Sanction and embargo are restrictive measures exercised by the government or international organizations. These are applied to a specified country or group of countries, organizations, or specific individuals to prevent illegal trade, terrorism, and financial crimes like money laundering.
If your business is a part of the fintech or crypto industry, understanding sanctions and embargoes is critical for adhering to the Anti Money Laundering (AML) norms. Non-adherence occurs when you facilitate financial transactions inadvertently between sanctioned countries or individuals.
In this blog post, we closely examine the meaning of sanctions and embargoes, their differences, real-life examples, and how AML screening protects your business.
What is an embargo?
Embargoes are imposed by the government or international organizations like the United Nations (UN) to prohibit trading with a specified country or a group of countries. Prohibition can be imposed on a particular product, service, or commodity. Such an action is taken to compel the targeted country to change its policies or actions diplomatically.
There are three main types of embargoes:
Trade embargoes: These embargoes restrict international trade with the targeted country
Financial embargoes: Such embargoes prohibit any form of financial transactions with the target country
Military embargoes: In military or arms embargoes, the imposing country stops entering into any form of military-related transactions like the import or export of weapons from or to the targeted country.
The EU arms embargo on China in 1989 after a violent upheaval in Beijing is an example of an embargo.
When the government imposes embargoes, it’s done based on the legislative acts. In the case of international organizations like the UN, the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) takes charge of imposing embargoes on countries that threaten international peace.
The impact of embargoes has a set of intended and unintended consequences. The intended consequences are to coerce a change in the policy or practice in the country without engaging in a war with them. Unintended consequences impact the economic situation of the target country due to the shortage of items. This often leads to inflation battering the daily livelihood of the population, especially those living in poverty.
What are sanctions?
As compared to embargoes, sanctions are more specific. Sanctions are applied to specific countries, industries, or even individuals. However, the intention behind levying sanctions is the same – to impose trade restrictions and prevent illegal activities like international terrorism. Financial institutions must always monitor the sanction list while dealing with international clients.
There are three most common types of sanctions:
Economic sanctions: Economic sanctions are penalties imposed on specified countries, their officials, or their citizens to restrict trade or any form of financial transactions with them.
Diplomatic sanctions: These sanctions are levied to cut down the diplomatic ties with a country. This is often exercised by an international body to put pressure on them and bring a change in their unfriendly actions or policies
Military sanctions: Military sanctions are intended to stop supporting a country with any military-related actions. This includes not supplying them with arms or military technology, or entering into a financial transaction to fund any form of military action.
Recently, the Biden-led US government imposed sanctions on 16 allies of Venezuela’s President Nicolas Maduro in response to the voter fraud in the country’s elections.
Sanctions can be implemented by the national government, regional organizations or even international organizations. Governments do that with the help of sanctioning authorities, for example, the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) in the US. The European Union (EU) is an example of a regional organization that can impose sanctions based on its policy. The UNSC is in charge of enforcing sanctions based on the rights granted to it by Chapter VII of the UN Charter.
The intended consequence of imposing sanctions is to stop the behavior of a country or its officials that is harmful to the international community. The unintended consequences of sanctions are economic isolation leading to a crisis or adverse impact on the lives of civilians in the country.
Key differences between embargoes and sanctions
Let’s go knee-deep into this and find out the six ways sanctions and embargoes are different from each other:
Scope
Embargoes have a more wide application – Imagine a fisherman casting a fishing net on a river. Embargoes are applied to a list of countries or entire regions to stop trade and economic activities with them.
Sanctions are more targeted – imagine a fisherman using a fishing rod. Sanctions are levied to restrict trade, economic or diplomatic ties with a specific country, individual or industry in that country.
Target
Embargoes put pressure on the government or the entire country’s population to change their behavior or actions detrimental to international interests.
Sanctions are levied on specific individuals or sectors in a country indulging in undesirable practices. For example, a certain group of citizens disrupt the peace with their acts of terrorism.
Goals
Embargoes are imposed to compel a country to change the course of action or behavior without taking any military action.
Sanctions are levied for different reasons like punishing a country for violating an international law. Or for stopping human rights violations or proliferation of weapons. For example, US and various international organizations have imposed sanctions on North Korea against its nuclear weapons programme.
