When it comes to KYC compliance, financial institutions face a crucial challenge: ensuring that they know their customers and protect against the increasingly sophisticated landscape of financial crime.
KYC is a cornerstone of AML (Anti-Money Laundering) strategies, requiring businesses to validate customer identities and assess risks to ensure transaction legitimacy. Yet, despite these efforts, a staggering 70% of fraud occurs after initial KYC processes, revealing that KYC alone isn’t enough.
This highlights the need for a broader approach to security. The stakes are high—non-compliance can lead to hefty penalties, as evidenced by the $6.6 billion in fines levied in 2023 due to inadequate KYC checks and AML controls. The rising pressure is pushing financial institutions to adopt digital KYC/AML solutions that enhance efficiency while safeguarding the customer experience.
In this article, we’ll unpack the role of KYC in the banking and finance sectors, explore the compliance landscape, and offer insights on building secure, seamless onboarding processes.
What is Global KYC?
KYC (Know Your Customer) is a crucial process in finance for verifying customer identities, assessing suitability, and managing risks. It involves stringent checks to prevent money laundering, fraud, and other financial crimes.
While domestic KYC focuses on the regulations of a single country, global KYC addresses a wider array of international rules across multiple jurisdictions. This adds complexity as financial institutions must navigate different legal frameworks.
KYC standards differ across countries and jurisdictions, as each government has its own set of rules and requirements. Despite these differences, there are common elements and principles that highlight KYC regulations globally. The main goal is to mitigate financial crime risks.
Key components typically include:
- Customer Identification and Verification: This initial step involves confirming a customer’s identity using reliable documents such as passports, driver’s licenses, or national ID cards.
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD): After identification, the customer’s risk profile is assessed. This involves analyzing various factors like their location, business type, and transaction patterns. Global CDD requires more in-depth analysis to account for diverse regulations and regions, including understanding the business purpose, source of funds, and occupation.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continuous tracking of transactions helps identify unusual or suspicious activities indicative of money laundering or other illegal acts. For global KYC, this monitoring must accommodate multiple regulatory environments and be aware of international crime trends.
- Risk-Based Approach: Resources are allocated based on risk levels associated with customers, transactions, or regions. High-risk customers need more stringent checks and frequent monitoring, while low-risk entities may face simplified procedures.
- Employee Training: Effective global KYC requires continuous staff training on international regulations, risks, and best practices to manage processes across different jurisdictions.
- Documentation and Recordkeeping: Maintaining detailed and accessible records is crucial for compliance and audits. In global KYC, this involves documenting all customer interactions, risk assessments, and decisions across different regions.
The Global KYC Regulatory Landscape
Going global with your business can open up a world of opportunities, but it also comes with a lot of regulatory headaches. Each region has its own mix of cultures, languages, and rules that can make identity verification and document scanning tricky.
Different countries have their own legal systems and tech setups, which affect how companies handle KYC and AML rules. Understanding these local requirements isn’t just about staying compliant—it’s also a smart move for breaking into new markets. Let’s explore how various regions, from North America to Asia, tackle KYC regulations.
North America
In North America, KYC regulations are well-established, with the US and Canada leading the way. In the US, the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and the USA PATRIOT Act mandate financial institutions to verify identities, monitor transactions, and report suspicious activities. The focus is on counter-terrorism financing (CTF) and anti-money laundering (AML), with the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) enforcing sanctions.
In Canada, the Financial Transactions and Reports Analysis Centre of Canada (FINTRAC) oversees KYC regulations, requiring robust identity verification and ongoing monitoring to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing. Both countries emphasize stringent verification and prompt reporting of suspicious activities.
South America
In South America, KYC regulations are advancing, with Brazil and Argentina taking significant steps against financial crime. Brazil, for example, has implemented KYC measures under the Central Bank’s regulatory framework, requiring banks to verify identities and assess money laundering risks.
In Argentina, the Financial Information Unit (UIF) oversees KYC and AML compliance, stressing due diligence and reporting suspicious activities. While other countries in the region are strengthening their KYC frameworks, inconsistent enforcement and varying tech adoption can impact effectiveness.
Europe
Europe is known for its robust KYC regulations, especially within the EU, guided by the 5th and 6th Anti-Money Laundering Directives (AMLD). These directives require thorough customer due diligence (CDD), including enhanced due diligence (EDD) for high-risk customers.
The EU framework mandates regular updates of customer information and reporting suspicious transactions. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) adds complexity by imposing strict data privacy rules, requiring institutions to protect customer data while complying with AML regulations.
Asia
Asia’s KYC regulations vary widely. Singapore and Hong Kong have advanced frameworks, with Singapore’s Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) and Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) enforcing rigorous protocols, including digital KYC.
