CTRs (Currency Transaction Reports) are a leading facet of Anti-Money Laundering compliance and, therefore, become very important for the integrity of financial systems and in the fight against money laundering crimes. This exhaustive guide showcases the role played by CTRs in the banking and finance space, the elements therein, filing procedures, exceptions, and processes involved in maintaining the same, penalties for failure to comply, and the benefits of automating the CTR process.
Understanding currency transaction reports
A Currency Transaction Report is a form of regulatory reporting that financial institutions have to file in case a customer executes any transaction more than $10,000 in cash on any given day. This threshold is based on requirements that help detect and prevent money laundering, terrorist funding, and other harmful financial activities. CTRs were created under the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) of 1970, which mandated financial institutions to help the American government law enforcement agencies in the war against money laundering and other financial crimes.
CTR is an intrinsic part of AML compliance that enables the authorities to trace major cash transactions through a paper trail in financial movements. Per the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network, more than 20.8 million CTRs were filed in 2023, making them a vital factor for monitoring and regulating currency transactions through the U.S. financial system.
Adherence to AML (Anti Money Laundering) legislation by financial institutions is key to preserving reputation and avoiding other severe penalties. Each entity is under an obligation to set up a strict AML framework involving meticulous customer due diligence, perpetual monitoring, and efficacious reporting systems.
An effective AML program involves the following components:
- Risk Assessment: Identify and assess the AML risks associated with the activities and customers of the institution.
- Policies and Procedures: Formulate and implement comprehensive AML policies and procedures that align with the risk profile of the institution.
- Training: Showing employees the requirements of AML regulations and how to identify and report suspicious transactions (like training a fintech or bank employee to report financial crimes or ill-gotten gains deemed critical to prevent money laundering).
- Internal Controls: An effective internal structure to monitor compliance with the institution’s AML policies and procedures.
- Independent Audits: Provide periodic independent audits to assess the effectiveness of the AML program and highlight areas that need improvement.
Be compliant with AML regulations and avoid hefty penalties.
Learn more about our AML solutions. Schedule a demo today!The key components of a currency transaction report
A CTR represents various fundamental elements that provide comprehensive information about the transaction. These reflect the following:
- Customer Information: This space contains the names of the customers, their residential address, account number, SSN/TIN, and date of birth.
- Transaction Details: The date, amount, type of transaction (deposit or withdrawal), number of transactions (like multiple transactions), and location where the transaction has taken place are duly recorded as part of the form.
- Institutional Data: This includes the financial institution’s name, the exact physical location, and the identifying number of the financial institution where the transaction happened.
- Filer Credentials: This report includes the name, title, and telephone number of the filer.
- Filing Date: The calendar date when the CTR gets filed with FinCEN (financial crimes enforcement network).
Accurate and complete filing enables adherence to AML regulations and plays a vital role in identifying possible suspicious activities.
Who must submit a CTR?
The requirement to file the Currency Transaction Report (CTR) applies to a broad range of individuals and entities involved in the financial sector, including:
- Banking Institutions: It refers to the broad banking sectors, which involve commercial banks, credit unions, and savings associations.
- Money Services Businesses (MSBs): These refer to businesses that deal in providing money orders, traveler’s checks, currency transaction dealers, or transmission of funds.
- Casinos and Card Clubs: Any gambling casino that accepts wagers and has gross annual revenues exceeding a threshold must comply with this requirement.
- Security Brokers and Dealers: Any company that sells equities, bonds, and a myriad of other securities is subject to this federal law.
- Cryptocurrency Exchanges: Any exchange that enables the buying or selling of cryptocurrencies falls within its purview.
These institutions are required to file a CTR for all large cash transactions exceeding the $10,000 threshold.
Exemptions from filing CTRs
The following are exempted from the filing requirement in terms of Currency Transaction Reports in certain transactions to specific entities, namely:
- Governmental Bodies: All transactions involving the federal government, state government, local governments ((including local government agencies), or political subdivisions or instrumentality need not comply.
- Domestic Banks: Interbank transactions between banks in the United States are exempt from this mandate.
- Publicly Traded Companies: This guideline does not affect transactions involving public corporations whose stocks are listed on the principal United States stock exchanges.
Additionally, the banks and other financial institutions reserve the right to exclude customers habitually having large cash transactions, provided that these customers have shown a history of compliance and do not introduce any identifiable risk of money laundering or potential financial crimes.
How does the currency transaction report work?
