The rise of synthetic identity fraud looms as a formidable threat, particularly in the United States. As fraudsters’ tactics continue to evolve and traditional fraud prevention methods struggle to keep up, businesses find themselves vulnerable to a pervasive adversary.

In this blog, we’ll delve deep into synthetic identity theft, how fraudsters create synthetic identities, and how a technology-led, proactive approach can safeguard your business.
What is a Synthetic Identity Theft?
Synthetic identity theft is a form of identity fraud where criminals create a synthetic identity using a combination of real and fake information. This fabricated synthetic identity is then used to open fraudulent accounts, make purchases, or commit financial fraud.
Let’s look at the types and methodologies of synthetic identity theft:
- Identity Fabrication: This involves creating completely fictitious synthetic identities. Here, the perpetrator uses no real personally identifiable information (PII), crafting an identity out of thin air. This type of synthetic identity is especially challenging to detect because it doesn’t leave a trail that connects to real individuals.
- Identity Manipulation: In these cases, there is a modification of real personally identifiable information. A fraudster may take a legitimate social security number and pair it with a different name and date of birth, creating a “new” individual. The subtlety of these changes can sometimes bypass basic verification checks, which is why advanced identity verification measures are critical.
- Identity Compilation: Perhaps the most sophisticated, this type involves a hybrid of real and fake personally identifiable information. The criminal might combine a real person’s social security number with a fabricated name or address. The mix of legitimate and false information can make these synthetic identities very convincing and hard to uncover without in-depth fraud detection techniques.
How Does Synthetic Identity Theft Work?
Synthetic identity theft isn’t a spontaneous occurrence; it’s a calculated, multi-step process that fraudsters meticulously craft to take multiple identities, bypass security measures and exploit financial systems. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how these criminals operate:
Step 1: Crafting a Fake Identity
Fraudsters first create a new identity. They might start with a legitimate piece of information, like a stolen social security number or, often one that hasn’t been used in credit transactions before—such as those belonging to minors. This can be obtained from data breaches or the dark web.
This number becomes the foundation upon which they construct a full-fledged, albeit fake, identity — including name, date of birth, credit history, and address.
Step 2: Establishing Credit
Once the fake name identity exists, it needs a history. The fraudster may apply for credit with this new fake identity to open bank accounts or commit financial fraud. Initially, they’ll face rejections, but these applications create a credit profile. Eventually, they secure small lines of credit, which they use responsibly—at first—in order to create a long credit history. This is where biometric verification could intercept the fraud by requiring physical proof of identity.
Step 3: ‘Bust-Out’ Scheme
After fostering a good credit score, the fake identities are now seen as trustworthy borrowers. Identity thieves now take out large loans or make significant credit card purchases and have no intention of repaying them. These transactions often go unnoticed until the delinquencies start piling up.
Step 4: Utilizing Fake Checks
In addition to credit fraud, these identities are used to fabricate checks or engage in check kiting—writing bad checks from bank accounts that don’t have sufficient funds. The moment the money is credited, they withdraw it, creating a loss for the bank.
Step 5: The Disappearance
The final act in this deceptive play is the disappearance. The fraudster, having maximized the credit potential and drained the accounts, abandons the synthetic identity. It leaves financial institutions grappling with the losses and the arduous task of untangling a web of deceit—a process made more efficient through sophisticated fraud prevention solutions.
Identity Theft vs Identity Fraud
You could contend that the definition of “identity theft” implies that it transpires when someone steals your identity. And when they use your identity to defraud someone or act illegally, that is called “identity fraud.” However, the phrases “identity theft” and “identity fraud” are now used interchangeably.
Identity fraud is the use of this stolen information, whereas identity theft is the act of stealing personal, confidential, or financial information.
When criminals have access to the private information of others, what types of crimes can they commit? As it turns out, all kinds of them. Although there are many more identity thieves, frauds and identity theft crimes, the Federal Trade Commission categorizes them as follows:
Examples of Identity Fraud Crimes:
- Credit card fraud: Using a stolen credit card or credit card number to make unauthorized transactions.
- Employment or tax-related fraud: Using stolen personal information to gain employment or file an income tax return.
- Phone or utility fraud: Using stolen personal information to unlock open cell phones or utility bills.
- Bank fraud: Using stolen personal information to gain access to financial accounts.
