Facial recognition is everywhere—unlocking your phone, speeding up airport security, and making check-ins seamless. But what happens when a mask covers half your face? That’s the challenge the COVID-19 pandemic threw at traditional face recognition systems.
Even though masks aren’t as common now, the problem hasn’t gone away. A masked intruder could bypass outdated security systems, or a regular customer under a bout of viral infection could be denied access to their account because they were wearing a mask.
That’s where masked face recognition comes in. It’s a smarter, more advanced way to verify identities. In this guide, we’ll explain how it works, why it matters, and what makes it the future of secure, contactless authentication.
What is masked face recognition?
Masked face recognition is an advanced form of facial recognition technology designed to identify people even when wearing facial masks. Unlike traditional systems that rely on a full view of the face, this technology analyzes key facial features (like the eyes, eyebrows, and forehead) to verify identities accurately.
Regular facial recognition depends on analyzing the entire face, including the nose and mouth, to match it with stored data. But when masks cover half the face, traditional systems struggle, leading to errors or failed verifications.
Masked face recognition overcomes this by using AI-powered algorithms focusing on visible features and adjusting for obstructions like masks, glasses, or even poor lighting conditions.
Masked face recognition technology most applies to industries like healthcare, airports, and retail establishments. Doctors and nurses can access different hospital areas without removing their masks. Airports will be able to accommodate masked travellers, and retail stores will be able to serve their mask-wearing customers better.
How does masked face recognition work?
If you look from the top, masked face recognition is based on Artificial intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), like any other facial recognition system. Inside, there is a lot more going on.
First, there are deep neural networks. They work as digital brain cells that help the system learn to recognize masked faces. This strengthens the system’s ability to analyze a person’s whole face based only on the visible features.
But how does the system analyze a face based on partial facial identification? There are three main steps involved:
Face detection: The system first identifies a face in the image, even when they’re wearing a mask or something similar
Feature extraction: This is where most of the work happens. The system focuses on the visible parts of the face, especially near the eye region. It then creates a detailed map of facial features like:
- Distance between the eyebrows
- Shape and curve of the eyes
- Texture and patterns around the forehead
- Face curve from the eyes to the ears
Pattern matching: Once the map is ready, the system compares it with the existing images in the database. Because it’s trained to identify faces with partial facial maps, it uses the upper facial features for accurate contactless identification solutions.
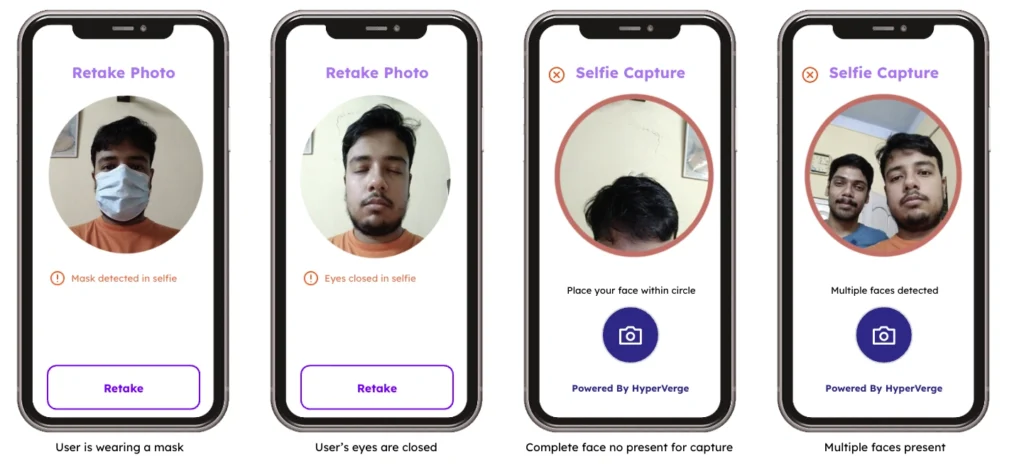
Most biometric and identity verification software is upgrading its systems. HyperVerge is one of the best-masked face recognition software for this change. Each time a photo is uploaded, HyperVerge checks it for face mask detection, face occlusion, multiple face detection, and more. The proprietary software is one of the best in the industry in terms of face matching and liveness detection accuracy.
Key benefits of masked face recognition technology
Face masks may hide features, but they shouldn’t hide identities. Masked face recognition ensures comprehensive security without compromise.
Here are the key benefits:
Improved accuracy despite masks
Traditional facial recognition systems rely on analyzing full-face structures, making them ineffective when covering key features like the nose and mouth. However, to maintain accuracy, AI face recognition with masked face detection uses face identification techniques focusing on visible regions—eyes, forehead, and unique biometric markers.
For industries using biometric identity verification, such as banking and healthcare, this ensures seamless authentication without compromising security. They can reduce false positives, prevent unauthorized access, and streamline digital KYC processes, all while accommodating masked individuals.
Enhanced security and fraud prevention
Fraudsters constantly evolve their techniques, using deepfakes, photos, and video spoofing to bypass security measures. Advanced liveness detection in masked face recognition prevents these threats by distinguishing real users from spoofing attempts. It analyzes micro-movements, blink patterns, and 3D depth to confirm identity, making fraud significantly harder to execute.
For businesses needing selfie identity verification and remote onboarding, this means more substantial fraud prevention and compliance with security regulations. They can authenticate users with confidence, even in high-risk environments.
