Money laundering is an illegal process of disguising the origins of illegally obtained money, typically by passing it through complex transactions. It is usually done to make illegally obtained funds appear cleaner. This worsens the problem by funding more crime, even terrorism financing, putting public safety and national security at risk.
According to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), money laundering schemes cost 2-5% of the world’s total GDP – an estimated $500 billion to $2 trillion. Money laundering is a financial crime that harms companies financially and reputationally.
This article will help you understand how money laundering works, the different stages of money laundering, and their negative impact on financial institutions and businesses.
What is money laundering?
Money laundering is the process of hiding the origin of money obtained from illicit activities, like drug trafficking, bribery, or other criminal activities. The purpose of the money laundering process is to make illicit money appear legitimate so that criminals can use it without getting caught by authorities.
Money laundering helps criminal groups clean money fund their activities and expand their power, which puts public safety and national security at risk. The laundered money is primarily used for criminal activities and financing terrorism.
There are several common methods used to launder money. Let’s understand in brief.
Methods used to launder money
Criminals use various methods for money laundering, from real estate to cryptocurrencies. Here are some common methods used in the money laundering process.
- Cash Smuggling: Cash smuggling involves moving large amounts of illegitimate funds (mostly in foreign currencies) across borders to deposit in foreign bank accounts or invest in less monitored assets. It helps criminals avoid detection and smuggle large illicit cash.
- Gambling and Betting: Gambling and betting, online or offline, are often used to launder illegal money. Money launderers might place low-risk bets to deposit dirty money and withdraw it as “winnings,” or use illicit funds to support betting as a free time activity.
- Shell companies: Criminal proceeds shell companies with fake employees, hide asset ownership for potential money laundering, making it hard to trace laundered funds and prosecute criminals by tax authorities. Invoice fraud is a common method used by criminals. Using shell companies to further obscure the money trail.
- Sports: Sports provide opportunities for money laundering through betting, sponsorships, and merchandise sales. Football, cricket, rugby, horse racing, motor racing, ice hockey, volleyball, and basketball are examples of sports used in money laundering.
- Money Mule: This is one of the most high-profile ways for money launderers to avoid law enforcement agencies. A money mule is someone criminals hire to launder illegal funds, often selected for their clean banking history and reputation, enabling them to discreetly transfer dirty money.
- Real Estate: Money launderers use dirty money to do real estate transactions, buy luxury assets, and sell them later, cleaning their illicit funds and putting them back into the legal financial system.
Read more: What are the AML red flags?
The three money laundering stages
The money laundering process involves multiple stages and financial transactions to clean these illegal profits. There are typically three stages of money laundering:
The placement stage
This is the first stage of money laundering. In this stage, illegal funds are placed in the legitimate financial system.
The most common method used in the placement stage is to divide large amounts of cash into less suspicious smaller amounts, which can then be deposited into a single bank account or multiple bank accounts (which could involve the ‘smurfing‘ technique).
Other methods of placement include false invoicing (over-invoicing and money orders for payment of non-existing goods or services), blending illegal money with legitimate funds, purchasing foreign currency, buying securities or insurance with cash, and engaging in gambling and betting on sports events.
Some examples of placement in money laundering are:
- Repayment of loans or credit card bills: Dirty money may be used to repay loans or credit card bills with digital lenders who may not be under the scanner of authorities.
- Dummy invoices: Criminals can send through dummy invoices to match cash lodged. Sometimes, they may also over-invoice or under-invoice, or falsely describe goods and services provided to others to match the amount of money to be placed.
- Blending funds: Mingling dirty money with the day’s sales from a legitimate business allows criminals to cover up the dirty money and make it difficult for AML (Anti-Money Laundering) enforcement agencies and the FATF to track them.
- Gambling: Purchasing gambling chips at a casino or placing a bet on a sports event in one of the many possible venues also allows a way to launder money, though there will be some loss incurred in such cases, due to the gamble.
- Currency smuggling: Criminals may also move illegal currency across the border to a country where the money can be used legitimately.
- Foreign currency exchanges: Purchasing foreign money by using illegal funding in exchanges.
The layering stage
The second stage of money laundering is “layering,” where criminals hide the source of illegal money by making several financial transactions. They do this to confuse the audit trail. This part is complicated in money laundering because it involves multiple business transactions, and sometimes even international transactions of illicit funds.
In the layering stage, money is moved around by buying and selling investments or using foreign bank accounts. Examples include investing in real estate, offshore companies, reselling expensive items, transferring money between countries, blending dirty money in legitimate business, and more.
Some examples of layering in money laundering are:
- Moving money: They may move money electronically from one country to another, taking advantage of loopholes that exist in legislation in both countries.
- Investing in stocks: Criminals might invest the money in stocks, long-term
- Investing in real estate: Investing in property not only gives criminals an asset they can own but it also may be difficult to track for authorities if the sale of the deed happens without proper documentation.
- Investing in shell companies: Criminals might invest their illegal money in shell companies that have a functional front.
The integration stage
Integration is the final stage of money laundering that must be carried out within a legitimate financial system. There are many different ways in which the laundered money can be integrated back such as purchasing monetary instruments, property, business ventures, or luxury items which seem to be legitimate sources.
Some examples of how integration happens in money laundering are:
- Fake employees: They can have a fake office setup where they can list several employees, people who don’t exist, and the payments can be made out to them regularly as salary, but which will be going to criminals.
