Money laundering isn’t just a plotline from a crime thriller—it’s a real and pervasive threat to the integrity of the global financial system. Imagine this: criminals disguising billions of dollars in illicit funds as legitimate income, infiltrating businesses, and destabilizing economies. According to the U.S. Department of the Treasury, a staggering $300 billion is laundered annually in the U.S. alone. To put that into perspective, that’s more than the GDP of some small countries!
The ripple effects of money laundering are far-reaching. It fuels organized crime, terrorism, and corruption, while undermining trust in financial institutions. For businesses, the risks are equally dire—fines, reputational damage, and even legal consequences. In 2022 alone, global regulators imposed $5 billion in AML-related fines, highlighting the urgent need for robust defenses.
Enter Anti-Money Laundering (AML) policies—the financial world’s frontline defense against these illicit activities. AML policies are a comprehensive framework of processes, rules, and regulations designed to detect, prevent, and report suspicious financial activities. From banks to crypto exchanges, any institution handling money must implement AML measures to stay compliant and protect themselves from becoming unwitting accomplices to crime.
Key components of an effective AML policy
A robust anti-money laundering policy helps financial institutions and regulated organizations combat money laundering and terrorist financing risks. It protects businesses from illicit activities and fines for non-compliance like armor.
A sound AML policy is built on these key components, also known as the pillars of an AML policy:
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
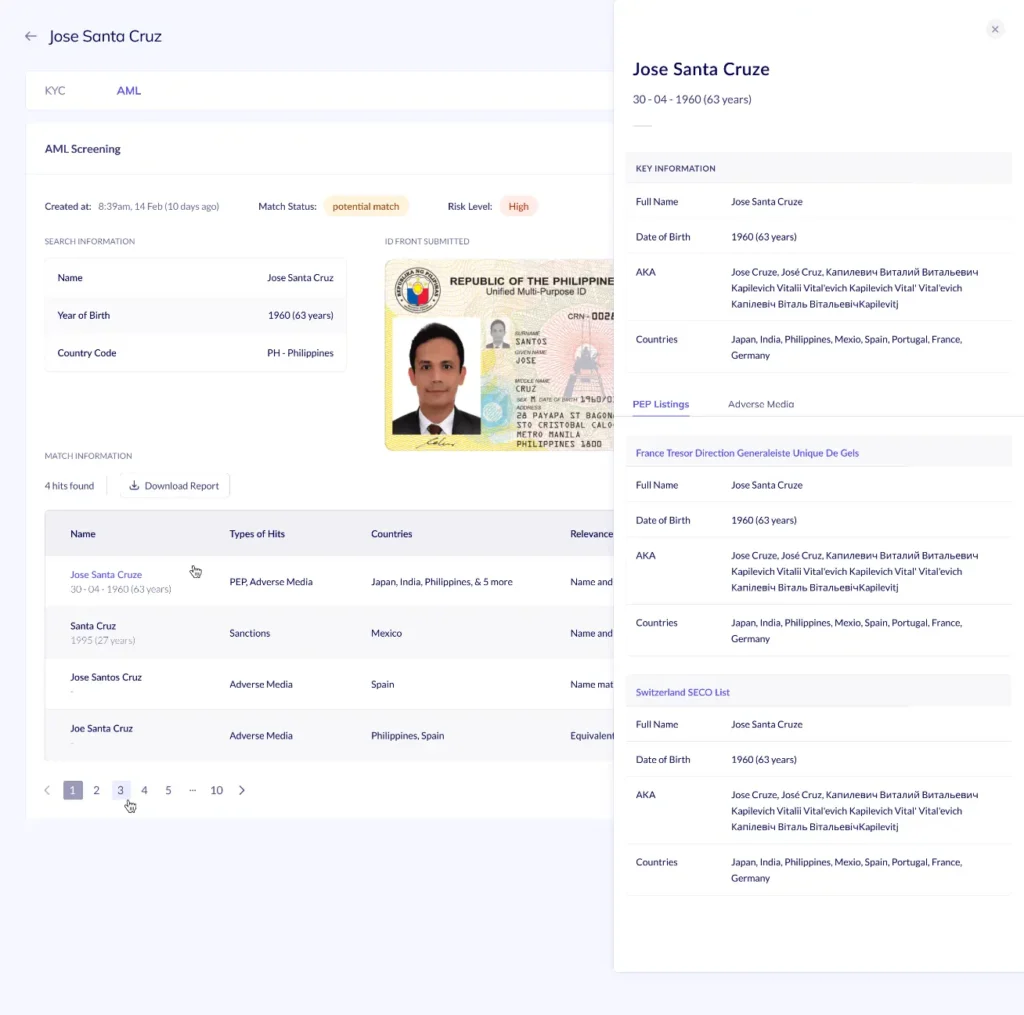
Businesses conduct due diligence based on each customer’s risk factors. It can be simplified, basic, or enhanced due diligence. Here the transaction patterns and personally identifiable information of customers are analyzed to detect illicit funds and suspicious behaviors.