- Loan or lease fraud: Using someone else’s information to obtain a lease or loan.
- Government documents: Using someone else’s information to obtain government benefits.
Cost of Synthetic Identity Fraud
Synthetic identity fraud is more than an inconvenience; it’s a costly epidemic with far-reaching implications for individuals and businesses.
Impact on Individuals
For individuals, the impact is both personal and financial. In 2017, synthetic identity fraud affected over 1 million children in the United States, exploiting their untapped credit histories to craft new identities.
While the financial toll can be quantified, the emotional and psychological stress on victims and their families is immeasurable. The violation of one’s identity can lead to years of credit issues and the arduous task of reclaiming financial health.
Cost Implications for Businesses
For businesses, the stakes are incredibly high. In 2020, U.S. banks and financial institutions bore the brunt of approximately $20 billion in losses due to synthetic identity fraud. This staggering figure reflects not only the direct financial loss but also hints at the broader consequences, such as increased insurance premiums, administrative costs for resolving fraud incidents, and the loss of customer trust, which can tarnish a company’s reputation irrevocably. The average amount fraudsters steal ranges between $81,000 to $97,000 per incident before detection.
The projected cost of synthetic identity fraud is expected to soar, with estimations pointing to nearly $5 billion by 2024. This projection is a clarion call for businesses to invest in robust fraud prevention measures. Companies can mitigate these risks by integrating advanced identity verification solutions and document verification processes and safeguarding their financial and reputational integrity.
Implement Sophisticated Fraud Detection Systems
In the fight against synthetic identity theft, businesses must stay ahead of the curve with cutting-edge technology. Investing in sophisticated fraud detection systems is not just an option; it’s a necessity to maintain integrity and protect against losses.
An identity verification solution goes a long way in detecting and preventing fraud. We’ve compiled a thorough checklist to help you make the right choice:
- Accuracy and Reliability:
- Confirm that the identity verification provider has a high accuracy rate in detecting fraudulent activities.
- Ensure the system is reliable under various conditions, including high volumes and diverse demographics.
- Document Verification:
- Check if the provider supports document verification, including the ability to authenticate government-issued IDs and other relevant documents.
- Ensure the system can identify any signs of tampering or forgery in submitted documents.
- Biometric Authentication:
- Look for solutions that offer biometric verification, such as facial recognition, to add an extra layer of security.
- Verify the provider’s ability to prevent the use of fake photos or videos in the authentication process.
- Compliance and Regulation:
- Confirm that the identity verification solution complies with relevant data protection regulations such as AML.
- Ensure the provider stays up-to-date with evolving compliance requirements to avoid legal issues.
- User Experience:
- Evaluate the user experience to minimize friction during the user onboarding process while maintaining a high level of security.
- Opt for a provider that offers a seamless integration into your existing systems and workflows.
- Machine Learning and AI Capabilities:
- Check if the provider employs machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to continuously adapt and improve its fraud detection capabilities.
- Ensure the system can identify patterns indicative of synthetic identity theft.
- Scalability:
- Assess the scalability of the solution to accommodate your business’s growth and increasing verification demands.
- Real-Time Verification:
- Prioritize providers that offer real-time identity verification to streamline processes and enhance the overall user experience.
- Data Security:
- Verify the measures taken by the provider to secure sensitive customer information.
- Customer Support and Training:
- Consider the quality of customer support and training provided by the identity verification provider to address any issues promptly and effectively.
Check out our blog for more details and a comparison of identity verification providers.
How HyperVerge Shields You From Synthetic Identity Fraud
At HyperVerge, we understand the critical nature of protecting your business from synthetic identity theft. Our AI-powered ID verification tool is designed to provide robust defense mechanisms against this ever-increasing threat. Here’s how our technology stands as a bulwark against fraud:
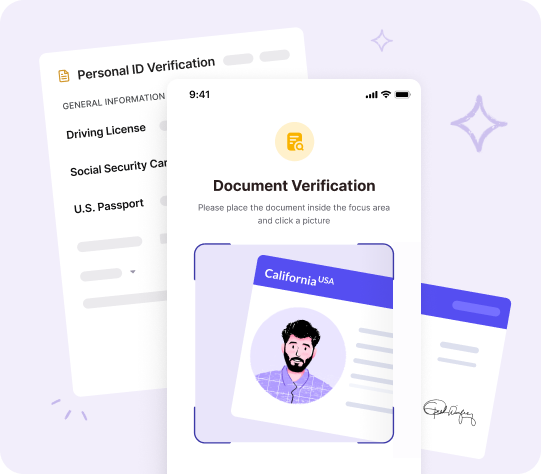
Document Verification
HyperVerge’s document verification system allows users to scan identity documents from any device. Our sophisticated technology rigorously checks the document’s authenticity, adeptly distinguishing between real and counterfeit documents. This level of scrutiny ensures that only genuine identities pass through, significantly prevent synthetic identity fraud risk.
