In 2023, banks paid over $500 million in (Anti Money Laundering) AML fines. It’s not only banks that become financial crime targets. Sectors like cryptocurrency, gaming sites, brokerage firms, and wealth management firms are also part of these penalties, accounting for a total global fine of $6.6 billion.
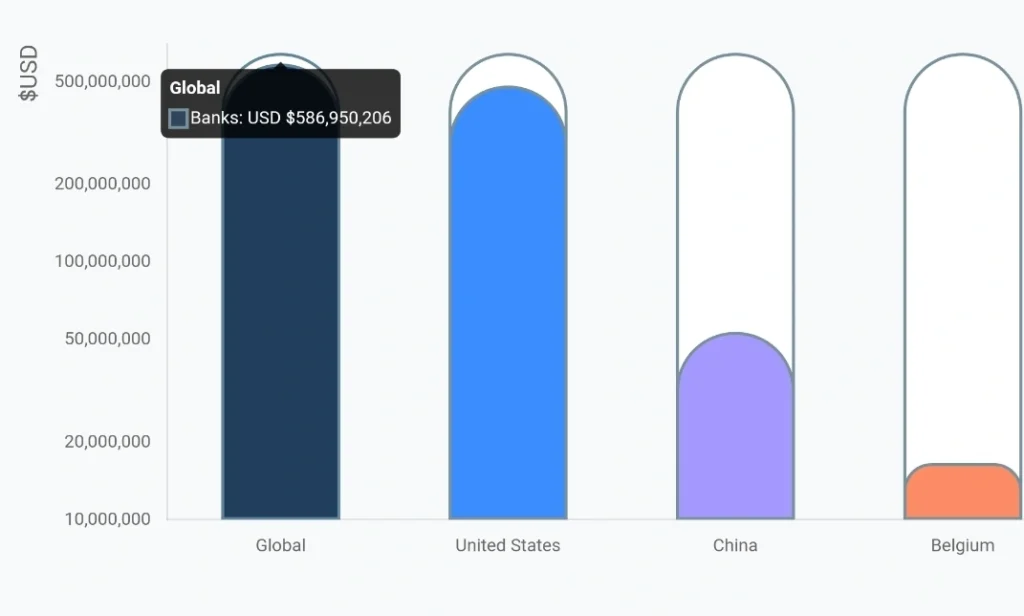
Source: Fenergo 2023 AML Fines Report
As technology has evolved, fraudsters are using smarter techniques to manipulate the financial system. Financial institutions also need to catch up with these techniques.
Basic verification isn’t sufficient to prevent serious financial crimes. Organizations need to build a robust KYC system that flawlessly serves two core purposes:
- Risk management – of all kinds
- Compliance regulation – across all cases, countries, and industries
This article is a simple and actionable guide for financial organizations. It provides a complete framework with practical scenarios and real-world examples to develop a KYC program that keeps them ahead of risks and compliance challenges.
The core components of a robust KYC program
Initially, KYC was a heavily manual process. Physical documents, in-person verification, and humans were involved. It took days to open a simple account or apply for a loan, and months if applicants required additional verification.
But modern-day KYC is different, it’s faster and more secure. Plus, it ensures better compliance with regulatory requirements.
Customer identification and verification (CIV)
Customer Identification and Verification (CIV) is a fundamental component of the KYC process in financial institutions. It involves collecting and validating essential information about customers.
CIV forms the foundation for ongoing due diligence and risk assessment throughout the customer lifecycle.
Data collection

Customer information
Institutions collect basic details to know about the person. This usually includes name, permanent address, and date of birth.
Data sources
The customers are required to fill out the application form during opening a bank account, applying for a loan, signing up on crypto exchange platforms, etc.
This data can also be auto-filled by fetching details from government databases and document issuing authorities. We’ll talk about this more later in this article.
Document verification
Types of documents
The customer’s data is verified through Govt-approved IDs and utility bills. This prevents identity thefts, forgery, and fraud.
