Among the most strictly regulated and monitored industries in the world is the Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance industry (BFSI). It handles various financial instruments, making it essential to maintain security, accuracy, and efficiency.
Currently, banks are rapidly adopting OCR automation technology to simplify operations. Optical character recognition (OCR) streamlines tasks, making banking procedures more effective and efficient.
Reports indicate that by 2030, the worldwide OCR market will be worth $70 million. Using an identification tool—natural language processing (NLP)—it replicates letters and characters in written format and order.
OCR is a revolutionary automation technology that helps transform banking operations. The article will walk you through the function of OCR in the banking industry, its valuable applications, and the revolutionary effects it can have on the business operations of your organization.
What is OCR in banking?
Within the fiercely competitive financial sector, ensuring both timely and accurate information is paramount. OCR is a technology that scans bank statements and other paper-based documents and converts them into machine-readable text that can be edited and searched.
OCR eliminates the tedious and error-prone manual processes involved in processing bank statements and entering the data from bank statements. Financial institutions (FIs) can acquire essential insights from data, improve customer experience, and streamline operations with the use of OCR.
How OCR works in banking
When we take a closer look at OCR in the banking sector, its incredible capabilities are revealed:
Technology at work:
Getting scanned papers ready for character recognition is the first step in image pre processing. This includes image enhancements such as sharpening, noise reduction, skew correction for tilted papers, and background removal. To simplify, think of it as wiping away dust from a dirty window to see through clearly.
Once the image is prepared, OCR algorithms begin feature extraction. It starts by analyzing an image’s form, edges, and pattern to identify individual characters. OCR applications examine each character form with great attention for accurate identification.
Following feature extraction, the next step involves comparing the retrieved features with the extensive character database integrated into OCR technology. The program identifies the type of element (letter, integer, or symbol) using pattern recognition algorithms. This process is similar to comparing a character identification guide with the extracted features.
Beyond basic character recognition, advanced optical character recognition systems incorporate language processing and contextual awareness. To understand the entire context of the recovered text, OCR applications use language processing tools. This technology is highly efficient in distinguishing between two similar characters, the alphabet letter “l” and the number “1.”
Envision the OCR program, enhancing its understanding of the material by drawing on its grammar and syntax vocabulary.
Finally, the extracted text is double-checked to spot any remaining mistakes. Spell checkers and business rules can be applied to guarantee the accuracy of the extracted data. Think of this process as reviewing the final product for errors and inconsistencies, much like proofreading.
Process and workflow:
Apart from technicalities, let’s take a closer look at the OCR workflow:
- Document intake: An OCR system is capable of handling various document formats, including scanned paper documents, digital images, PDFs, photos collected from mobile banking apps, and microfilm scans as well.

- Data extraction and preprocessing: In this step, OCR turns a picture into searchable and editable text, followed by language processing and post-processing.
- Data classification and integration: Various scanned files, such as bank statements, loan applications, etc., are used to classify the retrieved text. The data is prepared and error-proofed to ensure a smooth interaction with your current financial records and systems.
- Applications of extracted data: Banks use clean and correct data for several applications, aiding in improving and strengthening operations. The refined dataset is used for Know Your Customer (KYC) verification, customer onboarding, ID verification, loan approval process, bank statement analysis, and various other financial documents.
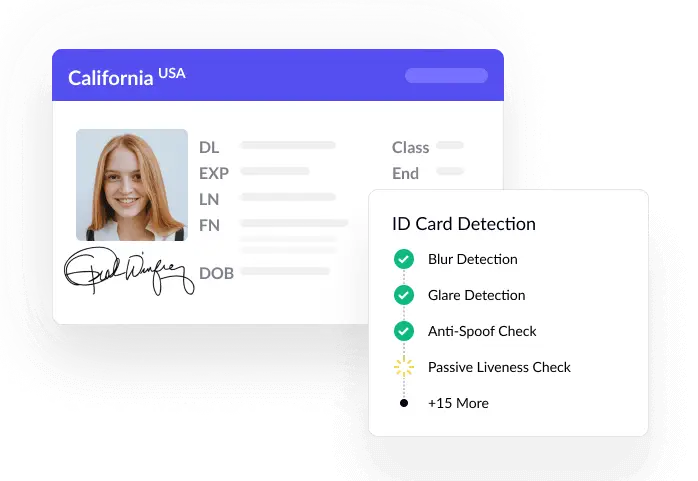
Benefits and efficiency gains
OCR tools aid the banking and financial services industry with noteworthy benefits such as:
- Improved efficiency: Using OCR software eliminates manual data entry tasks for your employees, freeing up their time to focus on strategic initiatives and delivering outstanding customer service.
- Increase accuracy: Physical data entry is a time-consuming process, leading to typos and errors. OCR minimizes such human mistakes and ensures data accuracy, resulting in faster processing and better decisions and lowering costs associated with error correction.
- Enhanced customer experience: OCR expedites data processing for customer service requests like loan applications, account openings, and related tasks. The rapid service boosts customer satisfaction by reducing wait time.
- Cost saving: By automating manual data entry and eliminating errors, OCR leads to significant cost savings. The increased productivity helps your bank yield a healthy return on investment (ROI).
- Better data management: OCR extracts data from paper based documents into easy-to-search digital formats. With this capability, your bank can take advantage of data analytics to make better decisions, manage risks, and discover new business opportunities.
