A Customer Identification Program (CIP) is an essential regulatory requirement for financial institutions in the United States, necessitated by the USA PATRIOT Act to fight monetary wrongdoings like money laundering.
The significance of CIP for financial services companies cannot be underestimated. It guarantees adherence to federal legislation and acts a pivotal function in decreasing dangers linked to financial crimes. According to a report, KYC and CIP-related fines saw a significant increase of 50% in 2022, with banks being charged almost $5 billion for violations related to money laundering activities.
Introduction to Customer Identification Program (CIP)
CIP stands as a critical regulatory mandate, born from the USA PATRIOT Act, aimed at enhancing the security of the financial sector. It obliges financial institutions to conduct thorough identity verifications of their clients before establishing any business relationship.
This verification process is comprehensive, requiring the collection of key details such as the customer’s full name, address, date of birth, and an identification number, which varies from a Social Security number for U.S. citizens to passport and alien identification card number for international clients.

Objectives of CIP
The primary goals of CIP are twofold:
- To bolster the reliability of financial transactions.
- To erect a formidable defense against financial crimes.
By ensuring a thorough vetting process, CIP helps in building a foundation of trust and security within the financial system, making it more difficult for illicit activities to take place.
Importance of CIP
Role in the Financial Industry
CIP’s role in the financial industry cannot be overstated. It acts as the cornerstone of anti-money laundering (AML) efforts, integrating seamlessly into a firm’s AML compliance strategy. This integration is crucial for maintaining the integrity of financial transactions and for fostering a secure environment that is resistant to the threats of financial crime.
Regulatory Requirements
Complying with CIP requirements does more than satisfy regulations—it strengthens a financial institution’s foundation of trustworthiness and safety. Meeting CIP standards confirms that an organization aims not just to obey the what AML laws requires, but to shield itself from vulnerabilities connected to financial wrongdoings through proactive precautions. Such adherence demonstrates a dedication to both principled procedures and security.
Is CIP Applicable to My Business?
Money Service Businesses
Money Service Businesses (MSBs) that offer services, such as currency exchange, check cashing, and money transmission, must implement CIP as part of their AML efforts. Proper customer due diligence is integral for avoiding financial wrongdoings and confirming adherence to expectations set by regulatory bodies.
Fintech
Fintech firms involved in payments, lending, and investment platforms are not always legally obligated in every location to carry out Customer Identification Programs. However, implementing CIPs is strongly advised. Doing so builds trust, strengthens security, and helps compliance with evolving financial regulations. These verification processes aid companies in reliably confirming users’ identities.
Insurers
Insurers must implement CIP procedures, especially for those providing plans that potentially enable more money laundering risks, as life policies with investment features. This guarantees they satisfy AML compliance rules and safeguard against monetary deception.
Brokers and Dealers
Brokers and dealers in securities are mandated to implement CIP to verify the true identity of their clients. This is a critical component of their compliance with the Bank Secrecy Act and AML regulations, helping to prevent fraudulent activities and illicit financial flows.
Other Financial Institutions
Other financial institutions, including banks, credit unions, and certain investment entities, are also required to implement CIP as part of their foundational compliance with AML regulations. The extent and specifics of a bank’s CIP implementation may vary based on jurisdictional requirements but are essential for operational integrity and regulatory compliance.
CIP vs KYC vs AML: Understanding Their Interconnection
Figuring out the abbreviations of monetary conformity can experience like decoding an intricate encryption. Yet, comprehending the contrasts and connections between CIP, Know Your Customer (KYC), and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) is fundamental for any element working inside or close to the budgetary part.
CIP plays a crucial role in the overall anti-money laundering framework. It serves as the gateway for KYC procedures, which involve a wider range of activities aimed at understanding and monitoring client behavior to effectively reduce financial risks.
KYC extends beyond the initial process to incorporate ongoing diligence and surveillance, ensuring that businesses stay informed about their customers’ actions and AML risk assessments continuingly. This persistent procedure is critical for identifying and communicating questionable behaviors, aligning closely with AML goals.