India’s Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has enhanced KYC compliance, particularly with digital methods. However, enforcement levels differ across other Asian countries, with some still developing their regulatory systems.
Africa
Africa is seeing growth in KYC regulation, though implementation varies across the continent. South Africa leads with the Financial Intelligence Centre Act (FICA), which mandates strict KYC compliance for financial institutions.
Nigeria and Kenya are also strengthening their KYC frameworks, but challenges like limited resources and inconsistent enforcement affect effectiveness.
Oceania/Pacific
In Oceania, Australia and New Zealand have established KYC regulations under their Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorism Financing (AML/CTF) Acts.
Australia’s AUSTRAC, and New Zealand’s Markets Authority (FMA) and the Department of Internal Affairs (DIA) oversee KYC compliance, emphasizing customer identification, risk assessment, and ongoing monitoring.
Both countries focus on preventing money laundering and terrorism financing, requiring detailed record-keeping and reporting of suspicious activities.
KYC rules vary significantly by region due to different legal frameworks, regulatory priorities, and technological adoption.
- Europe: The EU emphasizes harmonization and stringent data privacy (GDPR) alongside AML and CTF measures, requiring rigorous customer verification and data protection.
- United States: The US focuses on counter-terrorism and anti-money laundering, with detailed CDD and complex compliance due to multiple regulatory bodies like FinCEN and OFAC.
- Asia: Countries like Singapore and Hong Kong prioritize digital KYC for financial inclusion and efficiency, contrasting with Europe’s focus on data privacy and the US’s emphasis on counterterrorism.
- South America: While KYC rules in South America are evolving, challenges such as inconsistent enforcement and varying levels of technological adoption can impact their efficiency.
Emerging KYC Regulations and Trends
As the financial landscape evolves, KYC regulations are also changing. Emerging trends in digital assets, data privacy, and technology are reshaping KYC approaches.
These developments highlight the need for strong compliance mechanisms that balance modern finance’s complexities with efficiency and security.
Cryptocurrency and Virtual Assets
With the rise of digital currencies, traditional KYC methods face significant challenges. Cryptocurrencies operate in decentralized environments, making it difficult for financial institutions to apply standard identity verification processes. As a result, regulators are increasingly focusing on creating specific guidelines for virtual assets.
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), for instance, has introduced the “Travel Rule,” requiring cryptocurrency exchanges to share customer information during transactions. This evolving regulatory landscape aims to mitigate risks associated with money laundering and terrorism financing in the digital asset space.
Data Privacy
The intersection of KYC and data protection is becoming increasingly complex. Regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the US impose stringent requirements on how customer data is collected, stored, and processed.
Financial institutions must navigate these regulations carefully to ensure they comply with both KYC requirements and data privacy laws. This dual compliance challenge requires balancing the need for thorough customer verification with the protection of sensitive personal information.
Risk-based Approaches
Technology is playing a pivotal role in enhancing KYC compliance and efficiency. Regtech (regulatory technology) and fintech (financial technology) innovations are streamlining KYC processes through automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML). These technologies enable faster and more accurate identity verification, reduce human error, and improve risk management.
By integrating these advanced tools, financial institutions can stay ahead of regulatory requirements while also providing a smoother onboarding experience for customers.
[CTA] Prevent fraud with AI-powered OCR software. Get a demo now!
Challenges of Global KYC Compliance
Navigating global KYC compliance is no small feat.
As businesses expand internationally, they encounter a range of complexities that can make managing KYC processes challenging. From differing regulations to data security concerns and impacts on customer experience, each aspect adds a layer of difficulty to global operations.
Let’s break down these key challenges:
1. Managing KYC Across Different Jurisdictions
Managing KYC checks across various jurisdictions is a complex endeavor due to differing regulations, legal systems, and compliance requirements.
Financial institutions often struggle to keep up with these varying standards, which complicates the end-to-end KYC process. For example, while some regions mandate physical KYC documents for company ID verification, others are more lenient, allowing e-KYC and digital KYC methods. This inconsistency requires a tailored approach to compliance in each region.
2. Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Data privacy and security further exacerbate the situation, with 82% of global organizations citing them as top issues.
Regulations like GDPR in Europe and CCPA in the US impose strict requirements on handling customer data. Ensuring that KYC documents for company ID verification and other sensitive information are secure while still meeting regional data privacy standards is a significant challenge. A failure in data protection could lead to severe penalties and loss of customer trust.
Additionally, KYC compliance is costly, with financial institutions spending an average of $500 million annually, a figure expected to rise with stricter regulations. Balancing security and compliance is crucial for global businesses.
3. Impact on Customer Experience
Lengthy and stringent KYC checks can frustrate customers, leading to onboarding delays and potential loss of business. However, innovative solutions like e-KYC and digital KYC methods can streamline the process, balancing compliance with customer satisfaction.