Speed and convenience for seamless verification
A masked face recognition system doesn’t prompt users to remove their masks to get a complete view of the unmasked faces, making the process quick and convenient. This works perfectly in an airport or at the office entrance, as people can walk in unhindered—there is no need to remove their masks or share any identification information.
Customization for various industries
Masked face recognition isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It adapts to the specific security and operational needs of different sectors.
- Banking & Finance: Strengthen biometric security in digital banking and prevent fraud in financial transactions
- Healthcare: Enable masked identity verification for patients and staff while maintaining hygiene protocols
- Retail & e-commerce: Integrate face authentication to simplify customer logins and payment approvals
- Law enforcement & public safety: Assist in criminal identification and border security with advanced facial recognition systems
Industries leveraging masked face recognition
While masked face recognition will be omnipresent in the coming years, these industries are rapidly adopting it.
Security and surveillance
You might have guessed this already. The security and surveillance sector has the highest masked face recognition technology adoption. Corporate buildings use it to grant employees access to secure areas while maintaining mask-use protocols.
Likewise, security teams could use this technology with video surveillance to monitor open and vast areas like shopping malls.
Healthcare
Healthcare has two significant benefits in the healthcare industry. Doctors and nurses can enter restricted areas with their masks on, and patients can be stopped from entering these areas even when they have face masks.
Additionally, it is used in the patient identification system to maintain accurate patient records and track patient movement in the hospital.
Transportation
In airports, masked face recognition is helpful in streamlining the entire passenger identification process from check-in to final boarding. In railway stations, it integrates with the current ticketing system for contactless verification.
Retail
For retailers, masked identity verification means more than higher security. It means recognizing masked walk-in customers and tailoring the service offerings based on their buying behavior. It is also used for contactless payments and integrated with loyalty programs.
Government
Governments have started implementing advanced face recognition systems in different sectors. For example, border control systems incorporate masked face recognition to verify identities based on ePassport data. Soon, more government buildings will use this technology for visitor management and employee access control.
Challenges and how to overcome them with technology
Masked face recognition is a breakthrough technology, but it comes with challenges that impact accuracy and performance. Factors like mask variations, poor lighting, and low image quality can interfere with secure face verification with masks. However, AI-powered facial recognition for masks is helping overcome these obstacles.
1. Variability in masks and face coverage
Not all masks are the same—different colors, patterns, materials, and coverage levels can make it difficult for facial recognition systems to identify key features. Some masks sit higher on the nose, covering more of the face, while others leave portions of the chin visible, altering the face identification process.
Advanced AI models trained on diverse datasets can recognize faces even when key facial landmarks are obstructed. These models focus on distinguishing features like eye spacing, forehead contours, and unique biometric markers to enhance recognition accuracy across various mask types.
2. Poor lighting and image quality
Many facial recognition systems struggle in low-light environments or with blurry images, leading to false rejections or failed verifications. This is a significant concern for businesses implementing identity verification in high-security areas, retail, and remote authentication scenarios.
AI-driven facial recognition APIs leverage deep learning techniques to enhance image quality, detect faces in dim lighting, and reduce dependency on high-resolution inputs. Additionally, infrared and 3D sensing technologies allow systems to operate effectively even in low-visibility conditions.
3. Partial face visibility and occlusion issues
Masks, headgear, and even accessories like glasses or hats can cause partial occlusion, making it harder for traditional face recognition software to perform accurately. This is a major challenge in finance and law enforcement, where secure identity verification is critical.
Modern AI models use multi-factor authentication, analyzing not just facial features but also behavioral patterns, head movements, and even voice recognition for added security.
Future of masked face recognition technology
Masked face recognition is rapidly evolving, with the global market projected to reach $5.51 billion by 2025. The U.S. will lead this growth, with masked face recognition technology in the USA expected to reach $1.47 billion in the USA. Industries like airports, banks, and hospitals drive this growth as they need secure, contactless verification.
The technology is evolving fast. AI can now recognize faces even in low light or with masks, making authentication quicker and more accurate. Edge computing reduces delays by instantly processing data without relying on the cloud. Soon, we’ll see biometric security, IoT access control, and AR-powered verification working together to improve safety and convenience.
The benefits for businesses are clear—faster check-ins, stronger security, and fraud prevention. As cyber threats grow and rules get stricter, upgrading to advanced biometric solutions will ensure better security, smoother operations, and future readiness.
Don’t wait until outdated security slows you down. Upgrade to next-gen biometric authentication today. See how HyperVerge’s AI-powered face recognition can future-proof your business.
FAQs
1. Can someone identify you with a mask?
Yes, modern identity verification systems can identify you even when you’re wearing a mask. They study the visible parts of the face, like the eye region and the forehead, to map the lower facial features. They then compare the map with the image saved in the database to confirm if it’s you or someone else.
2. Does face recognition work with masks?
A masked face recognition system can recognize masked faces. The algorithms are trained to analyze the visible sections of the face to identify people with high accuracy.
3. What is face mask detection?
Face mask detection technology only identifies if a person wears a mask properly. It’s different from face mask recognition technology because it doesn’t confirm a person’s identity. Mask face detection systems were widely used in public settings like airports during the pandemic to enforce mask-wearing policies.
4. What technology is used in face recognition?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are at the core of face recognition systems. Deep algorithms process facial features and patterns. Computer vision technology analyzes faces and videos, and 3D sensing technology creates facial maps using depth sensors and infrared cameras. The system also uses biometric software to convert the facial features into mathematical data for matching and pattern recognition.