- Know Your Customer (KYC)
KYC is the process of identifying and verifying the identity of your customers before building relationships with them. KYC prevents businesses from becoming a tool for criminals’ money laundering endeavors.
- Ongoing monitoring
Ongoing monitoring involves carrying out a regular check on customers to reassess their risk positions. This involves analyzing patterns and flagging unusual transactions that may indicate money laundering schemes.
- Risk assessment
Risk assessment is the process of identifying and evaluating the potential money laundering threats to your business. The information is used to develop and implement appropriate controls in your policy.
- Reporting requirements
Defines clear procedures for reporting suspicious activities to the regulatory authorities.
Now, it’s the responsibility of financial institutions and banks to devise an AML policy that encompasses these key aspects comprehensively.
The benefits of having a strong AML policy
A strong AML policy safeguards your business from getting involved in any illicit activities or financial crimes. It protects your business from hefty penalties by ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
A well-rounded compliance policy builds a safe and secure business environment for customers. It strengthens the business’s reputation and credibility by fostering long-term customer relationships.
Compliance considerations
Banks and financial institutions must comply with AML rules from various international and national authorities. Some of the most popular compliance considerations include:
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF)
FATF is an intergovernmental organization that sets AML and FT policies. It protects the financial systems of its member countries.
Note: FT (Financial Terrorism)
- EU AMLD 6
The sixth anti-money laundering directive of the European Union offers AML guidelines for its member states.
- Financial Conduct Authority (FCA)
FCA’s AML requirements apply to the UK’s financial services industry. It regulates, supervises, and authorizes financial instruments to operate according to the anti-money laundering policy regulations.
This act establishes a program, record-keeping, and reporting requirements and guidelines. The BSA specifically applies to banks and financial institutions in the U.S.
- Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA)
HKMA provides the framework for AML record-keeping and CDD to fight money laundering.
- Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS)
MAS regulates the financial sector in Singapore with stringent AML regulations. It pursues allegations involving money laundering within the country’s financial institutions.
- Australian Transaction Report and Analysis Centre (AUSTRAC)
AUSTRAC is a financial intelligence agency for businesses in Australia. It imposes heavy penalties and fines on financial institutions for not complying with AML.
- Financial Crimes Investigation Board (FCIB)
This Turkish financial intelligence unit monitors transactions for suspicious activities.
Step-by-step guide to implementing an AML policy.
Translating complex AML regulations into sound AML policies is quite a challenge. However, this step-by-step guide can help you build and implement an effective AML program for your business.
1. Conduct a risk assessment.
The process of building an efficient anti-money laundering policy begins with a risk assessment.
Here, you assess your customer base, the nature of your product or service, and the geographical location of your business. Additionally, you review the international and national laws to understand the compliance requirements. This will help evaluate the potential money laundering risks associated with your business.
Further, assess the effectiveness of your existing risk management programs. Identify gaps and weaknesses in your current system and see where it seeks improvement. Focus on the most vulnerable risk areas. Then, craft a targeted AML policy that aligns with your business’s risk appetite.
2. Develop a comprehensive AML policy
Create a detailed AML policy document. This will ensure everyone in the organization understands the severity and importance of the AML program.
