According to Deloitte’s research, around 48% of banks and financial firms said their current technology for stopping money laundering needed improving or updating. This emphasizes the urgent need for strong, modern AML practices since financial crimes continue becoming more advanced.
Laws in different nations aim to stop laundering while allowing legal transactions. For example, in the United States, the Bank Secrecy Act requires banks to help authorities identify and prevent laundering. The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) also analyzes shared data to address financial wrongdoing. These rules highlight how important anti-money laundering efforts are for maintaining trust.
We have prepared this comprehensive guide to help you stay on top of AML compliance.
Stages of Money Laundering
Money laundering, an important issue in finance, disguises illegally earned money to make it seem legitimate. This deceptive process involves a sequence of interconnected steps that progressively hide where the money really came from. Financial firms must comprehend these phases to fight money laundering strongly. The three stages of money laundering are:
1. Placement: The first step involves putting illegal money into the banking system. Criminals may do this by depositing cash at banks, buying expensive items, or gambling with the cash. The money is most at risk of being caught here since large cash amounts can cause doubts. Financial companies have an important job, using AML transaction tracking to notice and report strange deposit habits or transactions.
2. Layering: When ill-gotten funds first enter the economic system, the layering process starts. This step aims to develop an intricate network of monetary exchanges to disconnect the dirty money from its origin. Techniques used at this stage involve transferring funds between disparate accounts, sometimes in foreign nations, investing in fiscal vehicles, or buying properties. The goal is to make tracing the cash back to the unlawful acts incredibly challenging. This step necessitates attentive anti-money laundering risk evaluation by financial organizations to identify abnormal transaction patterns that could point to money laundering.
3. Integration: The concluding phase is where the ‘cleaned’ money is reintroduced into the economy, appearing as authentic funds. This could occur through investment profits, property acquisitions, or other apparently legal financial actions. At this point, it becomes remarkably tricky to differentiate these monies from valid assets. Financial institutions must implement thorough customer due diligence processes to recognize the final integration of these funds into the financial system.
Read more about the stages and techniques of money laundering here.
- What are the three money laundering stages?
- What is Smurfing and How You Can Prevent it Proactively
- What is a money mule?
- What is Trade Based Money Laundering (TBML)?
- What is transaction laundering?
What is AML Compliance?
Money laundering laws try to stop people from making illegal money look legal. These rules and steps are called AML compliance or anti-money laundering compliance. AML compliance is not just a rule we must follow. It is important for banks and financial groups. They use it to fight crimes like money laundering and terrorist funding. Criminals try to hide illegally gotten money as real income. The financial industry uses an AML program as part of working against financial crimes.
When it comes down to it, achieving anti-money laundering compliance involves comprehensive screening of clients’ histories and continuous monitoring of customers to recognize and do away with possible dangers linked to money laundering behaviors. Financial establishments are necessary to execute AML policies and techniques that involve getting to know clients well (CDD), keeping an eye on customer relationships and transactions, and stating questionable activities to applicable administrators.
For example, financial organizations like banks must go through thorough identification validation procedures to make certain they are well acquainted with their clients. This is where resources like identity verification play an important part, assisting establishments foreign banks to validate the identities of their clients and evaluate their risk standings.
Each financial institution customizes its anti-money laundering (AML) efforts based on key aspects like the services offered, clients served, and transactions processed. These customized compliance programs are critical for finding questionable behaviors that could point to illegal deeds, such as money laundering or terrorism funding. By considering their unique situation, organizations can structure establish AML programs and solutions to spot suspicious patterns and adequately manage risk.
Read more: KYC and AML: Key Differences and Best Practices
Importance of AML Compliance for Financial Institutions
The AML landscape in the U.S. is continually evolving, with recent developments aimed at strengthening the fight against financial crimes. The Anti-Money Laundering Act of 2020, for instance, has introduced significant reforms, including enhancing whistleblower rewards and establishing a centralized beneficial ownership registry.
AML compliance is important for multiple industries. Securities, insurance, and real estate must also ensure proper protocols are followed. Even trades unrelated to money handle financial transactions that could enable illegal acts. Within each sector, complying with AML regulations aids in recognizing suspicious transactions and reducing dangers from criminal plans involving money.
