Imagine your business unknowingly facilitating a criminal’s illegal activities—simply because you didn’t know your customer well enough. With financial crimes like money laundering and terrorist financing on the rise, regulatory bodies have tightened the reins, making compliance with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations a top priority.
A core aspect of AML compliance is Know Your Customer (KYC), a process that ensures businesses verify the identities of their customers to assess potential risks. However, implementing an effective Know Your Customer checklist can be challenging due to constantly changing rules, rigorous verification, and ongoing due diligence.
This guide will break down the essential elements of a successful KYC process to help you protect your business and stay compliant.
Understanding KYC
To build a robust defense against financial fraud, it is crucial to understand the fundamentals of KYC. Let’s explore what KYC entails, its importance for businesses, and the regulatory framework guiding it in the U.S.
What is KYC?
As the name suggests, Know Your Customer is a process by which businesses verify the identity of their customers. It involves collecting personal information, such as name, address, date of birth, and government-issued identification, to ensure that the customer is who they claim to be.
KYC compliance goes beyond identity verification to assess customers’ risk levels – based on factors such as their occupation, geographical location, and financial behavior – so the business is equipped to take risk mitigation measures proactively.
Why KYC is crucial for businesses
KYC is vital for businesses, and implementing a robust program offers key benefits such as:
- Preventing financial crimes: KYC helps detect and prevent money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit activities.
- Mitigating reputational risk: By complying with KYC regulations, businesses can protect their reputation and avoid legal penalties.
- Enhancing customer trust: A strong KYC program demonstrates a commitment to responsible business practices, fostering trust with customers.
The regulatory landscape of KYC in the USA
KYC compliance is governed by several key regulations in the United States. They include:
- Bank Secrecy Act (BSA): Requires financial institutions to maintain thorough records of their customers and report any suspicious activities to the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN).
- Patriot Act: This legislation expanded the BSA’s requirements and introduced additional KYC obligations.
- AML policies: Mandate institutions to implement customer due diligence (CDD) and conduct enhanced background checks for high-risk customers.
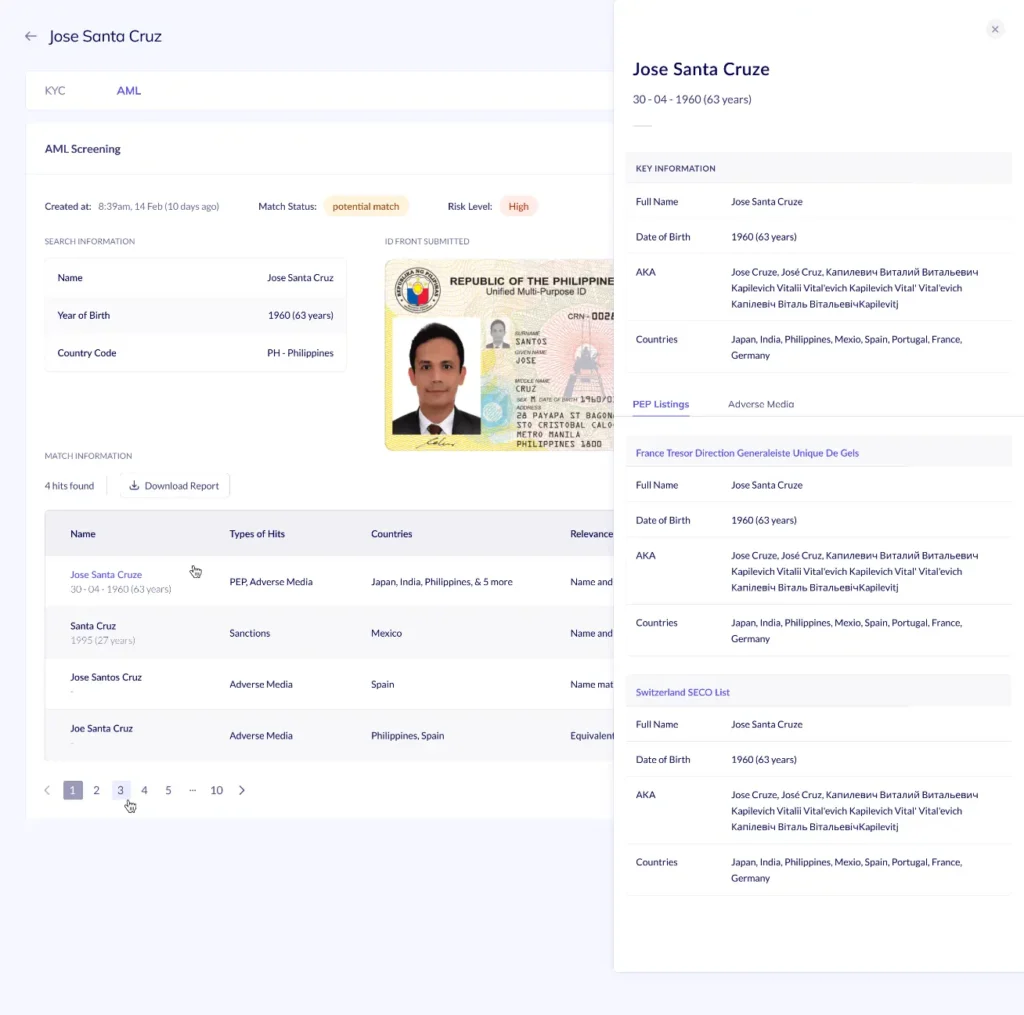
- Global watchlist screening: Ensures customers are checked against international sanctions lists to prevent financial dealings with blacklisted entities.