Implementation
Embargoes are usually implemented by a group of countries or international bodies to protest a country’s action collectively.
Sanctions are also implemented by international organizations, however, in most cases, it is implemented by individual countries.
Impact
Embargoes have a detrimental impact on the economic stability of a country often leading to a shortage of essential goods and services. For example, when the UNSC levied a comprehensive ban on Iraq, including a trade embargo and economic sanctions, Iraq’s GDP fell by 50%.
Sanctions impact specific sectors in a country or a certain group of individuals. Due to the targeted application, the negative impact is not widespread and doesn’t weigh down the economic situation of the country.
Flexibility
Once an embargo has been implemented, modifying or lifting it is challenging. When an embargo is implemented, the imposing countries or organizations do not lift the embargo until the government of the embargoed countries takes a step. The embargoes established by the UK, UNSC, and EU on South Africa to end the apartheid system started in 1985. But were only lifted in 1994 after the South African government abolished the apartheid system in 1991.
Sanctions are more flexible and they are adjusted according to the situation. If the sanctions are more relaxed in the initial phase, they might get more strict if the condition worsens. For example, US levied a series of sanctions on Iran in the early 2000s. However, these economic sanctions were relaxed when Iran entered into an agreement called the Joint Comprehensive Plan Of Action (JCPOA). After JCPOA the export ban was lifted and financial institutions were permitted to enter into transactions with Iranian banks.
Example
Embargo: US implemented an embargo on Cuba in 1960 after the Cuban Revolution. Businesses based in US are not permitted to engage in import or export with Cuba. This long-standing trade embargo has harmed the Cuban economy resulting in high prices and poor access to daily necessities.
Sanction: US imposed sanctions against Russia after the Ukraine invasion in 2022. These targeted sanctions are imposed on specific sectors and individuals in Russia. Sectors include finance – Sberbank and VTB Bank, Russia’s prime banks have no access to the US financial system. There is a ban on the import of Russian oil and sanctioned Russian individuals are not allowed to enter the US territory.
How do embargoes and sanctions work?
An embargo or a sanction can be implemented by a government unilaterally meaning doing it independently. Or the government of one nation works in coalition with the governments of other countries to take punitive measures and exert pressure collectively – also known as multilateral sanctions.
Once a sanction or embargo is implemented, countries need to adopt the rules and regulations abiding by their jurisdiction. For example, US has imposed a sanction on another country, then the domestic industries have to follow the laws mentioned in the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC).
In the case of multilateral sanctions where different countries and international bodies like the United Nations (UN) are involved, a special committee is formed by the UN to monitor compliance with the imposed measures.
Role of international organizations
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is empowered to impose sanctions under Chapter VII of the UN Charter to ensure international peace. It can impose asset freezes, travel bans, and arms embargoes to exercise its rights. Similarly, the European Union (EU) has the power to impose sanctions under the Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP). The EU can adopt the measures of the UN or can do it independently.
