulent activity, for example, trying to obscure identity or evade sanctions.
- Transactions with high-risk countries or entities: Business dealings with jurisdictions known for corruption, terrorism financing, or other illicit activities must raise immediate concerns, warranting closer scrutiny.
- Unusual activity patterns: Large, unexplained transactions, complex payment structures, or sudden changes in customer behavior can be red flags for potential sanctions violations.
- Identifying Politically Exposed Persons (PEPs): During customer due diligence, screening for PEPs is crucial. PEPs include individuals holding prominent public functions or those with close family or business ties to such individuals.
Transactions involving PEPs carry a higher risk of corruption and money laundering, requiring enhanced scrutiny.
Challenges in sanctions screening
While sanctions screening is essential, it’s not without its hurdles:
- False positives: Due to the vast amount of data processed, sanctions screening systems can sometimes flag legitimate individuals or entities as potential matches. If not managed effectively, this can require manual review, increasing costs and causing operational inefficiencies.
- Evolving sanctions lists: Sanctions landscapes constantly change, with new names added and existing ones removed or modified. Keeping up with these changes necessitates continuous updates, which 360-degree monitoring and system adjustments can support.
- Data quality issues: The effectiveness of sanctions screening highly depends on the data quality used. Incorrect customer information can lead to false negatives, increasing the risk of compliance breaches. Ensuring accurate and up-to-date data is needed for effective screening and compliance.
- Collaboration between different entities: Different countries and international organizations maintain their own sanctions lists, often with overlapping or conflicting data. This makes comprehensive and accurate screening across multiple jurisdictions complex.
Hence, collaboration between various organizations and regulatory bodies – such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) – is necessary to ensure consistent enforcement of sanctions across regulatory frameworks.
Tips to improve the sanctions screening process

To enhance the effectiveness of your sanctions screening program, consider these best practices:
- Keep customer data updated: Implement thorough due diligence practices during the onboarding process and maintain ongoing data verification to ensure data integrity.
- Screen using reliable sanction data: Rely on reputable sources for sanction lists to minimize false positives and negatives. Regularly update your screening system with the latest data to avoid lapses in compliance.
- Use reliable and proven screening technology: Invest in advanced technology that can efficiently process large volumes of data and identify potential matches with high accuracy; eliminate the incidence of false positives and need for manual review.
- Stay updated with rapidly changing sanction lists: Sanctions regulations evolve constantly. Implement a system to monitor changes and update your screening processes accordingly.
Make sanctions screening seamless and efficient
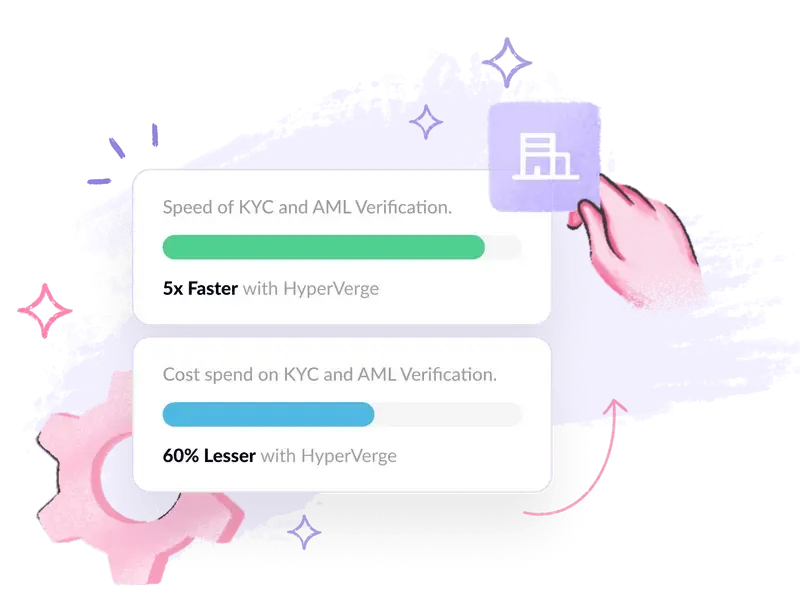
Sanctions screening can be a cumbersome process without the right tools. At HyperVerge, we understand the importance of streamlining compliance procedures while maintaining the highest standards of accuracy.
This is why our cutting-edge identity verification solution integrates comprehensive sanctions screening capabilities, empowering you to:
- Automate screening processes: Automate routine checks against global sanction lists, freeing up your team to focus on complex cases.
- Reduce false positives: Utilize advanced matching algorithms and data intelligence to minimize inaccurate alerts.
- Enhance efficiency: Streamline onboarding and customer management with integrated screening tools.
- Maintain compliance: Stay ahead of evolving regulations with ongoing updates to sanctions lists.

Ready to elevate your sanctions screening program? Explore HyperVerge’s AML solutions to learn how we can help.
FAQs
1. What is AML sanctions screening?
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) sanctions screening is the process of checking individuals and businesses against government-issued sanction lists to identify potential risks associated with money laundering and other financial crimes.
It’s a crucial component of a comprehensive AML compliance program, helping financial institutions avoid involvement with sanctioned entities and adhere to regulations. For a deeper dive into the subject, check out Definitive Guide to AML Compliance.
2. Which part of the account opening process provides information that is used for sanctions screening?
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is the stage in the account opening process where information used for sanctions screening is collected. This includes names, addresses, dates of birth, identification documents, and beneficial ownership information.
3. How to test sanctions and watch list screening software?
Testing sanctions screening software is crucial to ensure its accuracy and effectiveness. Here are some approaches:
- Scenario testing: Simulate real-world scenarios with known matches and non-matches on sanction lists.
- Negative testing: Test the system’s ability to identify potential false positives.
- Performance testing: Evaluate the software’s speed and efficiency in handling large volumes of data.
Vendors usually provide sample data sets or testing tools to evaluate sanctions screening software.
4. What is sanction screening of employees?
Sanction screening of employees is not as common as customer screening, but some institutions may choose to conduct it depending on the risk associated with their operations. This screening helps identify employees with ties to sanctioned individuals or entities, potentially indicating conflicts of interest or money laundering risks.
5. What is the difference between sanctions screening and transaction monitoring?
Sanctions screening focuses on verifying customer information against sanction lists at specific points in time, such as during account opening or periodically throughout the customer relationship.
Transaction monitoring, on the other hand, is an ongoing process that analyzes customer transactions for suspicious activity patterns that could indicate money laundering or other financial crimes.
6. What is sanctions screening due diligence?
Sanctions screening due diligence refers to the overall process of gathering customer information, conducting sanctions screening against relevant watch lists, and documenting the results. It’s an essential step in ensuring compliance with AML regulations and mitigating the risks associated with financial crime.
7. What is the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA)?
The Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) is a key piece of AML legislation in the US. Enacted in 1970, the BSA imposes anti-money laundering requirements on financial institutions. It mandates reporting suspicious activity to the authorities, helping to deter and detect money laundering and other financial crimes.