Research shows that a more efficient end-to-end KYC process could significantly reduce the 25% abandonment rate during customer onboarding in the UK alone.
These challenges highlight the need for continuous innovation in digital KYC solutions that streamline processes while maintaining compliance with evolving global standards.
How to Comply with Global KYC Regulations
In today’s interconnected world, global KYC compliance is crucial to prevent and combat money laundering and terrorism financing.
This section offers actionable steps to help organizations navigate and adhere to diverse and evolving regulations across multiple jurisdictions.
1. Develop a Comprehensive KYC Program
A robust KYC program is the foundation of compliance. This includes:
- Risk Assessment: Identify and assess the risks associated with different customer profiles, transactions, and regions.
- Customer Identification and Verification: Accurately verify customer identities through reliable KYC documents for company ID verification.
- Due Diligence: Conduct thorough due diligence to ensure that customers do not pose a risk.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continuously monitor customer activity to detect and report suspicious behavior.
- Recordkeeping: Maintain detailed records of all KYC processes and transactions for regulatory purposes.
2. Leverage Technology Solutions
Incorporating advanced technology into your end-to-end KYC process can streamline compliance efforts:
- Identity Verification Tools: Use digital tools for secure and efficient KYC checks.
- Customer Due Diligence Platforms: Automate the due diligence process with specialized software.
- AML Screening Software: Integrate AML (Anti-Money Laundering) screening to detect and prevent illegal activities.
3. Stay Updated on Regulatory Changes
KYC regulations are constantly evolving, so it’s crucial to stay informed about changes in different jurisdictions.
Regularly review regulatory updates and adjust your KYC process flow to remain compliant.
4. Train Employees on KYC Procedures
Ensure that your staff is well-versed in KYC procedures and understands the importance of compliance.
Regular training sessions help employees stay up-to-date with the latest regulations and best practices.
5. Conduct Regular Audits and Reviews
Performing regular audits and reviews of your KYC integration processes can help identify areas for improvement and ensure that your organization remains compliant with global standards. These audits are essential for maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of your KYC program.
By following these steps, your organization can navigate the complexities of global KYC regulations, ensuring both compliance and customer satisfaction.
The Role of Technology in Streamlining Global KYC
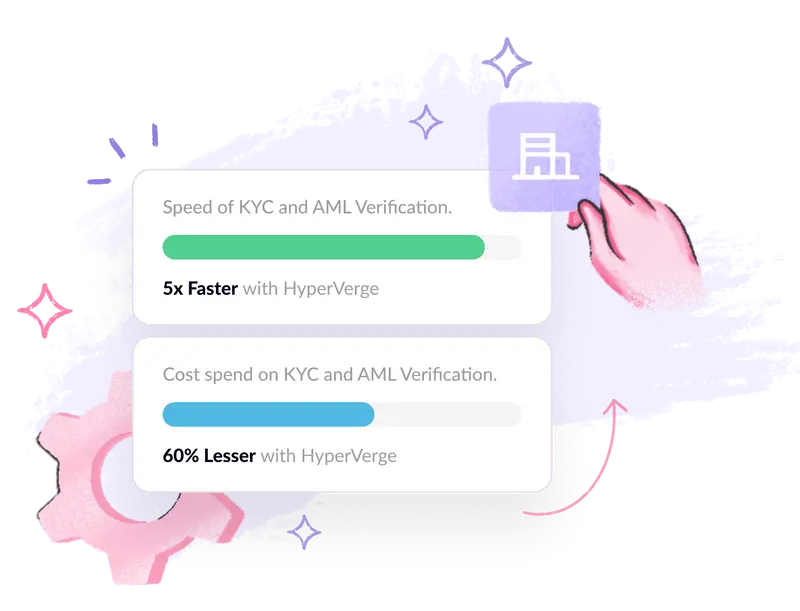
Technology is crucial in simplifying global KYC compliance, with significant advancements in KYC automation tools that streamline data collection, identity verification, and document processing. These tools reduce time and resources, speed up onboarding, and minimize human errors.
Identity verification platforms, using technologies like biometric authentication and document verification, are also essential. They confirm customer identities in real-time, ensuring compliance with local regulations while providing a seamless experience for cross-border operations.
HyperVerge, for instance, offers a robust identity verification solution that integrates digital KYC seamlessly into existing systems, making the entire process more efficient.
This is complemented by AML screening software, which is essential for identifying financial crime risks by scanning data against global watchlists and sanctions databases. The integration of AI and machine learning in AML screening further strengthen this process, adapting to new threats and regulatory changes in real time.
The benefits of integrating AI and ML into global compliance efforts extend beyond speed and accuracy. These advanced technologies also analyze large data sets to detect patterns invisible to human analysts, thus enabling proactive fraud detection and prevention.
