The present business growth has introduced a web of financial complexities. One of the most critical yet often overlooked challenges? Keeping financial records aligned between subsidiaries of the same parent company.
Imagine this: Your company has subsidiaries in the U.S., Germany, and Japan. Each entity operates in its local currency, adheres to different tax regulations, and manages its own financial transactions. Now, picture the chaos if these transactions aren’t properly matched or reconciled. Errors could snowball into compliance issues, financial misstatements, or even reputational damage.
This is where intercompany (IC) reconciliation comes in. It’s the financial glue that holds multinational organizations together, ensuring that transactions between subsidiaries are accurately recorded, verified, and balanced. Without it, financial reporting becomes a tangled mess, and the risks of errors, audits, and penalties skyrocket.
Intercompany reconciliation can reduce financial statement errors by up to 30%. Clearly, companies that master it gain a competitive edge—ensuring compliance, improving transparency, and enabling faster, more accurate financial closes.
In this blog, we’ll take a deep dive into the world of intercompany reconciliation. We’ll explore why it’s a cornerstone of accurate financial reporting, uncover common pain points (like currency fluctuations and mismatched entries), and share advanced strategies to streamline the process.
Understanding intercompany transactions
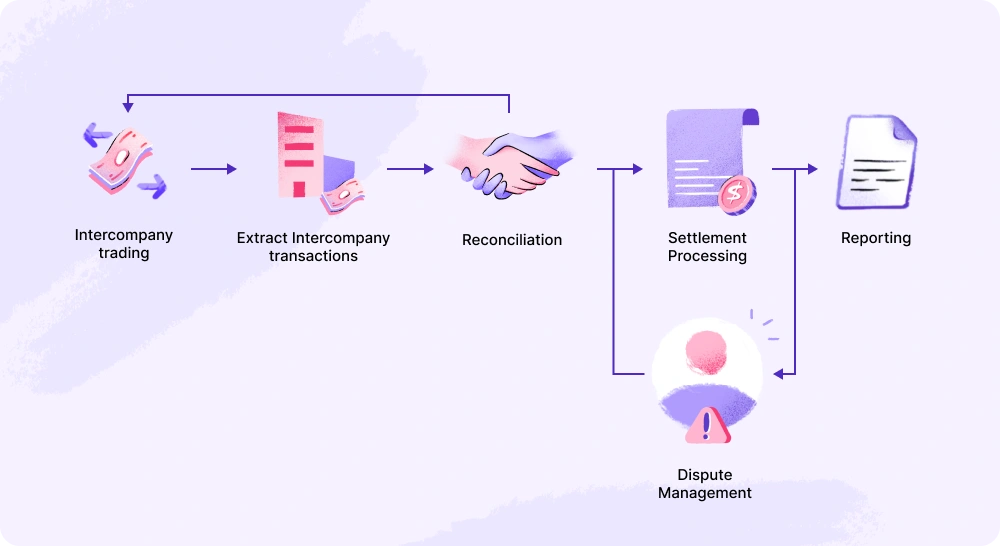
IC transactions are financial exchanges between different subsidiaries within the same parent company. Transactions between subsidiaries or divisions can affect the company’s financial data. If they aren’t recorded and checked, it can lead to mistakes in the financial reports. This makes it harder to see how well the company is doing.
Companies must conduct an intercompany reconciliation process. It involves cross-checking all transactions between the parent company and its divisions. This ensures the financial reports reflect the company’s true financial situation. It also helps avoid issues, such as counting the same transaction twice. Without it, the parent company might show an incorrect financial picture. This could mislead investors, managers, or regulators.
Common types of intercompany transactions
IC transactions can take many forms, each requiring careful tracking and reconciliation. Some common types include:
- Sales and purchases: Subsidiaries often sell goods and services to one another. Accurate recording of these transactions is key in both sets of financial statements. Otherwise, it could lead to misstatements in revenue and expenses.
- Loans: Financial support between subsidiaries often involves loans. Their documentation is important to reflect their impact on cash flow and liabilities. The loan terms, interest rates, and repayment schedules must be clear. Both subsidiaries’ books should record them.
- Service fees: Like with commodities, subsidiaries can use each other’s services. These charges can complicate financial reporting if not reconciled.
- Dividends: Another type of transaction between subsidiaries is dividends. Recording these transactions with accuracy is critical in reflecting the distribution of profits.
Understanding these common transactions is essential for any parent company.