The role of real-time AML screening and monitoring
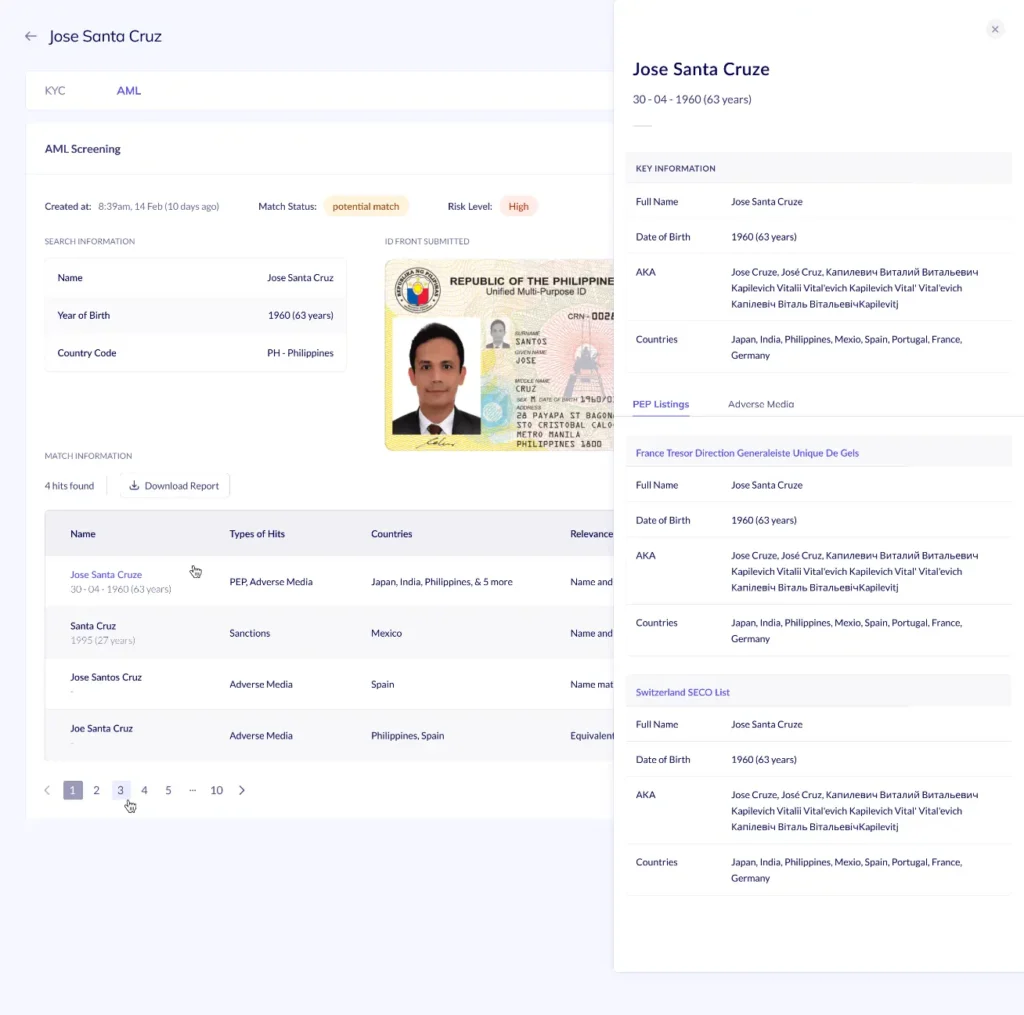
AML compliance is a list of steps that an organization or a business must take to prevent anti-money laundering. This includes performing comprehensive checks on a client’s identity, and their transaction histories along with continuously monitoring their future activities. Having an anti-money laundering policy is a must, so you can customize the requirements according to your business.
However, without an automated solution, implementing your AML policy would be a herculean task. You can hire more people to screen and monitor user profiles and activities, but as your business grows they will burn out quickly.
HyperVerge is a perfect companion for real-time AML screening and monitoring. It takes care of both customer due diligence and risk assessments. It runs 1000+ checks like global sanctions and watchlist checks, adverse media checks, and Politically Exposed Person (PEP) screening. All of these checks ensure that your business meets the AML compliance requirements to avoid loss of reputation and hefty fines. HyperVerge stands out by providing an all-in-one platform to comply with the AML norms and expand your business in 195+ countries.
Check out the HyperVerge AML Solutions page to get all the details. HyperVerge also offers a free trial, so if you want to go ahead and try the product, sign up here.
FAQs
What is the difference between an embargo and a sanction?
An embargo is usually implemented by a single government or an international organization like the UN against another country or a group of countries. Sanction is more specific as it is implemented on selective sectors, entities or individuals of a country.
Can a country impose both an embargo and sanction on another country?
Yes, a country can impose sanctions and embargoes on another country. US has imposed an embargo on Iran since 1979 prohibiting any form of trade. Additionally, US has also imposed sanctions on specific sectors and individuals in Iran.
What are the potential consequences of non-compliance with embargoes and sanctions?
Non-compliance with embargoes and sanctions could lead to serious consequences like:
- Financial penalties
- Legal repercussions
- Reputational damage
- Operational restrictions