AML incorporates the broadest set of laws, rules, and processes intended to stop criminals from disguising illegally acquired money as legitimate earnings. Core AML tactics encompass CIP and KYC protocols but additionally involve more extensive risk evaluation and administration practices, like screening against sanctions lists and observing transactions for indications of money laundering or terrorist funding.
Read more: KYC and AML: Key Differences and Best Practices
Six General Requirements for the Customer Identification Program
Here, we delve into the six general requirements that constitute the backbone of a robust CIP.
1. A Documented CIP Program
A foundational requirement for a Customer Identification Program is the development of a documented program that outlines the procedures and processes a financial institution will follow to verify the identity of its customers. This document serves as a blueprint for compliance, ensuring that all measures meet regulatory standards and are consistently applied across the board. It should detail the types of identifying information collected, the methods used for verification, and the steps taken when discrepancies arise. Establishing a documented CIP program is essential for demonstrating compliance with AML regulations and for providing a structured approach to customer verification.
2. Collection of Identifying Information
The second cornerstone of the Customer Identification Program involves assembling recognizing data from clients. This ordinarily incorporates the client’s name, date of birth, address, and a distinguishing proof number, similar to a Social Security number in the U.S. or taxpayer identification number. The objective is to gather adequate data to frame a sensible conviction that the monetary foundation knows the genuine character of its clients. This stage is basic for laying the establishment for powerful character confirmation and hazard appraisal.
3. Identity Verification Processes
Once identifying information is collected, the subsequent step is to substantiate the customer’s identity utilizing dependable, free source records, information, or information. Verification can be directed through different means, including checking government-issued business licenses, driver’s license, passport number, or other identifying documents, counseling with third-party identity verification services, or utilizing non-archive strategies for example customer due diligence processes. The chosen techniques ought to have the option to give a high level of confidence with respect to the customer’s identity.
Read more: What is Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)?
4. Recordkeeping