What is Customer Due Diligence (CDD)?
Ongoing customer due diligence refers to the continuous monitoring and updating of customer information and risk assessments over the course of the business relationship. Ongoing CDD helps businesses stay aware of changes in their customers’ circumstances or behavior that could affect their risk profile.
For example, ongoing customer due diligence might involve risk-based procedures such as reviewing a customer’s transactions, verifying their identity if there are significant changes, or updating risk assessments based on new information. This helps businesses fulfill regulatory requirements and mitigate the risk of being involved in illegal activities unknowingly.
How Do AML Compliance Programs Work?
The AML program is a multi-faceted approach designed to prevent and detect financial crimes. The anti-money laundering program involves several key components, each playing a vital role in safeguarding financial institutions and the broader financial system.
1. AML Screening
Performing anti-money laundering checks is the initial step in following AML regulations. Verifying client identities and analyzing their risk levels are involved. Details are compared to several lists to find the AML red flags, such as politically exposed individuals, sanctioned groups, and people mentioned in negative news. Successful AML screening helps spot probable issues upfront in working with customers, helping to ensure financial institutions do not unintentionally assist with money laundering.
2. AML Monitoring
Once the initial screening is complete, then conducting ongoing customer AML monitoring is crucial. This involves continuously observing customer transactions to detect any suspicious activities that might indicate money laundering. Financial institutions use sophisticated AML transaction monitoring systems to track and analyze transaction patterns, flagging those that deviate from a customer’s usual financial behavior. This continuous monitoring is essential for identifying and reporting suspicious activities as they occur.
3. AML Red Flags and Suspicious Activity Reporting
Spotting AML warning signs is key in the AML compliance journey. These signs could be strange transaction behaviors, transactions linked to high-risk nations, or actions not matching the client’s profile. When these signs appear, banks and other firms adhere to a set reporting structure, mainly by lodging Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs). SARs get sent to pertinent bodies, such as the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) in the U.S. They play an essential role in inspecting and tackling economic crimes.
4. Risk Assessment
When determining money laundering risks in anti-money laundering compliance, financial institutions must consider the probability and effect of criminal acts connected to clients or exchanges. As explained in more detail in AML risk assessment, regulations require firms to inspect numerous elements like a customer’s history, the essence of their financial transactions, and the danger degree of locations where they do business. By performing complete risk assessments, financial organizations can appropriately address risks based on their importance to decrease recognized dangers productively.
Regulatory Framework for AML
The regulatory framework for Anti-Money Laundering (AML) comprises several key legislations and recommendations that guide financial institutions in their efforts to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
Bank Secrecy Act (BSA)
The Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) requires financial institutions to keep records and report certain financial deals.started in 1970. It is an important American law that needs financial groups to help government and law enforcement agencies to find and stop money laundering.
USA PATRIOT Act
The USA PATRIOT Act, enacted in 2001, strengthens the BSA by imposing additional anti-money laundering obligations on financial institutions. It includes provisions for enhanced due diligence, increased information sharing, and stricter penalties for non-compliance.
The USA PATRIOT Act, enacted after 9/11, increased protections and regulations under the Bank Secrecy Act to better track financial transactions. New provisions required banks to know more about their customers through enhanced due diligence. Institutions could now share important financial information more freely. Non-compliance would bring stricter consequences as well. These changes aimed to make our financial system safer and help prevent criminal plans like terrorism from succeeding.
FATF Recommendations
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) provides guidance that sets a global standard for combating money laundering and terrorism financing. Their recommendations offer several solutions, like increasing openness, confirming suitable supervision, and more serious penalties for not adhering to the rules. The goal of these recommendations is to establish straightforward guidelines that bolster safeguards everywhere.
Anti-Money Laundering Act (AMLA)
The Anti-Money Laundering Act of 2020 (AMLA) significantly amends the BSA, enhancing the U.S. government’s ability to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. It introduces provisions for beneficial ownership reporting and expands the scope of entities subject to AML regulations.