Challenges associated with intercompany transactions
Despite their importance, IC transactions can introduce complexities and potential errors. Common challenges include:
- Timing differences: Different subsidiaries may record transactions at different times. This can lead to discrepancies in financial reporting. Let’s consider two entities buying goods from one another. Subsidiary A may record the transaction at the end of the month. While Subsidiary B might record it at the beginning of the next month. This timing difference will need reconciliation.
- Currency conversion: Subsidiaries can also operate in different countries. In that case, currency fluctuations can impact transaction values. Accurate conversion is essential for reflecting the correct amounts in consolidated financial statements.
- Incorrect coding: Mistakes in coding transactions can lead to misclassified expenses or revenues. Coding an intercompany transaction without errors is crucial for accurate reporting.
Not addressing these fast can lead to significant inaccuracies in financial reporting. As companies expand, intercompany transactions can increase at an exponential rate. This complexity requires robust systems to manage and reconcile these transactions with efficiency.
The importance of accurate intercompany reconciliation
Accurate intercompany reconciliation is vital. Especially for maintaining the integrity of an organization’s financial data. It ensures compliance and improves the accuracy of financial reporting. It also helps manage cash flow with efficiency.
Regulatory compliance
Companies must adhere to various accounting standards and regulations. Accurate intercompany reconciliation helps ensure compliance with these rules. Otherwise, the parent company risks penalties or fines.
Regulatory bodies have specific guidelines about intercompany payables. These are International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). Non-compliance can result in huge fines and damage the reputation of the parent company. Thus, maintaining accurate reconciliation is more than mere good practice. It’s essential for regulatory compliance.

Financial reporting accuracy
Discrepancies or errors can mislead investors, regulators, and internal teams. A parent company needs to reconcile intercompany payables before combining financial records. Without this, its consolidated financial statements may report inflated revenue or understated expenses.
Accurate reconciliation ensures the final consolidated financial statement shows the company’s true performance. This is essential for making informed decisions.
Improved cash flow management
An effective intercompany reconciliation process helps organizations manage cash flow with efficiency. Aligning transactions also helps understand the financial relationships between subsidiaries. They can optimize working capital and reduce the risk of liquidity issues. This ensures visibility in cash flow dynamics. This allows management to make informed decisions about resource allocation and investment opportunities. This financial clarity supports strategic planning and enhances operational effectiveness.
Common challenges in intercompany reconciliation
While intercompany reconciliation is essential, it is not without its challenges. Understanding these common issues can help organizations develop strategies to overcome them.
Data discrepancies
Data discrepancies often arise from the points mentioned above. From timing differences to incorrect coding, these inconsistencies can lead to significant errors. Prompt identification and rectification is crucial in financial reporting.
Manual processes
Many organizations still rely on manual reconciliation methods. These can be time-consuming and prone to error. Manual processes often lead to inefficiencies that hinder timely and accurate reconciliation. With numerous intercompany transactions, the burden of manual reconciliation also increases. This can overwhelm finance teams, and lead to increased stress and potential mistakes.
Additionally, manual processes may not provide real-time insights. Timely insights are necessary for effective decision-making and financial reporting accuracy. Delayed actions can lead to discrepancies that, in turn, impact financial reporting accuracy.
Complex corporate structures
Organizations with many subsidiaries face challenges in reconciling transactions across diverse entities. The complexity of corporate structures can complicate the reconciliation process. This nuance requires careful attention to detail.
For instance, consider a multinational corporation with subsidiaries in different countries. The parent company has to navigate various tax regulations, accounting standards, and cultural nuances. This can make reconciliation even more challenging. The lack of standardized practices across subsidiaries can further exacerbate these issues.
Best practices for intercompany reconciliation
Implementing best practices can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of intercompany reconciliations. Here are some strategies organizations can adopt.
Standardized procedures
Establishing standardized reconciliation procedures across the organization helps ensure consistency and accuracy. It also minimizes the risk of manual errors and streamlines the process.
Organizations can develop a centralized intercompany reconciliation policy. This policy can outline the procedures for recording, reconciling, and reporting transactions. Subsidiaries should be aware of all policies communicated. Regular updates are necessary to reflect changes in regulations.
Automation and technology
Utilizing automation tools and software can enhance the intercompany reconciliation process. It can automate the matching of transactions, generate reports, and other tasks. It can spot discrepancies in real time, generate insights and reduce human error. The finance teams are also allowed to focus on more strategic tasks.
Real-time data integration
Integrating data from various systems in real time is crucial for accurate reconciliation. One solution is using a centralized database. It consolidates financial data from all subsidiaries and enhances visibility of intercompany payables. This allows finance teams to track transactions and address discrepancies as they arise.