Document authentication methods
Document authentication is cross-checking customer details against valid IDs and documents. This can be done by two methods — manual and digital.
Manual KYC processes are painfully slow with high chances of human error. Hence, organizations are increasingly moving to digital modes like OCR and biometrics verification.
The OCR technology accurately captures details from AADHAR cards, PAN cards, passports, and so on. It pinpoints forged documents by detecting irregularities in text fonts or pixels.
Biometric verification
Facial recognition
Face recognition (FR) requires a person to click a selfie during KYC verification. This prevents situations where a person tries to open a bank account using a stolen identity
The FR software matches the live selfie to the photo in submitted IDs. These systems have a large database to identify if a person has a criminal record.
Fingerprint recognition
The digital fingerprint also helps confirm the person is the same as the ID he/she provided. It’s an effective alternative to facial recognition.
Institutions can also deploy two-factor authentication. In this setup, a person first enters a password and then scans a fingerprint or a face for added protection.
Liveness detection
Fraudsters might try to bypass the face recognition system by using fake face masks or showing pictures from stolen documents to the camera. Your organization needs a defense mechanism against this situation.
Liveness detection ensures a person is actually present there and clicks a selfie live. A powerful liveness detection software like HyperVerge can identify if a customer is using artificial identities like photos, screenshots, or silicone masks, instead of a real face.
Customer due diligence (CDD)
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is a set of procedures designed to analyze customer information.
This helps assess their risk profile and ensure compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorist financing (CTF) regulations.
Risk assessment
Risk factors
Organizations have multiple risks linked to the customers they do business with. Will the customer be able to return the loan amount with interest? Is the customer involved in a terrorist-funding alliance? Does the customer profile reflect potential traits for attempting crime?
So organizations must perform risk analysis and categorize customers into different categories.
Risk rating methodology
The risk rating approach involves assigning risk scores to customers based on various factors. It determines the level of due diligence required.
Modern KYC processes often employ machine learning to analyze huge data and detect patterns that indicate risk. Each factor is weighted and scored, often using a numeric scale (e.g., 1-5) or categories (low, medium, high).
Enhanced due diligence (EDD)
There are cases when CDD isn’t enough to mitigate risk and fulfill KYC compliance criteria. Organizations have to follow additional verification protocols, collectively called EDD.
When to conduct EDD
Customers who receive high-risk scores need to undergo an extended series of checks, called enhanced due diligence. These are usually corporate companies, high-net-worth individuals, and politically exposed people.
Besides, residents from countries with weak AML laws, terrorism prevalence, and sanction lists require EDD.
EDD measures
Financial institutions can follow various EDD measures depending on the type of customers.
For example, in the case of corporate clients, beneficial ownership identification is the most effective approach. For a person from a political background, PEP screening is the ideal method to go with.
Customer segmentation
Creating customer tiers based on risk
Customer data including financial history, transaction patterns, and business activities is run through advanced analytics. The institutions evaluate this data against various risk factors.
Based on these factors there are three customer tiers. That is low, medium, and high risk. These tiers determine the level of ongoing monitoring and the frequency of account reviews.
Tailoring KYC procedures
Different customers require different KYC procedures. Here’s how organizations can tailor measures for a particular customer’s identity type.
High net worth individuals (HNWIs):
- More extensive source of wealth and source of funds verification
- Deeper investigation into complex corporate structures or offshore holdings
- Regular reviews of large transactions and wealth management strategies
Politically exposed people (PEPs):
- Extensive verification of business interests and potential conflicts of interest
- More frequent account activity reviews
- Performing adverse media checks and public records for reputational risks
Clients from high-risk countries:
- Proactive monitoring of international transactions
- Sanction list screening to identify and block unethical transactions
- Scanning for money laundering, fraud, terrorist-funding, and other financial crime records.
Ongoing monitoring and review
Financial institutions that monitor customer activities and transactions can prevent fraud before it can happen. Doing this helps flag anomalies and begin further investigation at the right time.