Read more: A guide to anti money laundering laws in the US (2024 updated)
Make Your AML Compliance Seamless
Implementing an effective Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance program is crucial for financial institutions to prevent and detect financial crimes. The right AML solutions can streamline this process, ensuring compliance while minimizing operational disruptions. Key components of these solutions include global sanctions and watchlist checks, Politically Exposed Person (PEP) checks, and adverse media checks.
Global Sanctions and Watchlists Screening
Comprehensive anti-money laundering solutions screen individuals and entities against worldwide sanctions and watchlists. Checks involve comparing names to lists kept by numerous global groups and administrations. This ensures those screened are not tangled in actions like money laundering, terrorism financing, or other financial wrongdoings. Effective sanctions screening is a crucial step in the due care method. It helps institutions stay away from dealing with restricted or high-danger parties and possibly money laundering. Screening aids verify associations avoid working with sanctioned or risky players involved in activities related to money laundering, terrorism financing, or other financial crimes.
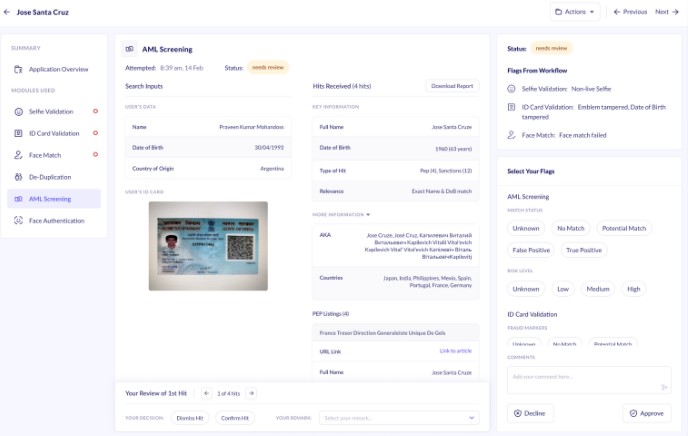
Politically Exposed Person Check
PEP screening checks are an essential aspect of AML compliance. Politically Exposed Persons are individuals who hold a prominent public position or are closely related to someone who does, making them at higher risk for potential involvement in bribery and corruption. AML solutions help in identifying such individuals and conducting enhanced due diligence to mitigate associated risks.
Adverse Media Check
Adverse media checks involve screening individuals and entities against news sources and other media to identify any negative reports about their involvement in financial crimes, legal issues, or other risky activities. This adverse media screening is vital as it provides additional context and insights into the risk a potential client may pose, beyond what traditional database checks might reveal.
Conclusion
Selecting the right AML solution involves considering factors like the comprehensiveness of the database, the frequency of updates, integration capabilities with existing systems, and the solution’s ability to adapt to changing regulations. The ideal AML software solution should offer real-time screening, robust data analytics, and user-friendly interfaces for efficient monitoring and reporting.

Financial institutions must take anti-money laundering compliance seriously. With financial crimes constantly changing, staying one step ahead requires comprehensive strategies. These include checking global sanctions, watchlists, politically exposed persons, and negative news reports. Following regulations is important, but so is protecting the integrity of the financial system. Varied sentence lengths keep readers engaged as complex ideas are explained clearly and concisely.
HyperVerge’s AML solution performs instant scans, full risk checks, and ongoing surveillance. These steps help keep your firm up-to-date with the latest AML rules.