Applications of OCR in Banking
Beyond simple document processing, OCR technology has far-reaching applications in banking operations. Here are some common and valuable uses of OCR in this industry:
- Customer onboarding: Automate data extraction from identity documents, address proofs, and other KYC paperwork to simplify the process of opening new accounts. This offers new consumers a streamlined and hassle-free experience.
- Document processing: Quicken document processing activities by automatically extracting relevant information from tax returns, income statements, bank statements, and credit reports.
- Fraud prevention: Detect potential signs of fraud by analyzing documents for discrepancies or abnormalities in the underlying data. For instance, identify theft cases by matching information from loan applications with data from ID proofs. OCR technology can be used to validate signatures, avoiding fraudulent transactions.
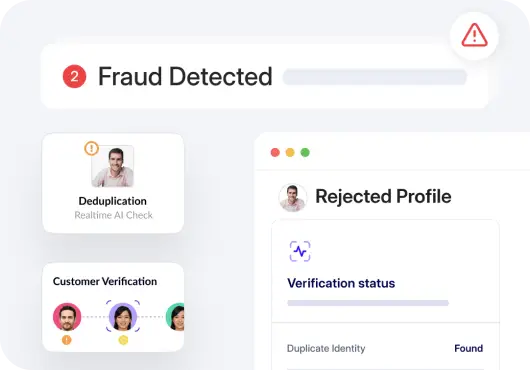
- Loan procedures: Quicken the loan application process by automatically extracting relevant information from tax returns, income statements, bank statements, and credit reports.
- Account maintenance: Automate data extraction from pertinent documents such as client information updates, bank statements, change of address requests, and lost/stolen card reports to streamline operations.
- Service to customers: Speed up response time to customer inquiries by quickly accessing information from scanned documents. Address client questions quickly without manually hunting for relevant documents.
- Process automation: Automate data extraction and identity verification to ensure compliance with KYC and AML regulations. This reduces the risk of fines or penalties and guarantees compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Easy retrieval: Paper documents are effortlessly digitized and saved in searchable formats for future archiving and retrieval. This method saves physical storage space and facilitates quick retrieval of historical records in emergencies.
- Ease in data analytics: Unlock valuable data from financial papers for in-depth research using data analytics and business insights. Understand your customers’ spending habits, trends, and risk factors to create tailored financial products and make smart business decisions.
Challenges and solutions:
While OCR provides a strong solution, there are obstacles and strategies to overcome them:
Accuracy and error handling:
Despite the remarkable advancements in OCR technology, challenges persist with certain document formats, image quality, and handwritten text. Let’s discuss ways to address these issues:
- Set up reliable error-handling systems to ensure that essential fields have data validation criteria and utilize human monitoring to correct mistakes.
- Use high-quality scanning equipment to capture images with enough illumination and resolution to improve OCR accuracy.
- Invest in high-quality optical character recognition software. Seek out OCR technology that incorporates machine learning to process intricate patterns and enhance accuracy with time.
Integration with existing systems
It is essential that your current core banking systems be able to seamlessly integrate with OCR technology. Here are a few important checks:
- Select an OCR system that provides access to a comprehensive application programming interface (API), allowing smooth integration with your existing infrastructure.
- Hire experienced and professional service providers. Collaborate with OCR service providers that have experience in the banking industry to facilitate integration.
- Set up data mapping and data standardization to facilitate effective data transfer across systems by establishing transparent data formats and mapping guidelines.
Security and data privacy
OCR technology recognizes the importance of maintaining stringent data security measures to protect sensitive customer information. To guarantee customer data and safety, follow these steps:
- Enforce regulations to protect identifiable information effectively. Make data handling policies articulate and assess the organization’s compliance with relevant data privacy regulations.
- Inform your staff about the best methods to protect sensitive personal and security information. Provide training to your employees, equipping them to handle clients’ sensitive digital data when using OCR securely.
Future trends and innovations
With the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), bank statement OCR technology and the global OCR market are set to undergo some fascinating developments in the future:
AI and ML in OCR:
OCR technology will be capable of processing more complicated documents and handwritten text efficiently with the help of AI and ML algorithms, further improving its accuracy.
To reduce the requirement for human interaction, OCR software will be able to autonomously adjust to various handwriting styles and such scanned paper documents.
OCR systems will provide banks of any size with more mobility, scalability, and accessibility. This will enable pay-as-you-go arrangements and reduce costly on-premise infrastructure, introducing OCR technology to a broader audience.
OCR systems are set to be closely integrated with Robotic Process Automation (RPA) software. The combination of these two technologies will become a powerful tool for automating document processing and data extraction, leveraging significant efficiency gains.
Regulatory impacts and compliance
Combining OCR with biometric authentication techniques, such as fingerprint or face recognition, will boost security measures. Customer onboarding and other delicate procedures will benefit from this as well.
With the goal of providing clients with self-service alternatives and user-friendly interfaces in multiple languages, the industry will focus on improving the user experience.
In summary
Optical character recognition technology is transforming the banking business by automating data extraction and data processing from both printed and handwritten text, as well as image based text files and other physical documents and digital documents.
It offers significant advantages, including increased productivity, reduced human error, and increased savings, along with fraud protection, customer onboarding, and processing unstructured documents.
Despite issues with accuracy, integration, and security, consistent improvements in AI and ML are improving OCR capabilities.
Incorporate optical character recognition technology into your banking processes to begin the road toward automation and efficiency. By utilizing this game changing automation technology, your business will be all set for success in the digital era.
If you wish to know more about OCR technology in the banking space and want to implement the same for your business, consult an expert in OCR technology.





