“If you can’t explain it to a six-year-old, you don’t understand it yourself.”
– Albert Einstein
In the recent Indiana Jones movie, actor Harrison Ford was shown to be younger by more than 40 years. Old photos of Harrison Ford were used to create a realistic and younger-looking version of him in the movie. Now, this is a classic example of Deepfake. According to a KPMG report (2023), depfakes are rising by 900% every year!
While Deepfakes are making waves in the media, understanding and decoding them has become a huge challenge.. In this article, we’ll break down the complexities of deepfakes in straightforward simple terms.
Deepfake – What is it anyway?
It’s media created by AI and altered using deep neural networks to change someone’s identity. This could be in the form of images, videos, or audio files. Simply put, deepfake meaning: fake but convincing media made to look real with AI and Machine Learning. They often swap faces in videos or images to create a false version of the original content, kind of like super advanced Photoshopped images. In the wrong hands, deep fake technology can cause serious trouble, representing AI-generated content designed to deceive.
How do you understand Deepfakes?
Deep fake technology is made using two algorithms: a generator and a discriminator. The generator creates fake content, while the discriminator checks if it’s real or fake. They work together in what’s called a generative adversarial network (GAN). This network learns from patterns to make better fake images as the process goes on.
Through this mechanism, GANs analyze patterns in data to understand the distinguishing features of authentic images, videos, or audio recordings. Consequently, they become adept at generating increasingly realistic synthetic media, blurring the lines between what is real and what is not.
Relevant read: How do deepfakes work
Exploring the two major types of Deepfakes:
Deepfakes are essentially synthetic media that employ AI techniques to convincingly alter or substitute existing content. Among the various forms of deepfakes, popular examples include face swaps and facial synthesis, highlighting the diverse range of manipulation techniques.
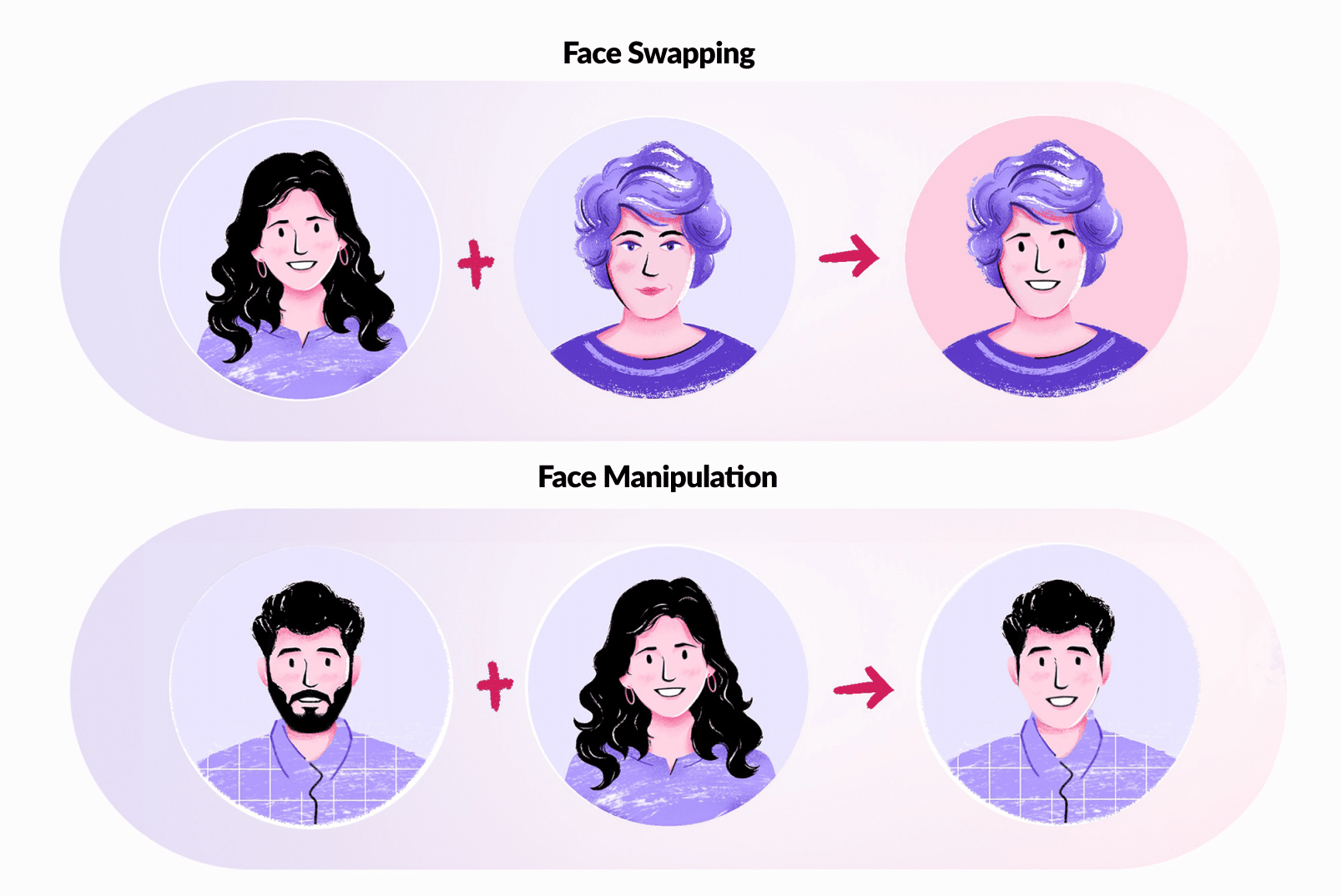
1) Face swaps:
Face swaps in deepfakes entail seamlessly placing one person’s face onto another’s, creating a convincing image that’s challenging to distinguish. Sophisticated algorithms meticulously analyze facial features, expressions, and lighting to achieve authentic results. This manipulation involves substituting the face of one individual in a video (source) with that of another individual (target), aiming to produce realistic fake videos with precision. Apps on playstore are easily available to download and use for such purposes making it all the more easy for a fraudster.
2) Facial Manipulation:
Facial manipulation involves crafting entirely new facial images that don’t exist in reality. These techniques yield remarkable outcomes, producing high-quality facial images with a realistic appearance. The synthesis of entire faces is achieved through robust GANs, resulting in images that captivate the observer with their authenticity.
Relevant read: What are the different types of deepfakes
Now meet the other troublemaker: CAMERA INJECTION
It’s like the blockbuster sequel you didn’t see coming after deepfakes.
But, what exactly is a camera injection, you ask?
Picture this: Remember Ocean’s 11, where Danny Ocean and crew pulled off that epic casino heist by swapping live surveillance feeds with pre-recorded ones? That’s basically how camera injections work. Fraudsters can pull off similar tricks in KYC processes, uploading manipulated images and videos to fool the system.
An injection attack can take many forms, but it always involves sneaking in forged or fraudulent data. Attackers might use virtual cameras or browser plugins to pull off their schemes.

A Common example of injection attack is Deepfake video injection.
In facial recognition systems, fraudsters can inject deepfake videos during the authentication process. Deepfakes employ AI and machine learning to generate realistic videos of individuals appearing to say or do things they haven’t done in reality. By injecting such videos into a system’s feed, attackers can imitate a genuine user’s appearance, bypassing facial recognition security protocols.
Is there a real distinction between Camera injections and Deepfakes?
No. Basically Deepfakes is just one of the most prominent techniques used in Camera injections.
Deepfakes take the spotlight in the world of camera injections. With “injection attacks,” shady characters can inject deepfake facial images/videos, pass liveness checks, setting the stage for creating and exploiting fake accounts scot-free. The most common example of Camera Injection is when fraudsters inject a deepfaked photo or video to fool facial biometric systems. As today’s deepfakes get more sophisticated, trusting our digital identities feels like navigating a maze blindfolded! That’s where we at HyperVerge want to help you combat Deepfakes.
Stay tuned for our upcoming blog, where we’ll dive into why image injections pose an equal threat and what you can do to protect your business against them. Meanwhile, get acquainted with some buzzwords related to deepfakes!
DEEPFAKE GLOSSARY:
Cheapfakes: Low-cost, easily produced manipulated media, often relying on simpler techniques than deepfakes for deceptive purposes.
Image Injection: The process of introducing manipulated or malicious images into digital platforms or systems, potentially to alter perceptions or spread misinformation.
Face swap: The act of digitally exchanging the facial features of one person with those of another in an image or video.
Spoofing: The practice of deceiving a system or individual by presenting false information or a fake identity, often in the context of cybersecurity or biometric authentication.