Here you clearly define the scope and objectives of your AML program. Additionally, you outline activities you will undertake to combat money laundering. This document can provide deep insights into processes and controls to effectively implement AML.
Here’s what an AML policy document must entail:
- Detail the customer identity verification process. Include the documents and personal information you will collect.
- State the technologies you will use to verify the identities.
- Briefly outline the method for risk assessment before onboarding the customer.
- Describe the customer due diligence for high-risk customers and the technologies to use.
- Specify the guidelines for monitoring transactions, establish protocols, and …
- Establish ongoing monitoring processes for different customers.
- Outline the method for maintaining records for regulatory compliance.
- Clarify the reporting process to flag suspicious and fraudulent activities.
- Explain what shall be done in case the customer’s identity cannot be verified.
This guide will ensure consistent AML policy use across the organization. It will also keep your business compliant with regulations.
Note: Highly regulated businesses must hire a money laundering reporting officer. They will oversee compliance with AML policies.
3. Train staff
Now, develop an effective training program to meet the company’s AML program requirements.
Begin by explaining the importance of the stringent AML framework. If needed, explain this through real-life case studies. However, ensure that the employees understand the legal and financial consequences of non-compliance.
Next, communicate the company’s AML policies. Outline the specific roles and responsibilities of each employee. Train the employee groups to build efficient customer relationships. Guide them to conduct thorough identity checks, due diligence, and transaction monitoring.
Additionally, train them to spot suspicious activities and provide clear guidelines to report these internally.
If a financial institution uses automated technology for AML compliance, conduct dedicated sessions to use these tools effectively.
Lastly, hold regular sessions to update employees on new regulations and policy changes.
4. Implement customer due diligence (CDD)
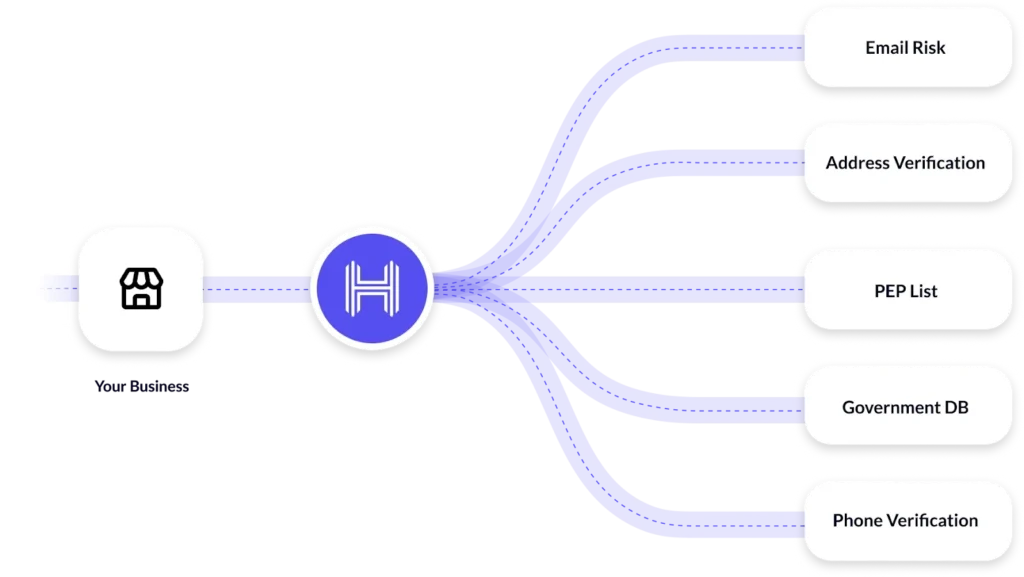
A financial institution must conduct customer due diligence throughout the lifecycle of its customer relationships to effectively address money laundering risks.
According to the guidelines of the Financial Crime Enforcement Network, the CDD process must fulfill these 3 requirements:
- Identifying and verifying the customer’s information using reliable sources. Ideally government IDs.