Effective recordkeeping is a critical component of Customer Identification Program, requiring financial institutions to maintain records of the information used to verify a customer’s identity. This includes copies or records of any documents reviewed, the resolution of any discrepancies in the identification process, and a clear description of the verification method and results. These records must be kept for a specified period, typically five years after the account is closed, to ensure they are available for regulatory examination or in response to a lawful request.
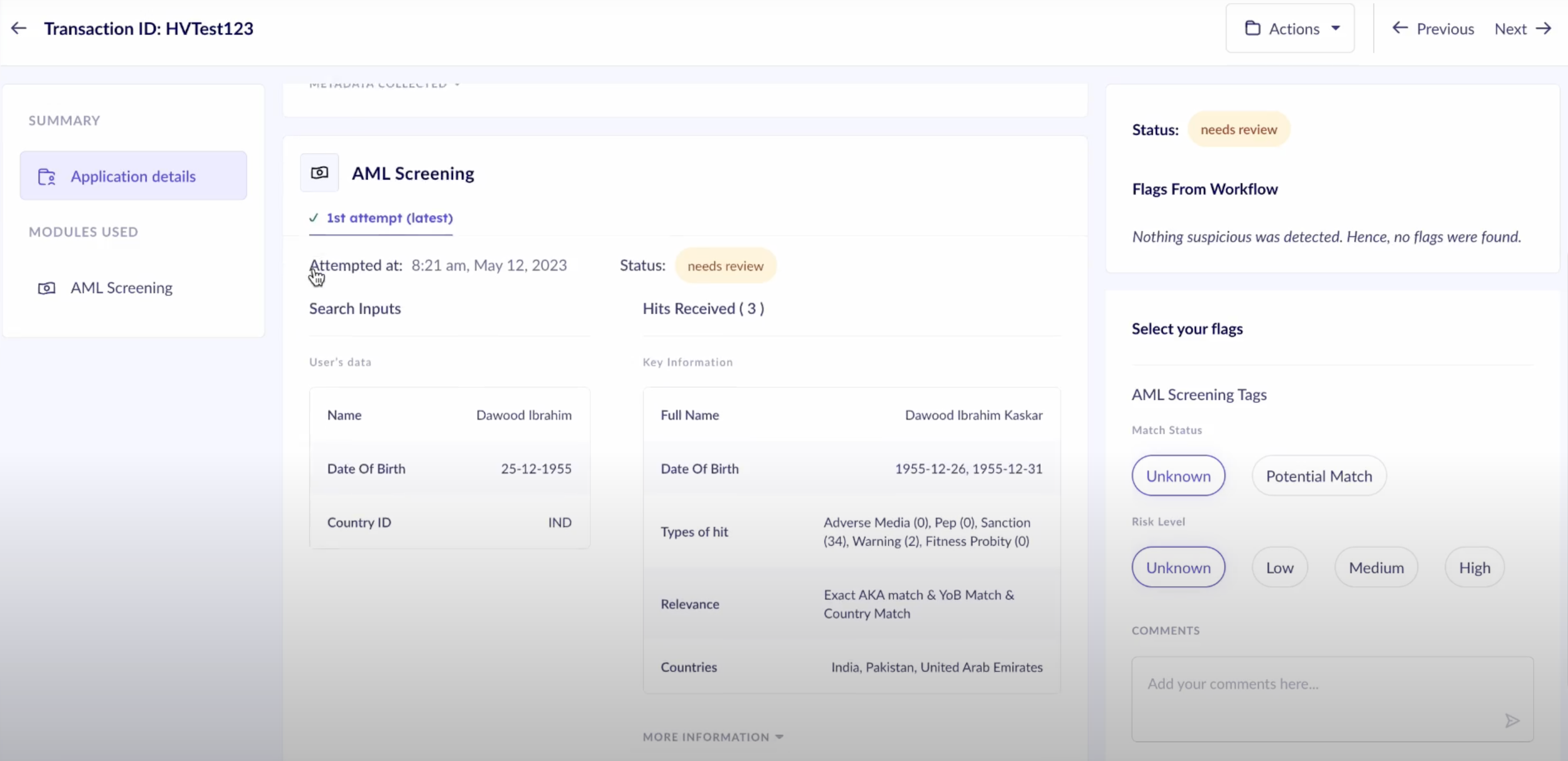
5. Comparison With Government Lists
When opening new accounts, financial establishments must match new clients’ identifying details against government-issued directories containing known or suspected terrorists. This matching seeks to bar people or groups connected to terrorism or terrorist funding from exploiting the financial system. Organizations must maintain processes to react properly if a possible match to terrorist organizations surfaces. Such a response may entail submitting a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) or taking other preemptive steps.
6. Adequate Customer Notice
Ultimately, the CIP necessitates that monetary organizations offer suitable notification to clients that information is being assembled to confirm their character. This warning guarantees transparency in the procedure and educates customers of the institution’s responsibility to prevent identity theft and financial fraud. The notice can be provided in various forms, such as signage at the institution’s premises, written or electronic notifications during the account opening process, or through the institution’s website.
Make Your CIP Process Seamless with HyperVerge
Through its array of artificially intelligent tools, HyperVerge has reimagined how companies conduct CIP and meet AML regulations. Where compliance was once a burden, HyperVerge’s technology has transformed it into an efficient and user-friendly process.
- Streamlining Identity Verification: HyperVerge’s technology simplifies the important identity verification stage of the CIP program, using advanced algorithms to swiftly and accurately verify documents and biometric information. This decreases the time and efforts spent on manual reviews, permitting financial organizations to enroll customers more rapidly while still upholding strict security and compliance standards.
- Boosting AML Compliance: With HyperVerge’s solutions, adherence to AML regulations becomes firmer yet less burdensome. The platform provides comprehensive tools for transaction monitoring, screening against worldwide watchlists, and identifying patterns suggestive of money laundering. This proactive strategy confirms that institutions can remain ahead of governing necessities and shield themselves from financial offenses.