- Investments: By purchasing things of very high value such as property, costly pieces of art, luxury vehicles, jewelry, etc, criminals can then sell these later for actual income.
- Loans: The company can give out loans to executives on the board or to shareholders and these loans will never have to be repaid.
- Dividends: These payments can be made to shareholders in companies that are controlled by the criminal behind the money laundering operation.
For businesses seeking to improve financial monitoring and compliance, exploring the best OCR software for invoice processing can help streamline the detection of discrepancies in financial transactions, ensuring better tracking and validation of invoice-based transactions.
If all these stages of money laundering are successful, the funds are now part of the legitimate financial system and can be used freely.
Read more: What is Trade Based Money Laundering (TBML)?
Money laundering is a serious problem
Money laundering is being given increasing importance by law enforcement agencies. The FATF or Financial Action Task Force was built to combat this very evil. Money laundering is a serious problem because the conversion of illegal money allows criminals the opportunity to spend the money in legal ways, like opening up a garment store or running a laundry business (from which the term “money laundering” was derived!). The clean money gained from the last of the three money laundering stages is virtually indistinguishable from clean money and helps fuel criminal activities undetected. Modern technological advancements and the extent of globalization of the financial services industry, with each country having its own set of policies (not necessarily robust) to combat crime also poses a challenge to agencies enforcing AML laws.
How businesses can prevent money laundering
To help manage KYC and AML compliance, most places where the laundered money is placed use what is called customer due diligence (CDD). The customer’s information, including name, date of birth, and a government ID such as a passport or a driver’s license is obtained before they pledge the money they have, to ensure that the customer is not involved in criminal activities of any kind. This process can simply also be referred to as KYC (know your customer). In countries where the risk of money laundering is higher, an additional check known as extended due diligence (EDD) may be performed. enhanced due diligence (EDD) generally checks for the source of the funding. If the source of the funding is clean, then the customer can go ahead and place his money. Otherwise, the customer is caught red-handed!
Read more:
- What is transaction monitoring in AML?
- KYC and AML: Key Differences and Best Practices
- What is a Suspicious Activity Report?
- Anti-Money Laundering Checks Explained: Everything You Need to Know
- What is a customer identification program (CIP)?
- AML risk assessment process: a step by step process
- What is sanctions screening?
- What is pep screening?
- What is Adverse Media Screening: A Step-by-Step Process
- What is transaction laundering?
How HyperVerge can help battle money laundering
At HyperVerge, we’ve built automated AML software with end-to-end KYC, high-accuracy OCR, robust identity verification services, and face recognition. The fact that the system is continually trained on samples in each region ensures that the accuracy is top-notch.
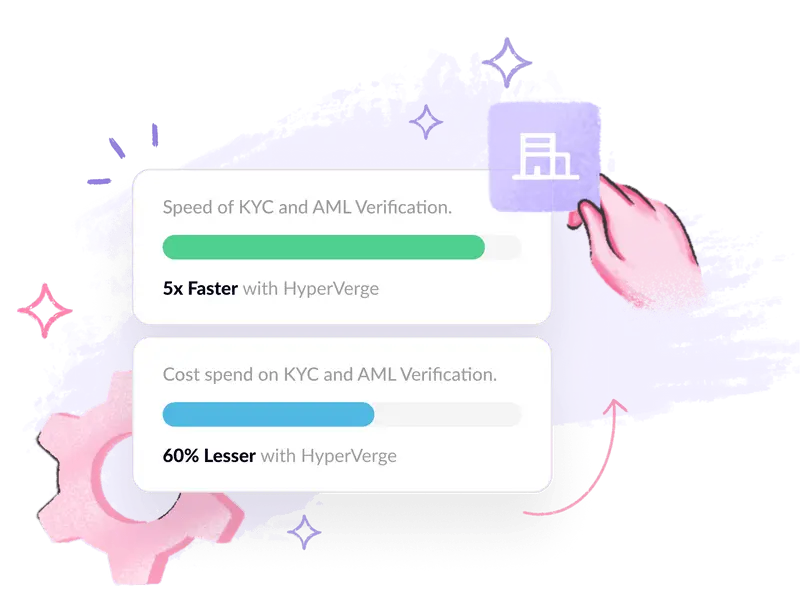
- The Hyper Turing engine, a proprietary in-house AI engine, helps sharpen the accuracy of the OCR.
- The face recognition system, which also runs parallel 1:N checks to determine identity is NIST ranked #3 in the world for its accuracy.
- The face recognition system is also iBeta certified for passive liveness detection, accurate, and extremely user friendly, allowing a larger number of users to onboard in a given period.
- The code for face recognition and OCR are also benchmarked against those of competitors to yield better accuracy over time.
If you are an enterprise that needs help ensuring AML compliance, talk to us today!
FAQs
What is the most common form of money laundering?
The most common form of money laundering is smurfing. In smurfing, a large amount of cash is broken down into smaller amounts that don’t invite suspicion, and then moved from one country to another in business transactions, to avoid falling under the radar of AML agencies.
At which of the three money laundering stages is money laundering most difficult to detect and where is it easiest to detect?
Money laundering is very difficult to detect during the integration stage of money laundering. This is because at this stage the launderer would have made it virtually impossible to tell the legal money from the illegal one as he has successfully obscured its source or replaced it with a genuine one. Money laundering is easiest to detect at the placement stage of money laundering.
In which phase of money laundering is the money clean?
Again the money is clean during the integration stage of money laundering, when the money is returned to the criminal and is virtually indistinguishable from clean money.