Biometric Verification
Our biometric verification process is straightforward yet powerful. Users are required to take a photo of their ID and a selfie. HyperVerge then rapidly cross-references these images to confirm a match, firmly anchoring the customer’s real identity to their account. This process not only enhances security but also streamlines the user experience.
OCR Verification
Leveraging Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology, HyperVerge ensures that the information provided during the data source verification matches the details on the government-issued document. This layer of verification adds another dimension to our fraud prevention strategy, ensuring the integrity of user information.
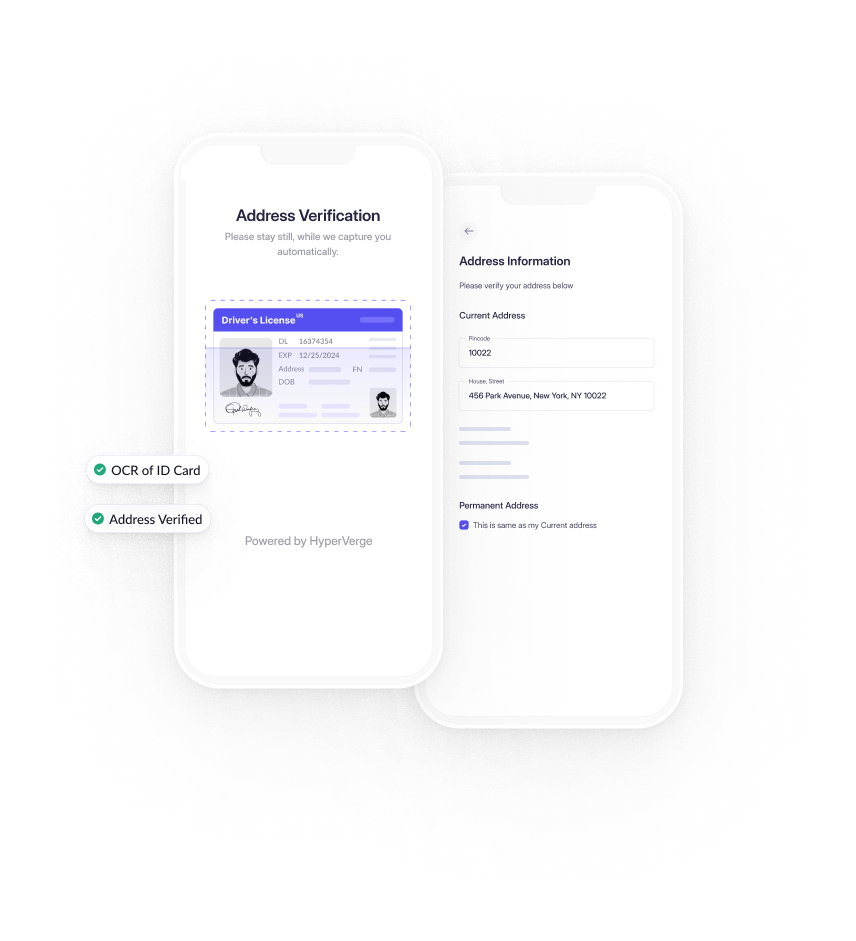
Face Authentication with Liveness Checks
We employ advanced face authentication combined with liveness checks to verify that the person present during the transaction is the real person. By analyzing factors such as skin reflectivity, screen patterns, and signs of image manipulation, HyperVerge can detect and prevent attempts at identity fraud using doctored images or deepfakes.

Prevent Synthetic Identity Fraud with HyperVerge
Discover how our technology can empower your business to operate with confidence safeguarded against the threats of traditional identity theft.
To unleash the full potential of HyperVerge’s powerful fraud prevention capabilities and receive tailored solutions that perfectly fit your unique needs, request a demo today.