Should a transaction exceed $10,000, the institution’s software would activate auto-filing of a Currency Transaction Report. The software should generate almost all relevant information regarding the customers’ account details and the nature of the transaction. In case of any indication of suspicious activity or an illicit currency transaction, it should enact a trigger for a Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) to be filed.
No provision makes it mandatory for financial institutions to inform their customers that a CTR is being prepared or filed unless the customer asks them to do so. In addition, if a customer is seen making efforts to avoid a transaction to prevent the preparation of a CTR, this activity is considered suspect and requires a SAR to be filed (think reportable transactions).
Consequences of violating CTR regulations
Breaking these CTR regulations can carry dire consequences for individuals and their financial institutions. Typical violations include structuring transactions to avoid the threshold of $10,000, failure to file the CTRs within the required timeframe, and filing reports that contain inaccurate information.
This attracts a hefty penalty for anyone who has flouted these regulations: running into hefty fines, incarceration, forfeiture of assets, and even business license withdrawal. Moreover, the financial institutions also have a possibility of incurring civil and criminal liability measures, posing a significant threat to operational continuity and reputation.
Automating the CTR process to ensure compliance
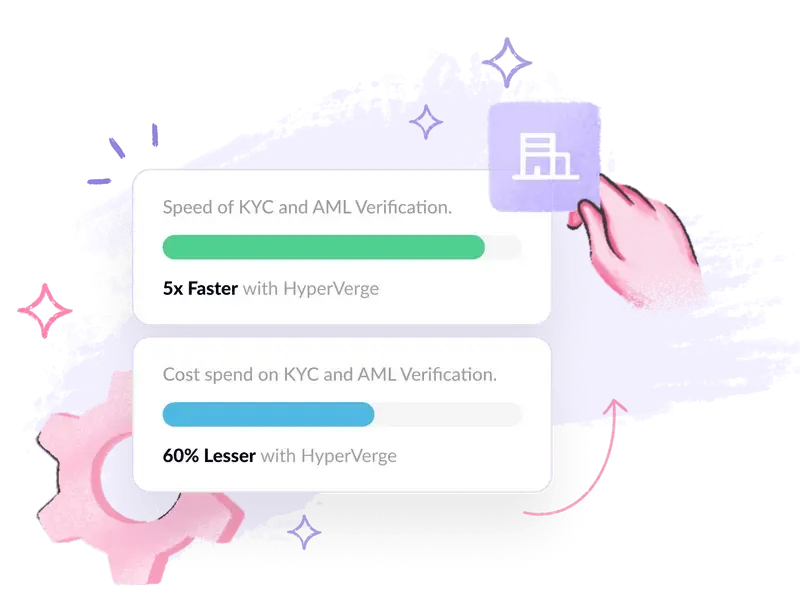
AI-driven compliance solutions have, in some significant aspects, increased the accuracy and speeded up the process involved in CTR filing. Following are some of the benefits realized from the automation of CTRs:
- Automated ID Verification: This reduces the risk of identity fraud and clerical errors.
- Real-Time Data Capture: This ensures the recording of accurate and complete information for every transaction.
- Transaction Aggregation: This detects structuring attempts specifically aimed at avoiding thresholds for reporting.
- Automatic Report Generation and Submission: This takes a short period and minimizes human errors.
- Improved Record-Keeping: Allows for easy electronic storing and access to CTRs for at least five years in line with existing regulatory expectations.
Modern technology advancements significantly boost compliance with AML. Various robust software solutions support the automation of filing CTRs accurately and efficiently. Some of the features of the technology in AML compliance include:
- AI and Machine Learning: These are top-of-the-game technologies, potentially very effective in detecting patterns and anomalies in transactions that may indicate suspicious activities.
- Real-Time Monitoring: This feature helps regular supervision of all currency transactions to identify suspicious activity and report it promptly to prevent money laundering.
- Regulatory Reporting: This approach automates preparing and filing CTRs and SARs with regulatory agencies and relevant authorities.
- Data Analytics: These help conduct a granular data review for trends and risks associated with money laundering activities.
- Secure Data Storage: This facility provides secure storage and compliant preservation of transaction records and reports (as well as relevant customer data) for audit purposes and future reference.

Advanced AML solutions ensure compliance, reduce penalty risk, streamline anti-money laundering efforts, and protect the integrity of the financial system in the banking and fintech space.
With advanced AML solutions from HyperVerge, it’s time to take compliance processes steeply ahead- Global coverage, quick integration, 24/7 real-time monitoring, and much more. Your businesses are equipped with actionable insights in sync with the current and emerging legal and regulatory requirements. Sign up now to gain a competitive edge and change the approach toward AML compliance.