Transaction monitoring
Suspicious activity reporting (SAR)
Any unusual activity initiated from the customer’s end is suspicious. Organizations must have a system in place to identify and report suspicious transactions as soon as possible.
SARs need to be filed within 30 days and stored for up to 5 years from the filing date. Regulatory bodies impose fines on companies that fail to meet SAR requirements.
Transaction pattern analysis
Regular and proactive analysis of customer’s transactions helps in timely SAR reporting and avoiding penalties. Let’s say an individual suddenly receives large amounts of money in the bank which is 10X of his regular income. This indicates a doubtful activity.
Similarly, banks need to file an SAR when an individual makes repeated transactions to a sanctioned country region. Trading apps also need to do the same if a customer is suspected of insider trading.
Customer behavior analysis
Identifying changes in customer profiles
Over time, your customer profiles may change and so do their risk rating. A sudden increase in high-value international transfers for a customer who previously only conducted domestic transactions might prompt an alert.
It’s also possible that a customer who has a clean record earlier might suddenly make the headlines for a prominent bribery case. Under all such scenarios, a customer profile needs to be updated from low to high risk.
Detecting anomalies
Anomaly detection involves flagging unusual patterns, such as out-of-character purchases or transactions occurring at odd hours.
Factors like transaction frequency, value, geographical locations, and types of counterparties involved help to decide whether or not a user requires intensified due diligence.
Periodic customer reviews
Review frequency
For instance, high-risk customers might undergo an account review once in three months. While low-risk accounts might be reviewed every three years. For moderate ones, annual reviews might be allotted.
Update customer information
Customer tiering is not static. Banks continuously monitor transactions and update risk profiles. They recategorize customers between tiers based on new information or changing behavior patterns.
Best practices for effective KYC
Streamlining the customer onboarding process
From digital onboarding to data pre-filing, financial institutions can remove friction during onboarding through multiple means.
Digital onboarding
Digital onboarding streamlines the KYC process for financial institutions. It offers better speed, convenience, and security.
Here are effective practices your company can adopt:
Automated ID verification: Use AI-powered optical character recognition (OCR) to extract and verify information from documents instantly.
Video KYC: Incorporate live video interviews for high-risk customers or specific complex cases, allowing for real-time verification and risk assessment.
Digital signatures: Implement e-signature solutions for fast document signing while maintaining legal validity.
Mobile optimization
People, nowadays, use their phones for almost everything. They prefer mobile apps to access banking, investing, gaming, etc. services too.
Here’s how you can build for the mobile-first era:
Responsive design: Ensure your onboarding interface adapts seamlessly to various screen sizes and orientations.
Mobile document capture: Implement high-quality mobile camera integration for document scanning, with features like automatic edge detection and image enhancement.
Biometric authentication: Leverage built-in smartphone features like fingerprint or facial recognition for secure and quick identity verification.
Push Notifications: Use mobile notifications to prompt customers to complete unfinished steps or provide updates on their application status, reducing drop-off rates.
Data pre-filling
What if customers can simply fetch their data from national databases and authorized sources with a few clicks? This removes data entry errors and makes the KYC process hassle-free.
Here are the best practices to have in place:
API integrations: Connect with trusted third-party data sources (e.g., credit bureaus, government databases like AADHAR in India, and Social Security in the US) to auto-populate customer information for KYC. Customers enter their AADHAR or social security number. The system fetches their information and validates it instantly.
Existing customer data: Pre-fill forms for current customers opening new accounts. Their information already exists in the company’s database. Ask only for verification and updates.
Document scanning: Use OCR technology to auto-extract relevant data. Customers upload the documents and OCR-powered software fills in the corresponding fields in the form within seconds.
Leveraging technology for KYC

A single KYC costs between $13 to $130. Financial sectors can cut down this cost by 70% with AI-driven KYC processes. Below is the overview of technologies making this possible.
AI and machine learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are simplifying KYC by automating complex tasks.