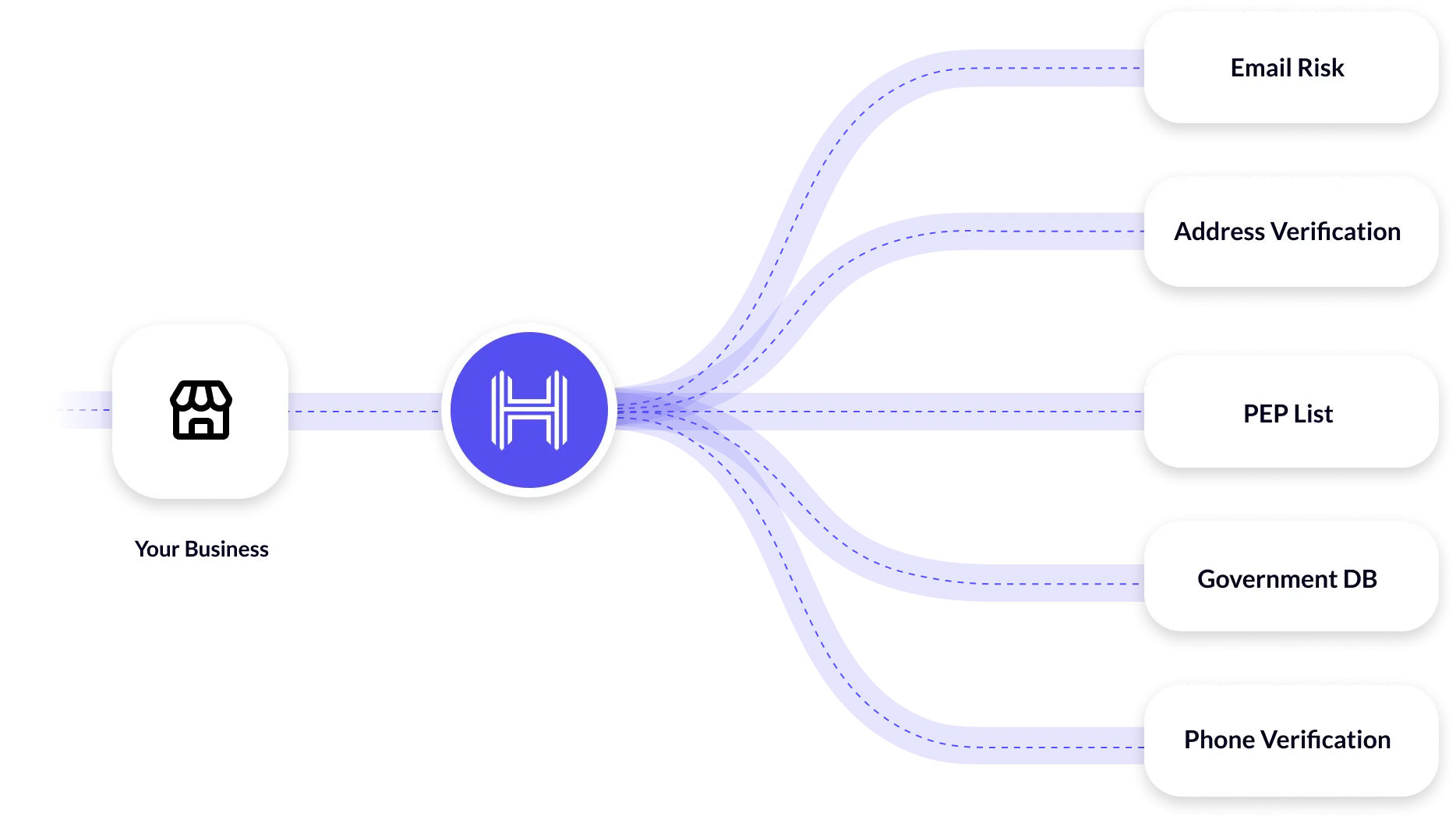
HyperVerge’s identity verification solution is designed to integrate seamlessly into existing systems, providing a smooth transition to a more automated and reliable process. By adopting HyperVerge’s technology, financial institutions can enhance their operational efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and ensure compliance with evolving AML regulations.
Discover how HyperVerge can transform your compliance and onboarding processes with AML solutions. Ready to take the next step? Sign up today.





