The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime estimates that illegal money transfers make up anywhere from 2% to 5% of the world’s GDP every year. This astounding figure shows why AML andKYC are important for keeping financial institutions safe.
KYC focuses on verifying who clients really are. On the other hand, AML regulations cover a wider scope, including KYC procedures as well as risk evaluation, transaction monitoring, and reporting suspicious activities.
In this blog, we’re diving into the key differences and best practices for eKYC and AML compliance.
What is KYC?
Know Your Customer (KYC) is used to check a customer’s identity in Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) industries. This process is a guard against risks like identity fraud, financial crime, money laundering, and funding terrorism.
Here’s a closer look at the core objectives of KYC regulations:
- Regulatory compliance
- Preventing identity fraud and crimes
- Risk management
- Enhancing customer trust
Applications of KYC in Diverse Sectors
- Banking Sector: In banking, an end-to-end KYC process is performed when opening new accounts or issuing credit. It ensures accurate customer identification, risk assessment, and ongoing transaction monitoring to prevent money laundering and fraud.
- Financial Services: Investment firms, brokerages, and financial advisors rely on KYC to align financial products with customers’ risk profiles and financial goals.
- Insurance Industry: KYC in the insurance sector aids in verifying policyholders’ backgrounds, preventing identity theft, and ensuring the legitimate use of claims and benefits.
- Real Estate: Implementing KYC in real estate transactions helps verify the identities of involved parties, ensuring the legitimacy of funds and compliance with anti-money laundering regulations.
- Legal Services: Law firms employ KYC to authenticate client identities, understand their legal issues, and prevent the misuse of legal channels for money laundering. This includes performing sanctions screening and PEP checks as critical steps in the KYC process.
Read more:
- What are the three money laundering stages?
- What is layering in money laundering?
- What is a money mule?
- What is Trade Based Money Laundering (TBML)?
- What is Smurfing and How You Can Prevent it Proactively
What is the KYC Compliance Process?
Here’s a streamlined overview of the main steps:
Step 1: Customer Identification Program (CIP)
This initial step involves gathering essential information such as name, address, date of birth, and ID numbers. Accurate identification is the foundation of the KYC process, crucial for validating the customer’s identity and setting the stage for the subsequent steps.
Read more: What is a Customer Identification Program?
Step 2: Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
This involves evaluating the customer risk profiles and understanding their financial behavior. CDD ensures customers are not involved in illegal activities that could pose a risk to the financial institution.
Read more about customer due diligence
Step 3: Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for High-Risk Customers
This deeper investigation assesses the customer’s source of funds and scrutinizes their transactions. This is done to mitigate associated risks effectively while fulfilling anti-money laundering compliance standards.
Read more about Enhanced Due Diligence
Step 4: Ongoing Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of customer transactions and activities ensures that their behavior aligns with their risk profile and the institution’s standards.
What is AML?
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) is a very important system meant to stop illicit money from being washed into the financial system. Let me explain more about why AML regulations are so important by breaking it into key parts to show all the ways it affects things.
Core objectives of AML compliance:
- Combating money laundering and terrorist financing – By implementing robust AML transaction observation frameworks, financial institutions can monitor and report suspicious activities, effectively reducing AML risks.
- Promoting transparency and accountability – AML compliance ensures that financial institutions operate transparently, maintaining accurate records and conducting thorough customer due diligence.
- Adhering to international compliance – Following global standards such as the FATF Travel Rule, AML compliance rules help countries and financial systems align with international efforts against financial crimes.
- Protecting consumers and financial institutions – By identifying and mitigating AML risks, these regulations protect consumers from fraud and institutions from reputational damage and operational risks.
Applications of AML Across Diverse Sectors
Here are some applications of AML regulations in different sectors:
- Banking Sector: Rigorously monitoring of transactions and customer activities to detect and report suspicious behavior to prevent money laundering
- Financial Services: Identifying unusual investment patterns to ensure that funds are not being misused for illicit purposes
- Insurance Industry: Preventing identity theft and false claims by verifying the source of funds and conducting thorough background checks on policy applicants
- Legal Services: Ensuring that legal services are not exploited for laundering money, particularly in high-value and international dealings
- Cryptocurrency Exchanges: Monitoring transactions, identifying suspicious activities, and preventing the misuse of digital platforms for money laundering
How does AML Compliance Work?
Here’s a concise overview of the AML compliance process:
Step 1: Establishing an AML Program
Develop an AML compliance program tailored to the specific risks and nature of the institution, incorporating policies, procedures, and controls to combat money laundering and terrorist financing.
Step 2: Implementing Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
Conduct thorough customer due diligence checks to verify customers’ identities and assess their risk levels, essential for understanding their financial activities and detecting potential threats.