- Ultimate beneficial ownership (UBO) identification: Requires businesses to identify and verify the individuals who ultimately own or control a customer entity.
- Politically exposed persons (PEP) screening: Helps institutions identify customers with political influence who may present a higher risk due to their positions.
The three pillars of a robust KYC program
A successful KYC checklist process is built on three foundational pillars: customer identification, customer due diligence (CDD), and ongoing customer monitoring.
1. Customer identification
The first step in KYC is accurate customer identification before establishing a relationship. This involves collecting and verifying various pieces of information.
i. Individual customer identification
For individuals, identification typically involves collecting personal information, such as:
- Legal name
- Date of birth
- Physical address
- Email address
- Phone number
- Government-issued identification number (e.g., SSN, passport number)
Verification of this information is often done using government-issued documents like passports or driver’s licenses. This step is crucial for financial services companies as they work to comply with AML regulations.

ii. Business customer identification
For businesses, you’ll need to gather additional information, such as:
- Business name
- Structure (e.g., corporation, partnership)
- Registration details, including physical address
- Beneficial ownership information
For financial service providers, additional information such as beneficial ownership can help safeguard dealings with high-risk clients.
iii. Required KYC documents
A range of documents is required to verify customer identities. Common KYC documents include:
- Passports or driver’s licenses (for individuals)
- Articles of incorporation (for businesses)
- Utility bills or bank statements (to verify addresses)
- Government-issued identification numbers (e.g., SSN or tax identification number)
iv. Leveraging technology for verification
Advanced technology can significantly enhance the speed and accuracy of the customer identification process. Firms can use tools like AI-powered document scanning and biometric authentication to automate the process.
2. Customer due diligence (CDD)
Once you’ve identified your customers, it’s essential to conduct CDD to evaluate a customer’s risk level and determine whether risk mitigation is necessary.
i. Assessing customer risk profiles
AML risk assessment helps determine the potential risks posed by each customer. Customer risk profiles are assessed based on various factors, including:
- Occupation: Certain professions may pose higher risks.
- Geographic location: Customers from high-risk countries or regions may require additional scrutiny.
- Transaction history: Unusual or suspicious activity can indicate potential risks.
ii. CDD for high-risk and low-risk customers
The level of CDD required will vary depending on the customer’s risk profile. High-risk customers may require enhanced due diligence (EDD) such as thorough background checks, additional document verification, and closer scrutiny of transactions. Low-risk customers may only require standard identification checks.
iii. The importance of background checks
Background checks can provide valuable insights into a customer’s history and potential risks. This can include screening against global watchlists, identifying any politically exposed persons (PEPs), or checking for adverse media coverage.
3. Ongoing customer monitoring
KYC is not a one-time process and must continue post customer onboarding, ensuring early detection of any suspicious activity.
i. Why continuous monitoring matters
Continuous monitoring can help identify signs of illegal activity early on, protecting your business.
ii. Tracking transactions and account activity
AML transaction monitoring helps institutions observe transactions in real time. By leveraging the right AML tools, businesses can flag unusual behavior, like large or frequent, unexplained transfers between accounts.
iii. Periodic customer reviews
Conduct periodic reviews of your customers’ risk profiles to ensure they remain accurate and up-to-date. This involves updating customer information and reassessing their risk levels.
Building a comprehensive KYC checklist
A well-structured KYC checklist is key to ensuring thorough compliance and reducing the risk of financial crime. Consider the following while building your checklist:
1. Tailoring KYC checklists to your industry
Different industries face varying levels of risk and regulatory requirements, so it’s important to customize your KYC checklist accordingly. For example, financial institutions might focus on customer identification and due diligence, while the real estate sector may prioritize verifying the source of funds.
By understanding the specific risks your industry faces, you can create a checklist that ensures you meet all necessary regulatory standards.
To create the best results:
- Identify the unique risks your business and industry face.
- Ensure your checklist covers all regulatory requirements relevant to your sector.
- Regularly update the checklist to accommodate new regulations or changes in business operations.