Here are efficient practices your organization can implement:
Intelligent document processing: AI-powered systems can quickly extract and verify information from various document types. During the 2020 pandemic, accelerated processing time was the most prominent benefit of IDP. It cuts processing time by 50% and more.
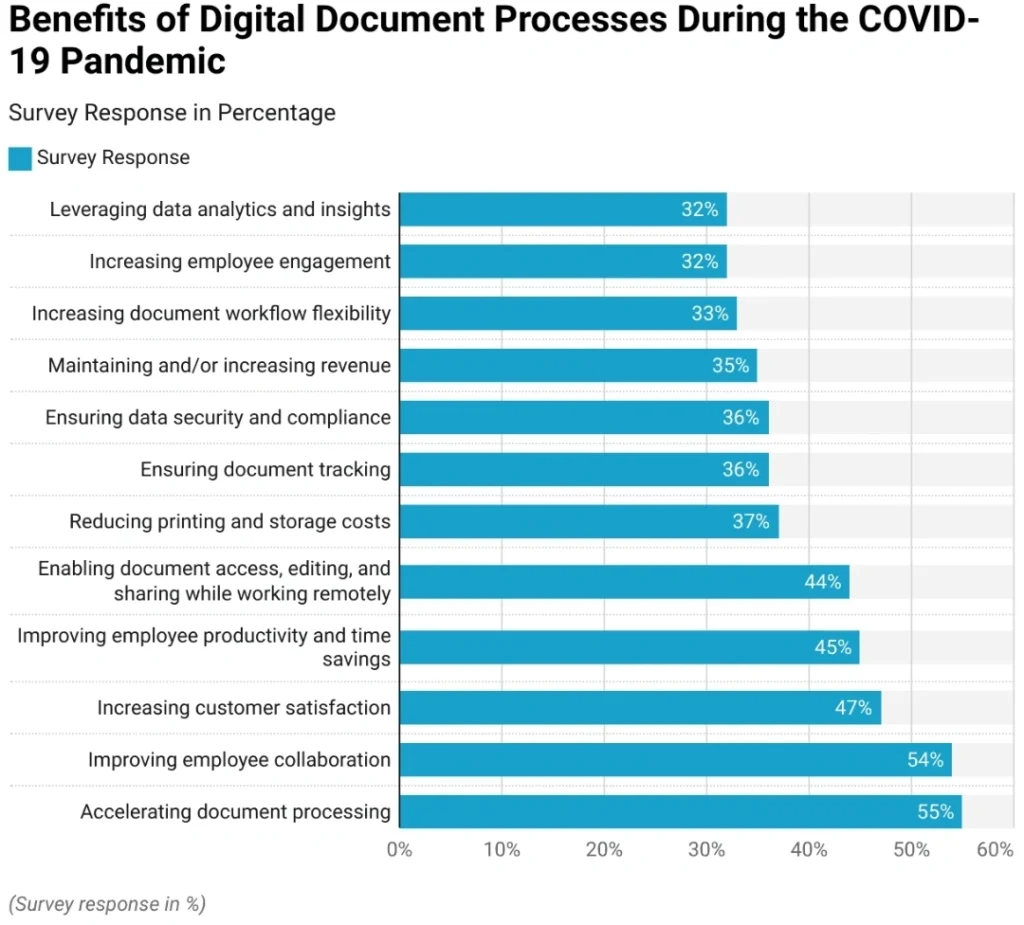
Source: Market.us Scoop
Fraud detection: ML techniques can detect unusual patterns in customer behavior that might indicate fraud or money laundering. JPMorgan Chase employs such models to analyze billions of transactions. It detects fraud by 25% more effectively.
Risk scoring: AI can assess customer risk profiles by scanning large datasets. Barclays employs algorithms for credit risk assessment. They predict a customer’s risk of default and their ability to afford repayments when applying for credit products.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP-powered tools can scan news articles and social media to identify the reputational damage risks associated with customers. Organizations can employ such tools for faster adverse media checks.