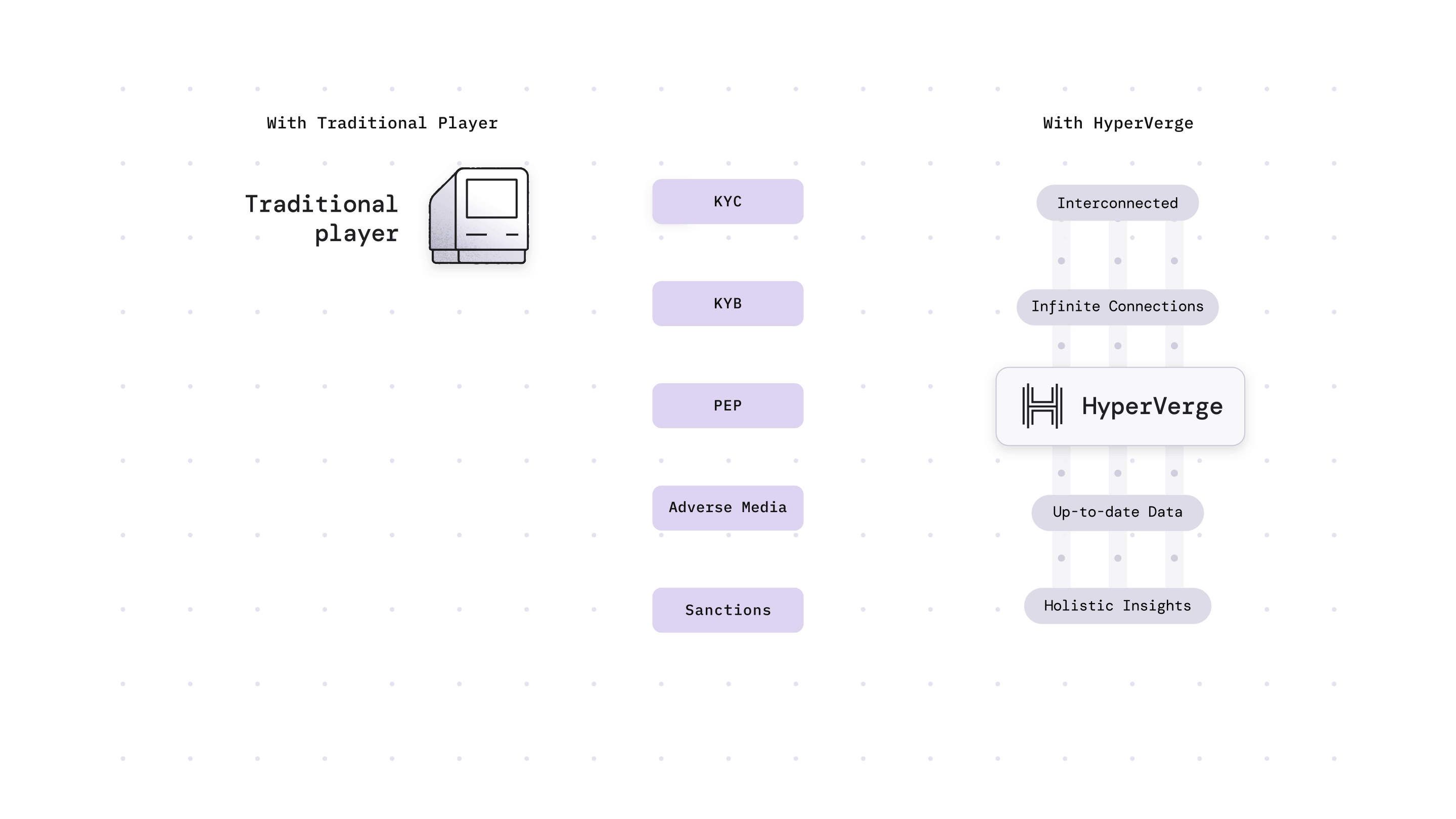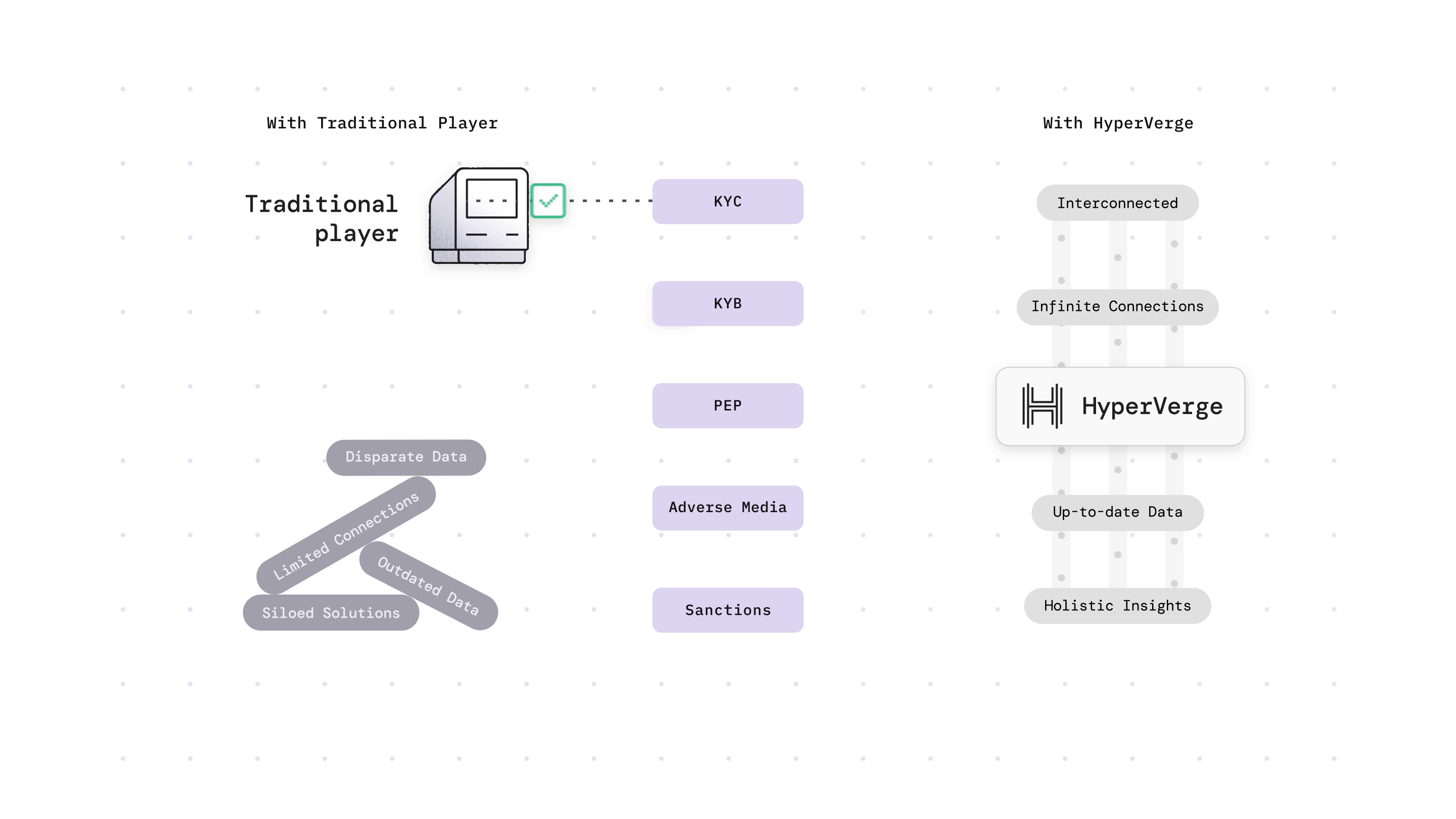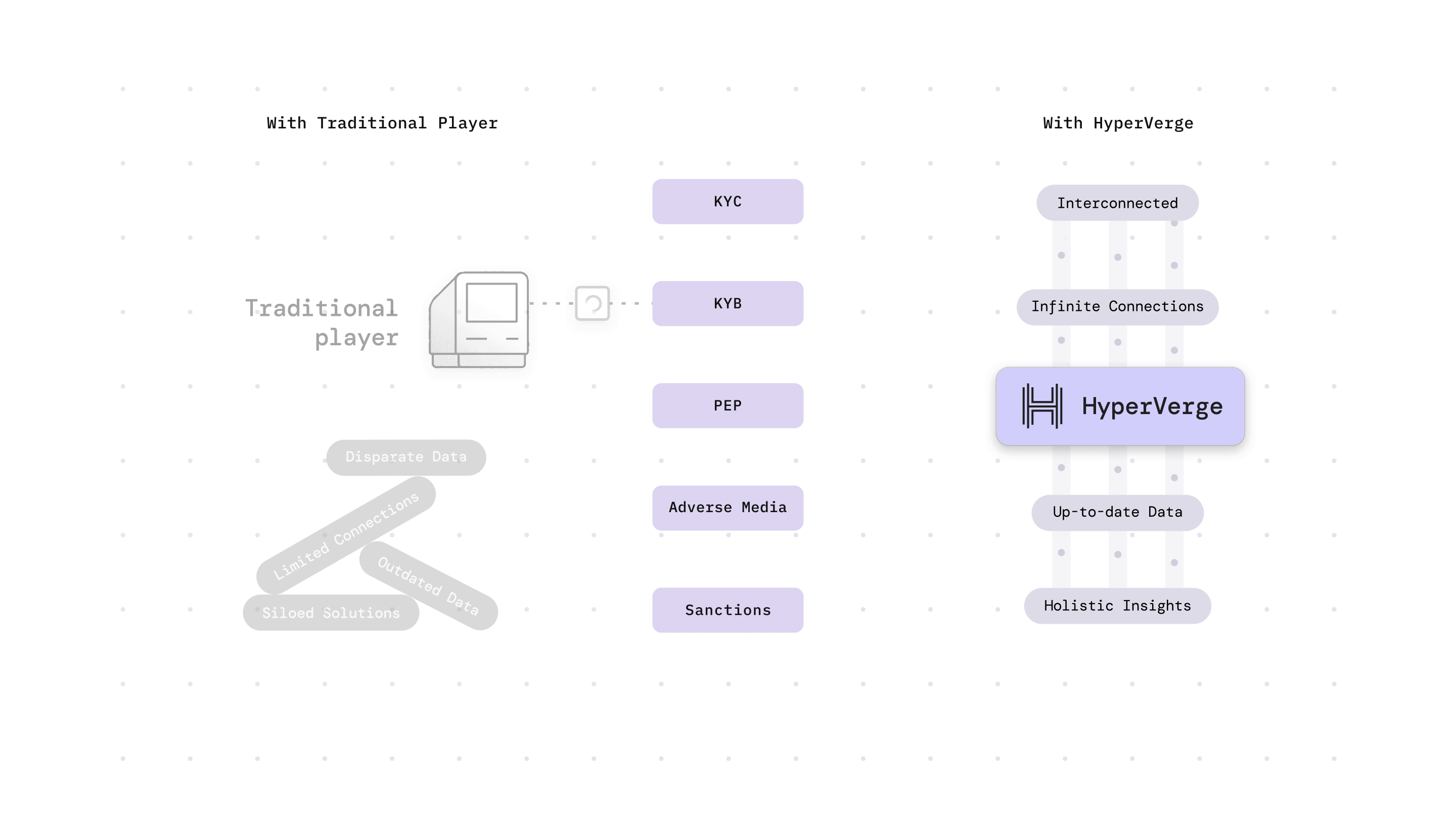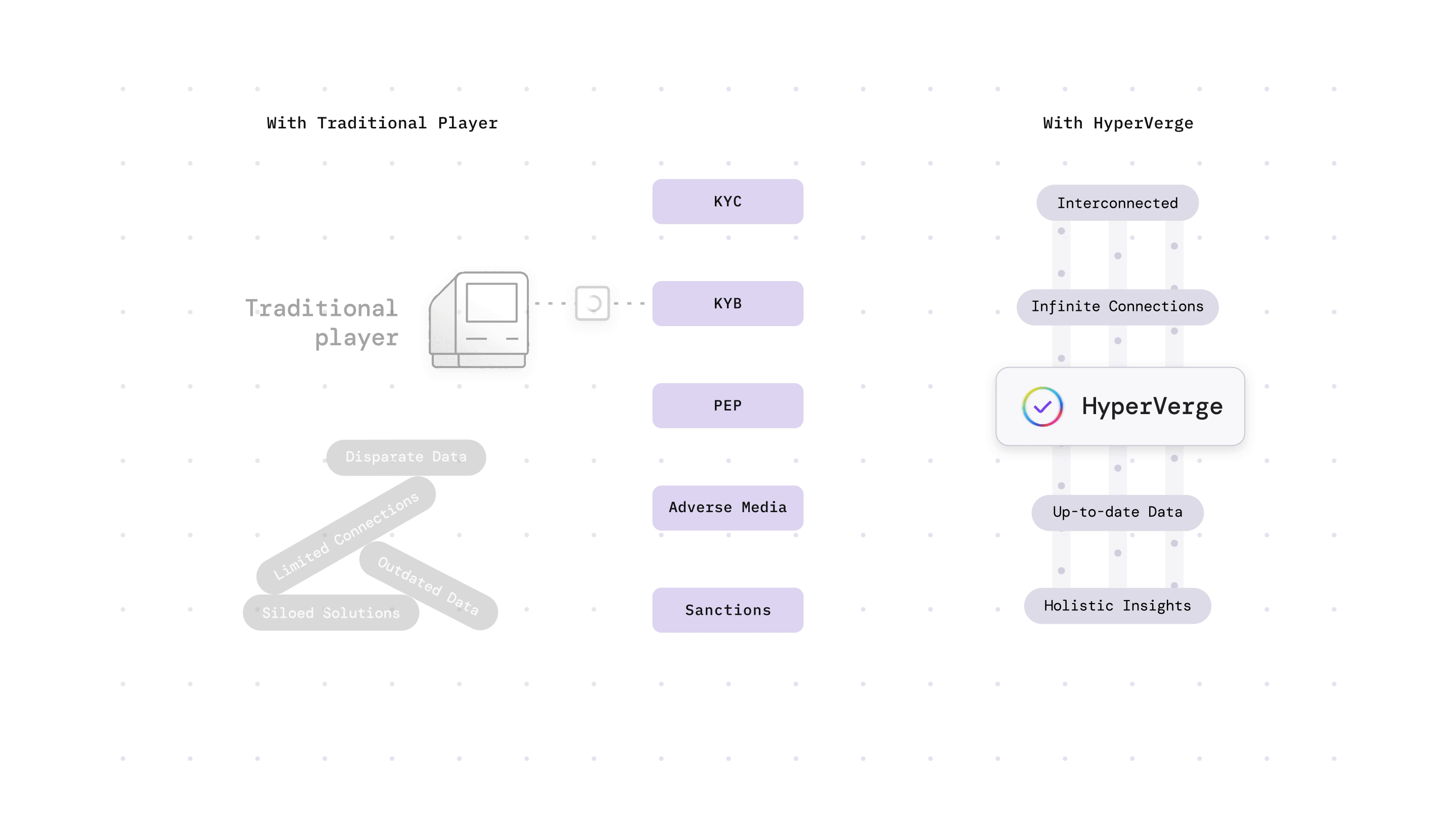
Want to strengthen your anti-money laundering compliance efforts? Check out our anti-money laundering solution for more details and sign up now to see it in action!
FAQs
1. What are legal entity customers and why are they important in AML compliance?
Legal entity customers are businesses or organizations that operate within the financial system. Identifying and understanding these entities is crucial for AML compliance because they can be used as vehicles for money laundering activities. By implementing robust customer identification programs and obtaining beneficial ownership information, financial institutions can mitigate the risk associated with legal entity customers.
2. What is anti money laundering program?
AML program helps a company to prevent money laundering and ensure compliance. The AML program requirements include customer due diligence, ongoing transaction monitoring, and reporting suspicious transactions. Financial entities should develop internal controls to handle the risks of money laundering.
3. What are the responsibilities of an AML compliance officer?
An AML compliance officer is responsible for overseeing an institution’s adherence to anti-money laundering regulations and policies. This includes implementing regulations, maintaining procedures, and ensuring ongoing monitoring of transactions for suspicious activity. Additionally, the compliance officer is tasked with training appropriate personnel, reporting suspicious transactions to regulatory authorities, and liaising with senior management to achieve compliance. Compliance officers play a critical role in safeguarding financial institutions from money laundering activities and financial fraud.