2. Streamlining the KYC process
Once you’ve built a comprehensive checklist, the next step is to streamline your KYC process. This involves minimizing friction during customer onboarding while ensuring all necessary checks are completed. Consider the following strategies:
- Digital onboarding: Implement digital onboarding solutions to automate customer identification and verification.
- Data integration: Integrate KYC data with your existing systems to avoid duplication and errors.
- Workflow optimization: Design efficient workflows to guide your staff through the KYC process.
By making the process user-friendly, you’ll reduce delays, improve customer satisfaction, and ensure compliance.
3. The role of automation in KYC
Automation plays a transformative role in making the KYC process faster, more efficient, and accurate. AI-powered tools can assist with identity verification, global watchlist screening, and transaction monitoring in real time.
These tools can efficiently gather and verify customer information, analyze data to assess risk levels, and continuously monitor transactions while generating necessary reports, helping businesses flag suspicious activity and reduce manual errors.
Leveraging automation not only enhances compliance but also boosts the overall effectiveness of your KYC program.
KYC checklist for businesses in the US
For businesses operating in the US, adhering to a robust KYC program is a must to ensure compliance. Here is a detailed checklist covering key components of the KYC process:
1. Customer Identification Program (CIP)
- Collect customer information:
- Legal name
- Date of birth
- Physical address
- Email address
- Phone number
- Government-issued identification number
- Verify customer identity:
- Obtain government-issued identification documents (e.g., passport, driver’s license)
- Conduct document verification (physical or digital)
- Leverage biometric verification for added security (e.g., facial recognition, fingerprint)
- Determine customer risk level:
- Assess the customer’s risk profile based on various factors
- Apply a risk-based approach to KYC procedures
2. Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
- Understand the nature of the business relationship:
- Determine the purpose and expected nature of the business relationship.
- Identify beneficial owners if applicable.
- Conduct enhanced due diligence (EDD) if necessary:
- For high-risk customers, conduct additional checks such as background checks and adverse media screening.
3. Ongoing monitoring
Monitor customer activity:
- Continuously monitor customer transactions for suspicious activity
- Update customer information as needed
- Review customer risk ratings periodically
4. Recordkeeping
Maintain accurate records:
- Keep detailed records of the KYC process, including documents, verification results, and risk assessments.
- Retain records for the required retention period, as mandated by regulations.
5. Additional considerations
- Employee training: Ensure employees are trained on KYC procedures and regulations to stay compliant and minimize errors.
- Technology implementation: Utilize KYC automation tools to streamline the process and improve efficiency.
- Compliance with regulations: Stay updated on relevant KYC regulations and industry standards to ensure ongoing compliance.
The future of KYC
As money laundering becomes more sophisticated, businesses must adapt their KYC compliance strategies to become more resilient. By employing cutting-edge technologies and staying ahead of industry trends, organizations can remain compliant and strengthen their defenses against financial fraud.
Emerging technologies in KYC
Several technologies are revolutionizing the KYC process, making it faster, more secure, and scalable:
- Artificial intelligence (AI): Automates tasks like customer identification, document verification, and risk assessment.
- Blockchain: Provides secure and transparent storage and sharing of KYC data.
- Biometrics: Enhances accuracy through facial recognition and fingerprint verification, strengthening customer identity checks.
Industry trends and best practices
To future-proof your KYC program, consider adopting these key trends:
- Risk-based approach: Focus resources on high-risk customers while streamlining processes for low-risk clients.
- Continuous monitoring: Detect changes in customer behavior and risk profiles in real time.
- Data privacy and security: Prioritize secure handling of customer data in line with global regulations.
- Cross-border collaboration: Standardize processes and share data with global partners to combat financial misconduct effectively.
Given the criticality of being compliant, especially for financial firms, having a well-structured KYC program is a necessity. By leveraging the three pillars of KYC—customer identification, due diligence, and continuous monitoring—you can protect your organization while optimizing operational efficiency with the help of emerging technologies.
Recap of key points
- Customer identification: Accurate verification is the foundation of any KYC program.
- Customer due diligence (CDD): Risk assessments help identify potential threats.
- Ongoing monitoring: Continuous tracking of customer behavior is crucial to detecting changes in risk.
- Tailored KYC programs: Adapt your KYC processes to meet your industry’s specific needs.
- Leveraging technology: Automation and AI can streamline processes, improve accuracy, and reduce manual workloads.
Stay compliant with HyperVerge’s comprehensive AML solutions
Take a proactive approach to AML compliance with HyperVerge:
- Automated AML screening against global sanction lists and PEP databases.
- AI-powered risk assessment to generate dynamic customer risk profiles.
- Seamless digital onboarding for enhanced customer experience and compliance.
- Continuous transaction monitoring to detect suspicious activity in real time.
- Customizable workflows for flexible compliance approaches.
- Enhanced reporting for comprehensive audit trails and regulatory demonstration.
Sign up for a 30-day free trial to see our product in action!