Collaboration and communication
Effective communication between finance teams in different subsidiaries is essential to improve intercompany reconciliations. Collaborating can help resolve discrepancies fast and maintain alignment across the organization.
Advanced strategies for intercompany reconciliation
Besides best practices, organizations can install advanced strategies to enhance their reconciliation efforts. These strategies leverage technology and analytics to improve the process.
Data analytics and visualization
Data analytics can identify patterns and anomalies in an intercompany transaction. Utilizing data visualization tools can help finance teams visualize transaction flows between subsidiaries. This visualization can highlight unusual patterns. Unusual patterns can include unexpected spikes in intercompany sales or unusual payment delays.
By analyzing transaction data, organizations can pinpoint discrepancies. They can also take corrective action before they escalate.
Blockchain technology
The emergence of blockchain technology offers a revolutionary approach to intercompany reconciliation. A decentralized ledger can provide a transparent and immutable record of transactions. It can streamline the documentation of intercompany transactions. It can also make it easier to verify and reconcile transactions in real-time.
Blockchain provides an unmatched level of transparency. That can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of reconciliation efforts.
Machine learning and AI
Another revolutionary approach is Machine learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI). This can automate transaction matching and anomaly detection. By leveraging algorithms, organizations can enhance the efficiency of the reconciliation process.
Machine learning can analyze historical transaction data. This analysis can identify patterns and predict potential discrepancies. This proactive approach allows finance teams to address issues. Particularly before they impact financial reporting.
The role of technology in intercompany reconciliation
Technology helps organizations navigate the complexities of IC transactions. The following technologies can enable an accurate and efficient reconciliation process:
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems
ERP systems integrate various business processes, including finance, procurement, and supply chain management. Implementing an ERP system can centralize financial data. This makes it easier for tracking transactions and performing reconciliations.
For example, an ERP system can automatically record intercompany transactions as they occur. It also ensures that all entities have access to the same information. This integration minimizes the risk of discrepancies and streamlines the reconciliation process.
Cloud-based solutions
Cloud-based solutions offer scalability and flexibility for intercompany reconciliations. Organizations can leverage cloud technology to store and access secure financial data. This technology also enables real-time collaboration between subsidiaries.
For example, cloud-based tools let finance teams collaborate from anywhere. This is especially useful for multinational corporations with subsidiaries in different regions.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA can automate repetitive tasks involved in intercompany reconciliations. This includes data entry, transaction matching, and report generation. By utilizing RPA, organisations can free up valuable time. Finance teams can use this time to focus on more strategic initiatives.
For example, RPA can streamline the process of matching intercompany invoices and payments. This reduces the potential for human error and accelerates the intercompany reconciliation timeline.
Conclusion
In conclusion, intercompany reconciliation is essential for organizations operating across many subsidiaries. Companies can see vast improvement by using the best strategies and technology. They can enhance financial reporting, compliance, and cash flow management.
The business landscape continues to evolve. To keep up, organizations must embrace innovative approaches to the intercompany reconciliation process. By leveraging technology and data analytics, companies can streamline their reconciliation processes. They can reduce the risk of discrepancies, and improve financial performance.
Thus, there’s more to effective intercompany reconciliation than fostering financial integrity. It also strengthens organizational resilience in an increasingly competitive environment. Prioritizing accurate intercompany reconciliation helps organizations achieve sustained success in the dynamic finance world.
Learn more about how you can optimize your entire end-to-end reconciliation with HyperVerge here.
FAQs
1. How do you reconcile an intercompany?
Intercompany reconciliation means matching financial transactions between subsidiaries to ensure accuracy. It helps remove the scope of errors, like duplicate records or mismatched entries.
2. What is intercompany reconciliation?
IC (Intercompany) reconciliation is the process of verifying transactions between subsidiaries. It ensures that all records match, preventing financial discrepancies.
3. What is the intercompany process?
The intercompany process includes recording and settling transactions between subsidiaries. It covers sales, loans, service fees, and dividends. Thus ensuring all entries are accurate for financial reporting.
4. What is intercompany matching and reconciliation?
Intercompany matching is comparing related transactions, like invoices and payments, between subsidiaries. Intercompany reconciliations ensure these records align by correcting mismatches or missing entries.
This reconciliation process is crucial for accurate financial reporting, compliance, and smooth business operations. It prevents errors and improves cash flow. It also ensures that the company’s financial statements reflect its true position.