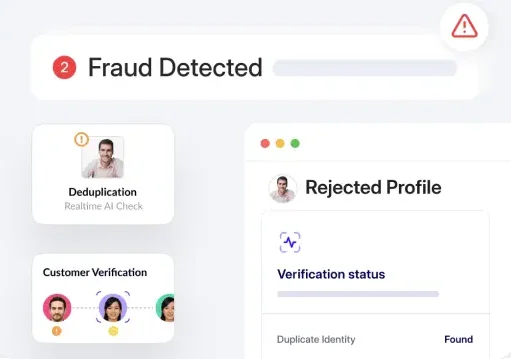
HyperVerge stands out in this landscape by offering an advanced suite of tools that leverage AI and ML to enhance the end-to-end KYC process.
Whether it’s through KYC automation, robust identity verification, or sophisticated AML screening, HyperVerge provides the technology needed to streamline compliance and protect businesses from regulatory risks.
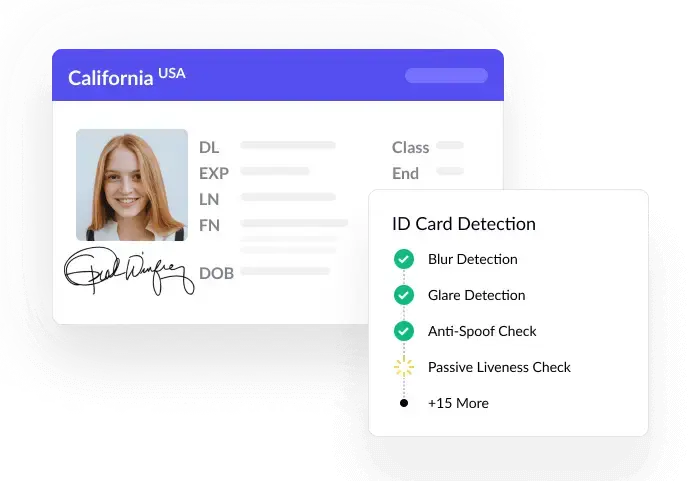
HyperVerge’s Identity Verification solution offers robust capabilities designed to streamline and enhance the authentication process for businesses across various sectors. Leveraging advanced AI and ML, HyperVerge ensures secure and accurate identity verification, minimizing fraud and enhancing user experience.
Comprehensive Identity Verification
It encompasses Document verification using OCR and machine learning to validate IDs like passports and driver’s licenses.

It combines this with Face verification, employing facial recognition to match individuals with their documents.
Additionally, Liveness detection ensures that the person undergoing verification is physically present, preventing fraud from static images or videos.
Advanced Technology Integration
The solution leverages Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to enhance accuracy and efficiency. These technologies enable continuous improvement in document and facial recognition. Real-time processing ensures swift verification, essential for applications needing immediate results. HyperVerge’s system supports Global Document Support, adapting to various international documents and needs.
Security and Compliance
Security and compliance are key features of HyperVerge’s platform. It upholds data privacy standards in line with regulations like GDPR and CCPA, safeguarding personal information. The system also incorporates measures to detect and prevent fraud, reducing identity theft risks. Its scalability allows it to handle increasing volumes of verification requests, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes.
User Experience
HyperVerge emphasizes a seamless User experience and seamless integration into existing systems, reducing workflow disruptions. The platform’s intuitive design simplifies navigation for users and administrators alike. Robust customer support ensures users can effectively utilize the solution.
Wrapping It Up
Maintaining a robust global KYC program is crucial for businesses to navigate complex regulatory landscapes and protect against financial crimes. Key practices like thorough customer identification, continuous monitoring, and regular updates on regulatory changes ensure compliance and security.
Moreover, integrating advanced solutions such as HyperVerge can significantly streamline these processes, enhancing both efficiency and reliability. By staying proactive and leveraging the right tools, organizations can confidently meet global KYC requirements.
Ensure your organization is ready to meet global KYC standards. Explore how HyperVerge’s digital identity verification solutions can help streamline your compliance efforts. Book a demo now!
FAQs
1. What is the meaning of KYC?
KYC refers to the process that financial institutions use to verify the identity of their clients, ensuring they are not involved in illegal activities such as money laundering or terrorism financing.
2. What is global KYC?
Global KYC is the practice of applying KYC protocols across multiple jurisdictions, ensuring compliance with international regulations and standards.
3. What is a global KYC compliance program?
A global KYC compliance program is a set of policies and procedures that a company implements to meet KYC regulations in different countries. It ensures customer identity verification, due diligence, and ongoing monitoring.
4. What does the Global KYC compliance program do?
The Global KYC compliance program helps organizations verify identities, assess customer risks, and monitor transactions, ensuring adherence to international KYC regulations and preventing financial crimes.