- Identifying and verifying the identity of the company’s ultimate beneficial owners. This includes verifying their incorporation papers, tax identification numbers, financial statements, and documents as outlined in the company’s diligence process.
- Establish the nature of customer relationships and develop risk profiles for each customer, i.e., low and high-risk customers.
Now, companies must establish clear guidelines for identifying high-risk customers, such as politically exposed persons (PEPs). They must outline a process for conducting enhanced due diligence on such customers.
Additionally, banks must screen through economic and trade sanctions lists to ensure they don’t onboard any individuals subject to sanctions, restrictions, or other legal limitations.
Note: Diligence isn’t a one-time thing. It’s an ongoing process that requires regular assessment of risk profiles to maintain compliance.
5. Monitor transactions
Consider this an extension of the due diligence process. Here you monitor the transactions of each customer to identify suspicious financial crime risks. Some of these risks include smurfing, layering, or terrorist financing.
However, given the level of transactions processed by financial institutions, manual transaction monitoring isn’t feasible. They must rely on real-time monitoring technologies to prevent, detect, and investigate any suspicious activity.
In your AML policies, establish clear thresholds for determining unusual financial activities. Also, set your system to flag such activities. Define the protocols to investigate these transactions and outline appropriate actions for each finding.
6. Maintain records
As part of the AML compliance program, financial institutions must maintain accurate, detailed records of collected data.
This includes filing identification documents, due diligence findings, transaction histories, and anything that may offer insight into customers’ potential money laundering endeavors. It’s important to keep these records safe and confidential within reach.
Ideally, one should maintain the records for the time frame of 5 to 7 years. However, depending on federal regulations, this time frame may vary.
7. Report suspicious activity
In case a business detects any suspicious transactions, it must file a suspicious activity report (SAR) within the deadline. The SAR must include detailed, relevant information to support the claims of the financial crime mentioned.
Businesses must have a clearly defined process to share data with law enforcement units. This process must be secure and confidential such that it doesn’t allow any data leaks or breaches.
8. Conduct regular reviews
Schedule periodic assessments to assess the effectiveness of your anti-money laundering policies. Through internal audits, find the gaps and weaknesses in your current policy. Identify the areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments to address evolving risks in the global financial system.
9. Stay Updated on Regulatory Changes
The regulatory bodies continuously evolve AML rules, regulations, and guidelines to combat the most sophisticated forms of money laundering. Businesses must keep an eye on these regulatory developments and introduce essential changes to remain relevant.
As you introduce the new changes, make sure that you communicate them to your team. Host training sessions to incorporate these changes efficiently.
10. Seek professional guidance
Now, it’s hard to keep track of changing regulations, especially when you’re bogged down with other important business aspects. In such cases, consult AML experts. They can review your policies and suggest essential changes to make them proactive.
Additionally, incorporate technologies that can streamline and automate the AML processes. This will save time and monetary resources while ensuring maximum compliance with the AML program.
Conclusion
Building a sophisticated AML program isn’t sufficient. Financial institutions and banks must look after its efficient implementation. This ensures that no fraudster bypasses their control checks.
However, as technology advances, so do the fraudsters. Despite the checks, terrorists and money launderers are exploiting gaps in the AML policies.
It’s more important than ever to create an AML program that mitigates the risks unique to your business.
Now, manual compliance can be challenging. However, with Hyperverge’s AML solutions, you can streamline and automate your AML programs without any complexities.
Try now.
FAQs
1. What is AML policy?
An AML policy is a set of guidelines and processes used to detect and prevent money laundering activities.
2. Who needs an AML policy?
AML policies are essential for businesses that are potentially exposed to money laundering risks. Some of these businesses include,
- Financial institutions
- Money service businesses
- Gambling units
- Banks
- Insurance companies
- Credit companies
3. How often should I review my AML policy?
Businesses must review their AML policy at least once a year to keep it effective. A review process can help address the changing regulatory and operational policies.
4. What are the consequences of not having an AML policy?
In case of non-compliance, businesses face hefty penalty charges. Sometimes, regulators put those businesses on a sanctions list. This would damage their reputation and hurt their business.