Robotic process automation (RPA)
RPA streamlines repetitive, rule-based tasks in the KYC process, improving efficiency and reducing human error:
Data entry and validation: RPA bots can automatically input customer data into various systems and cross-check for accuracy. This technology enables loan cost reduction by 30% and loan processing time by 80%.
Watchlist screening: Bots can quickly screen customer names against multiple sanction lists and PEP databases. Infosys 2023 report features sanction list screening as one of the promising RPA applications for financial sectors.
KYC automation: RPA can automate the process of requesting, tracking, and organizing customer documents. UBS, a multinational investment bank, has deployed RPA bots to manage document collection and follow-ups, reducing the workload on KYC analysts.
Cloud-based KYC solutions
Cloud technology offers scalable, flexible, and cost-effective KYC solutions.
Centralized data management: Cloud-based KYC platforms provide a single source of truth for customer data across an organization.
SWIFT’s KYC Registry, a cloud-based platform, allows banks to share and access standardized KYC data, reducing duplication of effort.
Real-time updates: Cloud solutions enable real-time updates to customer profiles and risk assessments.
For instance, a cloud-based screening platform provides continuous monitoring and instant updates on customer risk profiles.
Scalability: Cloud-based systems can easily scale to handle increased volumes during peak onboarding periods.
HyperVerge, a cloud-based identity verification service, can process millions of verifications daily across multiple countries.
Enhanced collaboration: Cloud platforms facilitate secure information sharing between different departments and even between institutions.
The Nordic KYC Utility, a collaborative project between major Nordic banks, uses a cloud-based platform to share KYC information, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Regulatory compliance: Cloud solutions can quickly adapt to changing regulations across different jurisdictions.
HyperVerge’s cloud-based AML and KYC solutions help businesses comply with evolving global regulations.

Building a culture of compliance
Your organization can’t gain the maximum benefits of advanced KYC technologies unless your employees use them efficiently.
Here’s how you can prepare a tech-oriented team:
Employee training
Comprehensive and ongoing training is the foundation of a strong compliance culture:
Interactive workshops and sessions: Conduct regular interactive sessions to engage your employees in real-world KYC scenarios.
Companies like Goldman Sachs actively organize ‘ask anything’ sessions and mentorship programs. This culture can be extended to include sessions where KYC experts and industry leaders prepare employees to tackle challenging situations during the process.
E-Learning modules: Develop customized and role-specific e-learning courses to build a competent team.
For example, HSBC University offers many online learning modules including a global anti-money laundering training program. As a minimum requirement, every employee must complete these online courses before joining HSBC.
Certification programs: Implement internal certification programs to motivate employees.
Citibank’s Global AML University offers tiered certifications, encouraging continuous learning and expertise development. This initiative aims to enhance the anti-money laundering (AML) knowledge and support professional competency of Citi’s employees.
Regular updates: Establish a way to provide frequent updates on changing regulations and emerging risks.
JPMorgan Chase sends weekly compliance newsletters to keep employees informed about the latest regulatory changes and best practices.
Compliance policies and procedures
Clear, accessible, and up-to-date policies and procedures are essential for maintaining compliance.
Clear documentation: Develop concise, simple, and jargon-free policy documents. Your organization can use a “Policy on a Page” approach. The whole policy is simplified into crisp short bullet pointers.
Accessibility: Ensure policies are easily accessible to all employees. A good way is to maintain a centralized, searchable policy repository on its intranet. Employees can quickly find relevant guidelines at the required time.
Regular reviews: Establish a schedule for policy reviews and updates. Companies can conduct quarterly reviews of their KYC policies, involving both compliance experts and frontline staff.
Feedback mechanisms: Create channels for employees to provide feedback on policies. Organizations can have internal groups where employees can suggest improvements to KYC procedures based on their practical experiences with customers.
Third-party risk management
Involving third-party vendors with your company’s sensitive data can be challenging. But you can work confidently using these practices:
Contractual safeguards: Include clear compliance requirements in vendor contracts. Banks must incorporate specific KYC and data protection clauses in their vendor agreements. Including regular compliance audits as a contractual requirement is also prudent.