Step 3: Conducting Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)
For higher-risk customers, carry out in-depth EDD investigations to understand their transaction patterns and source of funds, crucial for managing increased risks.
Step 4: Ongoing Transaction Monitoring
Continuously monitor customer transactions to identify and report unusual or suspicious activities, using AML transaction monitoring systems for effective surveillance.
Step 5: Reporting Suspicious Activities
Document and submit Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) to the relevant authorities promptly, adhering to regulatory requirements and aiding in the broader effort to combat financial crimes.
Step 6: Training and Awareness
Regularly train staff on AML regulations, detection methods, and reporting procedures to ensure they are equipped to identify and deal with potential money laundering activities.
Step 7: Regular Audits and Reviews
Periodically evaluate the AML program to ensure it remains effective and up-to-date with current laws and AML risks, adjusting policies and practices as necessary.
Read more:
- Anti-Money Laundering Checks Explained: Everything You Need to Know
- What are the AML red flags?
Key Differences Between AML and KYC Regulations
| KYC | AML | |
| Origin | It is a part of AML directives but has since evolved into a distinct set of requirements focusing on customer identity verification. | AML encompasses a broader set of regulatory standards and practices aimed at preventing money laundering and financing of terrorists. |
| Purpose | To verify the identity of customers to prevent identity theft, financial fraud, etc. | To prevent, detect, and report money laundering activities and terrorist financing. It includes a wider range of activities beyond identification of customers, such as transaction monitoring and reporting suspicious activities. |
| Process | Involves customer identity verification, conducting due diligence, and ongoing monitoring. | Includes KYC procedures but extends to developing internal policies for combating money laundering, risk assessments, and ongoing monitoring. |
| Scope | Focused primarily on the onboarding process and periodic reviews. | Encompasses the entire operational framework including internal audits and global AML compliance. |
How to Automate AML and KYC Compliance?
Automating KYC and AML processes significantly boosts efficiency, accuracy, and security for financial institutions. Here’s how technology facilitates these essential compliance measures:
KYC Checks
The KYC process, a cornerstone of customer onboarding and ongoing relationships in financial institutions, involves 2 major checks to verify the customer’s identity.
- ID Document Verification: Utilizes technology to swiftly authenticate identification documents like passports and driving licenses, ensuring their legitimacy and enhancing the security of the KYC process.
- Face Match: Employs facial recognition to compare the customer’s live image with the photo ID, adding an extra layer of fraud prevention.
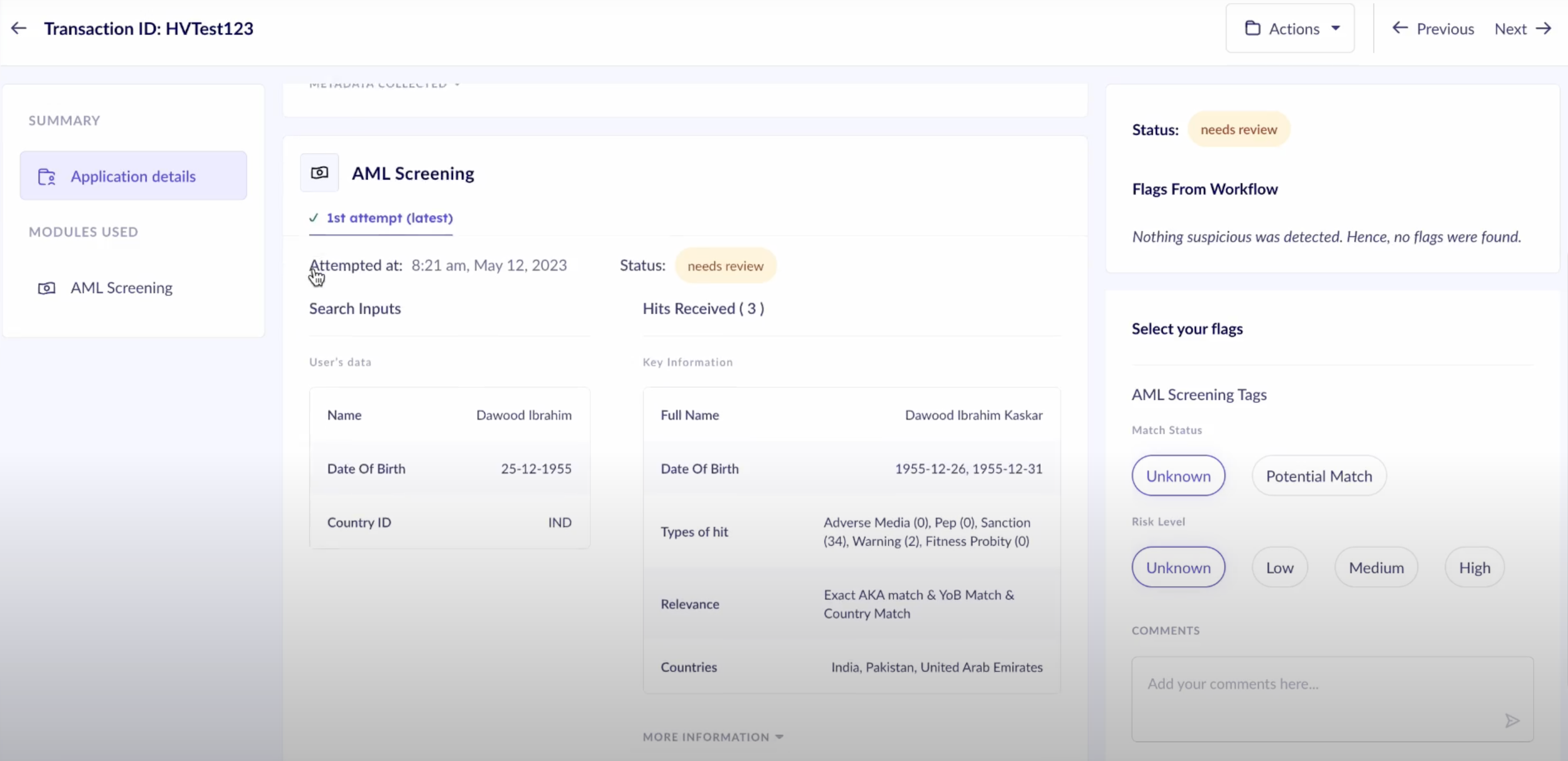
AML Regulations and Sanctions Screening
AML compliance involves thorough screening processes to ensure that institutions are not inadvertently facilitating money laundering or any associated financial crime.
- PEP Lists and Sanctions Screening: Automated systems screen individuals against PEP lists and sanctions databases, identifying risks associated with high-profile individuals to ensure compliance and manage risk effectively.
- Adverse Media Lists: Involves automatic checking of customers against media sources to uncover any negative information that could signal money laundering risks.