Ongoing monitoring: Establish processes for continuous monitoring of third-party compliance. Your organization can use automated tools to monitor your vendors’ compliance status.
Vendor training: Extend compliance training to third-party partners. Your company can offer online compliance training modules to its critical vendors, ensuring alignment with your industry-specific KYC standards.
Collaborative platforms: Utilize industry platforms for third-party risk management. The Dow Jones Risk & Compliance platform is used by many financial institutions to collaboratively manage and share information about third-party risks.
Regular audits: Conduct periodic audits of third-party KYC practices. Financial institutions can implement a rotating audit schedule for their critical vendors. Include on-site visits to assess compliance with KYC requirements.
The future of KYC
The future belongs to technologies that bring security, speed, and convenience on the same pedestal.
Here are trends leading the way.
Biometric authentication
Organizations and users are likely to embrace biometric identification as part of 2-factor authentication. People tend to forget passwords. But their fingerprints and faces remain intact as the permanent keys to their credentials.
The brilliance of biometric authentication lies in,
- Providing heightened security for both financial institutions and customers
- Combining stronger fraud protection with improved customer experience
- Offering unmatched accuracy over traditional methods.
Financial institutions that embrace this technology now will not only meet current needs but will be well-positioned to lead in an increasingly digital and security-conscious world.
Decentralized identity
Decentralized identity revolutionizes how personal information is managed in financial services. Using blockchain technology and cryptographic principles, individuals can create and control their own digital identities. They don’t have to repeatedly provide sensitive data for each new account or loan application
This system relies on 3 key elements:
1. Decentralized identity platforms: a platform that allows users to create and store digital identities safely.
2. Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs): unique, cryptographic tokens for each individual for identification purposes. These store information about a person’s identity cryptographically so data remains tamper-proof.
3. Verifiable Credentials (VCs): digital tokens storing identity attributes like biometrics, PAN numbers, passport details, and so on. These help during due diligence.
These benefits include,
- Users own and control their data
- Reusable verified information across financial institutions
- Reduced risk of large-scale data breaches, as there will be no central repository of personal data
Implementing a decentralized identity comes with challenges. It requires significant infrastructure and regulatory changes.
RegTech solutions
Regtech stands for regulatory technology. Simply put, its tools and technology are used to manage compliance requirements.
For instance, anti-money laundering (AML) software can analyze transaction data in real time. Major banks like HSBC have implemented such systems, significantly reducing false positives and improving their ability to detect actual fraud.
Regtech is also transforming other KYC components like,
- Automated reporting through tools gathering data from multiple sources, ensuring accuracy, and generating reports in the required format for different regulatory bodies.
- Risk management through various scenario modeling which helps banks stress-test their portfolios.
Regtech solutions offer financial institutions agility and efficiency. It enables staying compliant with ever-changing regulations while focusing on core business activities.
Adapting to a changing regulatory environment
Staying updated on regulatory changes
Establish a committee within an organization to oversee compliance. This committee will be responsible for equipping employees with the latest resources.
The tasks can include sharing recent articles/news/reports from FinCEN, FIU-IND, or FATF, providing training modules, and publishing newsletter editions to keep everyone on track.
Building flexibility into KYC programs
Organizations can enable customized workflows in their KYC process. Software must be able to identify specific use cases and perform accordingly.
For instance, if algorithms identify particular customers to be from a political background. The system must trigger EDD including source of funds verification and adverse media checks.
Implement a robust KYC program
Build an efficient KYC system that serves as a strong line of defense against all kinds of risks and challenges in your organization. Leverage Hyperverge’s advanced and powerful capabilities to implement KYC best practices.
- End-to-end KYC automation
- High-end video KYC and face recognition technology
- OCR-powered document verification
- GDPR/ISO/SOC/FATF compliant
- Customizable workflows that align with your organization’s unique needs
- 5X faster user onboarding with an analytics-rich dashboard, progress bars, and review portal
Get started with HyperVerge KYC solutions today.