Read more:
- What is pep screening?
- What is sanctions screening?
- What is Adverse Media Screening: A Step-by-Step Process
Best Practices for AML and KYC in Financial Services
Here are detailed best practices for ensuring AML compliance:
Understand Regulatory Requirements
Financial institutions must continuously monitor and understand changes in AML and KYC regulations both locally and globally. Regular training sessions and updates for staff ensure that the institution’s practices remain compliant and up-to-date.
Implement a Customer Identification Program (CIP)
Establish a robust CIP to effectively verify the identities of all customers engaging in monetary transactions. This should include the use of digital verification methods and biometric technologies to reduce errors and fraud.
Conduct CDD
Carry out thorough CDD to evaluate and classify the risk levels of all customers. Initial verification should be complemented by continuous monitoring to spot any suspicious activities.
Conduct Internal Audits
Regular internal audits should assess the adequacy of policies, procedures, and controls related to AML and KYC compliance. Feedback from these audits should lead to immediate rectification actions and adjustments to strategies to close any identified gaps.
Stay Ahead of Industry Best Practices
Engaging with industry forums and regulatory bodies can provide insights into emerging trends and best practices in AML and KYC compliance procedures.
Boost your AML and KYC process with HyperVerge
At HyperVerge, we enhance your financial institution’s KYC and AML processes with our advanced suite of tools, designed for both compliance and operational efficiency. Here’s how we can transform your compliance procedures:
- End-to-end automated KYC process, including document verification, face match, and deepfake detection.
- Enhanced AML Compliance including ongoing transaction monitoring, risk assessment, suspicious activity reporting, averse media and PEP screening, and Customer Due Diligence.
Our AML and KYC solution is built with global compliance in mind so you don’t have to keep up with the ever-evolving regulatory landscape. Want to give it try? Sign up here and get a customized demo.
FAQs
1. What do AML laws refer to, and why are they important for financial service providers?
AML laws, or Anti-Money Laundering laws, are regulations designed to prevent financial crimes such as money laundering and terrorist financing. They require financial service providers to implement AML compliance programs to monitor and report suspicious transactions.
2. What is the difference between AML and KYC checks, and how do they relate to each other?
AML refers to the broader set of laws and measures aimed at preventing financial crimes, while KYC, or Know Your Customer, refers to the process of identity verification of customers. KYC falls under the umbrella of AML compliance, as it is a crucial component in assessing and managing risks associated with customers’ financial transactions.
3. How do AML compliance programs assess and manage risks associated with customers and transactions?
AML compliance programs typically employ a risk-based approach, where factors such as the nature of the customer’s business, their transaction history, and the geographic location of their activities are considered to determine the risk level. This assessment guides the implementation of appropriate AML measures, including KYC verification, ongoing due diligence, and monitoring processes, tailored to the identified risk factors.





